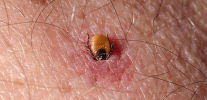
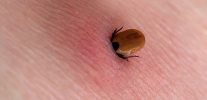
The most comprehensive measures to provide first aid for a tick bite are required in regions with a severe epidemiological situation, that is, where the probability of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection is greatest. This is primarily Siberia - the Irkutsk, Tomsk and Krasnoyarsk regions, as well as Altai and the Far East. Also, permanent foci of virus circulation and infections are registered in the Kaliningrad and Leningrad regions, the Baltic countries, Belarus, the Transcarpathian region of Ukraine. Here, in addition to the simplest steps to remove the tick, you also need to go to the hospital for special tests.
Next, we will talk about how to start helping the injured person in general, and at what points special attention should be paid ...
Why is it important to provide the injured person with first aid when a tick bites?
When a tick bites, first aid is required to remove the parasite as quickly as possible and to prevent a possible allergic reaction to its bite. The faster the tick is removed from the body, the less likely it will be to infect a dangerous infection, even if the tick was actually infected.
There is even a possibility that a tick already stuck into the skin can be torn off before it releases the first portion of its infected saliva. But even if the parasite has already managed to inject saliva into the tissues, the probability of infection will be the higher, the more saliva has entered the human body. Simply put, the longer the tick sucks blood, the greater the risk that after such a bite an infection in the human body begins to develop.
The second reason for which may require emergency assistance to the victim - an allergy. In general, for tick bites, it rarely occurs and almost never threatens life-threatening conditions. Nevertheless, the risk of its severe course is present, and first aid is designed to minimize it.
Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to destroy infectious agents that have already entered the body after a tick bite (if they have already fallen). With a certain probability, you can immediately eliminate a borrelia infection if you take an effective antibiotic, but in practice specifically Borreliosis is safer and easier to cure if you diagnose it in its early stages with the first symptoms, rather than insure against it with antibiotics that can often cause serious side effects.
Therefore, it is necessary to understand well that in a real situation it will not be possible to protect the victim from infection with 100% reliability only by giving him first aid.
The very sequence in providing such assistance is relatively simple.
Step 1. Remove tick
This is the most important thing to do when detecting a sucked tick. It makes no sense to take any other measures if the tick will continue to suck blood.
Moreover, the very removal of the parasite is quite a specific procedure. The mite removal algorithm is as follows:
- Grab the head of the parasite as close as possible to the skin. Well, if a person or an assistant has long nails - they can grab it under the swollen tick body.In the ideal case, a special device is used for this - for example, Tick Twister, but it is difficult to find it on sale, and in cases where it is needed, it is usually not at hand. You can also use tweezers (it is also not always possible to find it in your pocket during a walk in nature) or a simple thread. The latter is tied into a tightening knot, it is thrown over the tick, so that the loop envelops the head, and is tightened;
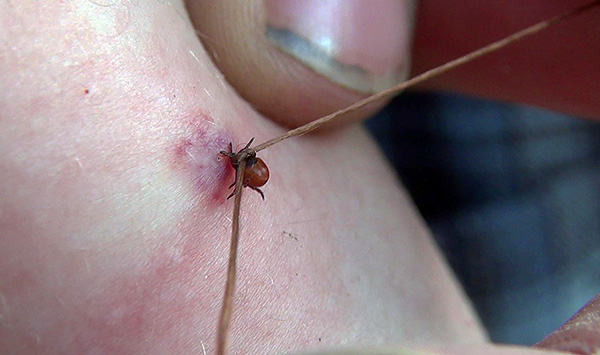
- Slowly and gently move the tick from side to side, gently sipping up from the skin. Sharp movements here are unacceptable, since it is possible to accidentally tear the body of the tick from the head, and then remove the head from the skin after this will be much more difficult. It is also useful to try to rotate the parasite, but this can only be done if he has already sucked blood and can grasp his body;
- As soon as the tick was removed from the wound, it should be put on a napkin (it is no longer dangerous), a well-closing container (bottle, matchbox, bag) should be found and put there;
- If, when removing the tick, the head or parasite mouth apparatus remains in the wound, then (if it is not possible to see a doctor quickly), you should take a needle, heat it on the fire and try to remove the remnants from the skin.If this is not done, then the wound will fester with a high probability in a few days.
On a note
In the same way, it is necessary to remove ticks from the skin of a dog or cat. In veterinary practice, diseases carried by ticks are highly relevant, although they differ from those in humans. In general, the rules for protecting animals are the same as for humans.
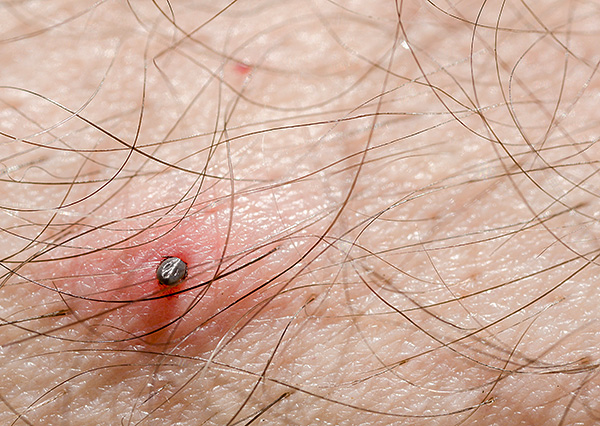
The photo below shows the so-called forest mite, just extracted from the skin:

If you do not panic and do not fuss, then even without special devices with normal-length nails, it is quite possible to remove the tick from the skin so as not to tear its head. However, it is even more effective and safer when you walk in nature once every 20-30 minutes to stop, raise your trouser legs and inspect the legs under them. So it will turn out to detect ticks that have just grasped the skin and remove them even before they start to suck blood.
Step 2. Process the bite site
This step is required to mitigate to some extent the skin’s reaction to the bite and components of the mite’s saliva, as well as to partially disinfect the wound. However, the effectiveness and significance of such treatment should not be overestimated - the local treatment of the tick bite is not a reliable prevention of infection.However, sometimes this helps prevent blistering at the site of the bite and protect damaged tissues and exposure to additional infectious agents from the environment.
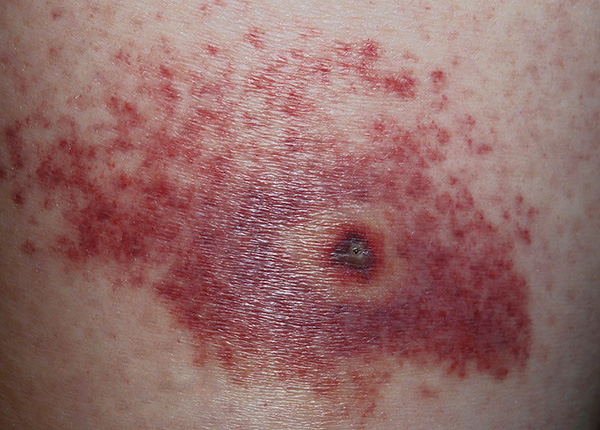
To disinfect her wound after washing with soap and water, it is treated with antiseptics (alcohol, iodine alcohol solution, Miramistin) or with natural preparations - celandine juice, for example. Due to the small diameter of the hole, the wound from the bite is quickly tightened, practically does not bleed and is protected from secondary infection.
To alleviate the unpleasant symptoms, the bite is usually smeared with ointments with anti-inflammatory components (hydrocortisone, Advantan, Pimafukort, Flutsinar).
On a note
If a progressive and rapidly spreading rash appears on the skin near the wound or on any other part of the body after an attack of the tick, it is necessary to take an antihistamine drug, Suprastin, Loratadin, Ebastin or others, to the victim. This item is especially important, because immediately after a tick bite, it is hypersensitivity reactions that pose the greatest danger to the patient, despite their relative rarity.
If the rash is very abundant and becomes similar to urticaria, it is necessary to immediately call an Ambulance, without waiting for further deterioration of the victim (this can happen quickly).
At this stage, in fact, the first pre-medical care ends. All other means and methods are available only in specialized medical institutions and do not apply to emergency care - they can be performed within the next 3-4 days after a tick bite. But it is also useful to know about them, because the victim must show the initiative in applying them.
Step 3. To carry out emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis
Emergency prophylaxis of tick-borne encephalitis consists in the introduction into the body of an injured drug of a specific immunoglobulin, which, by binding to viral particles, inactivates them, prevents the spread in the body and is likely to stop the development of the disease.

It is important that the injection of immunoglobulin is able to prevent the development of tick-borne encephalitis after the bite, which differs from the anti-encephalitis vaccine. (the latter is required to enter just before the pathogen enters the body). Emergency prevention performs its tasks within 4 days after the bite, but it is better to apply for it within the first two days.
It is interesting
The effectiveness of such prevention of tick-borne encephalitis (especially correctly and on time) is very high. Depending on the region, 93-95% of people who received an immunoglobulin injection with a tick bite do not get encephalitis. This does not mean that the effectiveness of the tool has the same magnitude - after all, not every tick is a carrier of the virus and not even every bite of an infected tick leads to the development of the disease. Plus, the remedy is often introduced too late, and often in areas endemic for one virus strain, immunoglobulins are used against other strains (for example, an Austrian drug is used in Siberia). Nevertheless, the indicator of security still remains quite high and allows us to consider this method as the most reliable protection of the victim from the development of a dangerous disease.
Such prophylaxis is carried out in most public clinics and hospitals located in areas with high epidemiological risk of tick-borne encephalitis. However, in reality, it can be associated with various difficulties: different institutions are supplied with drugs to varying degrees, in some periods because of the influx of victims, immunoglobulin stocks are quickly exhausted, and in some places simply because of poor organization it is very difficult to see a doctor. Moreover, today the production of immunoglobulins is sharply reduced abroad, where the frequency of tick-borne encephalitis has decreased significantly, and the drug itself is constantly becoming more expensive.
At the same time, it is impossible to buy an immunoglobulin on your own and it is impossible to give yourself an injection - drugs of such an action are distributed only in medical institutions and are subject to strict accounting.
Therefore, in this step, it is necessary in the shortest possible time to come to a state medical institution and try to make an injection of immunoglobulin. It is not very cheap because of the high cost of the drug itself.
The introduction of immunoglobulin is required only once. After each subsequent bite, these injections should be repeated, although the immunoglobulins themselves remain active in the body for several months.
On a note
You can also find recommendations for taking jodantipirin with a tick bite - as an antiviral and prophylactic agent, but the validity of its use is ambiguous. The tool has not passed the full clinical trials, and its effectiveness has not been confirmed. In any case, it can be taken only in accordance with the instructions for use, taking into account all contraindications and possible side effects.
If in the city where the victim lives, there is a special laboratory in which it is possible to conduct a tick study, then it is more rational to first take the parasite removed from the body for analysis, and only if the study confirms the fact of its infection with the encephalitis virus, then already carry out emergency prophylaxis. Such a study is carried out very quickly - if the tick is taken for analysis in the morning, then usually after lunch there will be results.
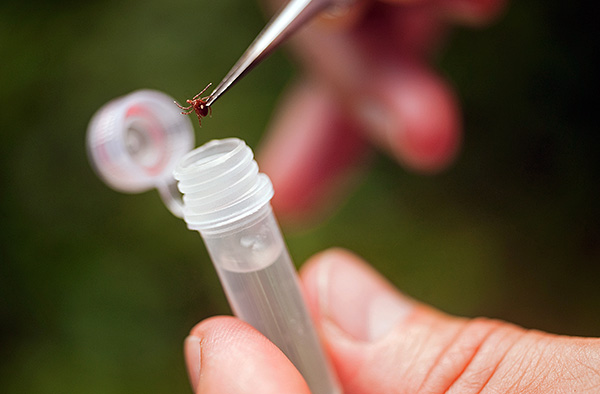
It is only important that the tick be alive - fragments of the body for the presence of antigens may not be investigated in every laboratory, and such a study itself is more lengthy and complex.
In some laboratories, the analysis of a mite is de jure free, but it costs money de facto - fortunately, relatively inexpensively, within 300 rubles. Analysis of the parasite in Borrelia costs around 500 rubles.In almost all clinics, ticks are taken for analysis around the clock.
Step 4. Conduct emergency prevention of borreliosis
Similarly, the prevention of tick-borne encephalitis, emergency prevention of Lyme disease is the introduction into the body of the victim drugs that can suppress the activity and spread of the causative agent. These are mainly antibiotics of the penicillin and tetracycline groups.
However, the need for such actions is not as straightforward as in the case of tick-borne encephalitis. The fact is that even after the appearance of clear diagnostic signs, borreliosis is relatively simple in treatment, and the probability of infection with a tick bite is very small. But its specific prevention requires the use of antibiotics, which can sometimes cause undesirable side effects.
Simply put, both prevention and treatment of borreliosis are carried out by the same means and are about equally effective. At the same time, even without preventive measures, tick-borne borreliosis develops only in about 2% of bitten people - this casts doubt on the need to prevent borreliosis with each tick bite.
On a note
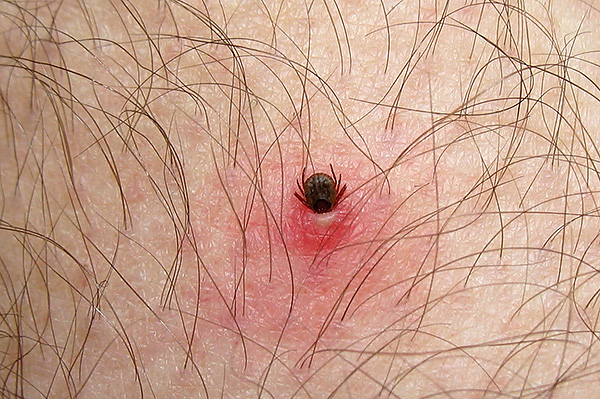
It should be borne in mind that the probability of infection with Borreliosis correlates with the duration of tick blood sucking. It is believed that the bacteria infect humans if the sucking lasts more than 36 hours. In most cases, the parasite is removed from the body much earlier.
The photo below shows a tick that drank blood:

The standard of protection against borreliosis in the United Kingdom and the United States is the administration of a single dose of doxycycline or amoxicillin to an injured person whose body has had a tick for more than a day. Adults most often prescribed tetracyclines, children - penicillins. If the parasite was removed earlier, then emergency prevention is not carried out, and treatment is prescribed only when symptoms of the disease appear.
In other words, drinking antibiotics immediately after a tick bite is impractical. It makes sense to do this if, after checking the parasite, Lyme disease causative agents were found in it, or when the unequivocal symptoms of the disease already appeared.
What not to do when providing first aid for tick bites
For truly effective help, it is important not only to know what measures to take when attacking a tick, but also to understand what not to do so as not to harm the victim.Sometimes the wrong actions in first aid can even increase the risk of contracting diseases caused by ticks.
For example, you can not:
- Try to remove the tick by dripping oil or alcohol on it. It is not always possible by such methods to force the parasite to detach. In any case, these measures are long enough, and when a tick bites, it is important to remove it as soon as possible to minimize the risk of transmitting a significant amount of infectious agents;
- To burn a tick with a cigarette, a match, a cigarette lighter. There is a risk of killing the parasite before he unhooks himself;
- Tear off the tick, grabbing it with your fingers to the torso. This is fraught with not only tearing off the parasite's head, but also crushing it with the release of a large amount of infected saliva into the wound. It is necessary to remove the tick, gently grabbing it with the nails behind the head, under the abdomen - at least, in this case it will not be so easy to crush it;
- Leave the tick in the skin (some plan the next day or even in a few days and show it to the doctor). The longer the parasite sucks blood, the greater the risk of infection from it, so you need to remove the tick as soon as possible.
In general, as in any situation, when a tick bites you can not panic and sleep, because you can make mistakes, which then respond to undesirable consequences.
It is useful to keep in mind that in other places hunters and fishermen dozens of ticks bite every day, and no serious consequences from this happen. The probability of infection after each particular bite is not so great, so you should calmly treat tick attacks, but do everything to minimize the risk of infection.
What to do next?
When first aid is already provided, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the victim for several months.
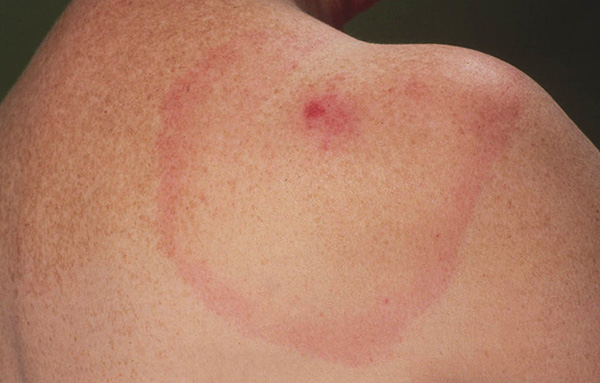
Lyme disease is characterized by the fact that with timely diagnosis and the start of treatment, it is quickly cured, and therefore it is important not to miss the onset of the first manifestation of its symptoms. Tick-borne encephalitis, as a viral disease, requires significantly more complex therapy, however, here timely diagnosis plays a crucial role in the success of treatment.
The incubation period for infection with tick-borne encephalitis lasts from 4 to 16 days, and for infection with Lyme borrelia lasts 1-2 weeks (but sometimes much longer, up to several months).In children, the duration of the incubation period of these diseases is somewhat less than in adults — the parents are responsible for monitoring the condition of the child.
Therefore, after a tick bite for at least 1-2 months, you need to pay special attention to the following symptoms in the victim:
- Heat, fever - are characteristic of both diseases;
- Pain in the head, impaired coordination of movements, frequent dizziness, clouding of consciousness are signs of encephalitis and, to a lesser extent, borreliosis;
- The appearance of erythema migrans - a characteristic redness at the site of the bite, around which there is a “ring” separated from it. This is the main and most pronounced symptom of Lyme disease;
- Cough and runny nose, stiff neck.
If any of these symptoms appear within a few days or weeks after a tick bite, you should immediately consult a doctor and inform him of the fact of the bite. Even if such signs appear a few months after the bite, it is advisable to tell the doctor about the attack of the parasite, as this sometimes helps to correctly carry out differential diagnostics. It is extremely important to consult a doctor as soon as possible.because these symptoms indicate the onset of the acute phase of the disease, and the safety of the affected person largely depends on the promptness of remedial measures.
The nuances of first aid for a tick bite
A good example of the removal of bite mite with a thread