The introduction of immunoglobulin with a tick bite is a fairly widespread practice in Russia of emergency protection against tick-borne encephalitis. This is, first of all, important for people who have bitten in epidemiologically dangerous areas and have not received prior vaccination. The injection is made to prevent the development of the disease and is designed to destroy the first virus particles that have entered the bloodstream from the parasite's saliva.
Immunoglobulin is used for the prevention of tick-borne encephalitis (but not Lyme borreliosis), as the most dangerous disease among the variety of tick-borne infections. Emergency injection is considered to be a very effective procedure, and in many cases it really helps to prevent the development of the disease even with the simultaneous suction of several infected ticks at once.Thus, it is possible with a high probability to avoid the severe effects of tick-borne encephalitis in those people who did not inoculate it.
However, despite the seemingly indicative statistics on the reduction in the number of cases among those who receive emergency prophylaxis of TBE, in the West, immunoglobulin is not used after tick bites. Next, we will understand what this is connected with, and also see if such an injection can be a health hazard and in which cases an immunoglobulin injection will be practically useless ...
What is anti-encephalitis immunoglobulin and why it is needed
In their chemical nature, immunoglobulins are proteins, and their other name is antibodies. They are very specific to strictly defined infections and are produced by the body (namely, white blood cells) only after a collision with the corresponding pathogen.
For example, tick-borne encephalitis virus particles have a surface structure that is unique to them - it is precisely because of this that the human immune system can accurately recognize this virus, and then learn how to react precisely to its appearance.Immunoglobulins are involved in the recognition and destruction of infectious agents.
On a note
Once in the bloodstream along with tick saliva, viral particles of tick-borne encephalitis provoke a cascade of biochemical reactions. Receptors on the surface of blood lymphocytes recognize an antigen and begin to produce immunoglobulins that surround pathogenic particles, preventing them from multiplying and penetrating other cells of the body.
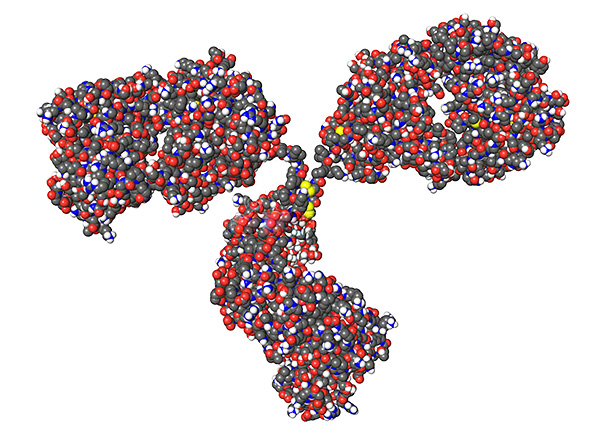
The following is a 3D model of an immunoglobulin molecule:
Antibodies bind viruses spatially, and, in addition, activate other cells of the immune system for more effective protection. The successful outcome of the fight against immunity with infection is determined by how much a virus has entered the blood and whether there are enough immunoglobulins that can destroy it.
See also, what exactly happens when a tick bite - The article shows what determines the amount of infected parasite that falls under the skin.
It is worth noting that the production of antibodies takes time, and at the first collision with an infection, this process is often delayed compared with the rapid reproduction of pathogens, which is why the disease develops. To help the body cope with the infection that has fallen into it, patients are given an injection of ready-made antibodies that have been previously concentrated and purified. Thus, the dependence on the rate of formation of own immunoglobulins disappears, and the chances of staying healthy when bitten by a tick infected with a virus sharply increase.
However, no method of prevention provides a 100% guarantee. According to statistics, about 20% of people with tick-borne encephalitis received timely prevention, that is, they got sick, despite the timely injection of immunoglobulin. On the other hand, in the group of patients after an emergency injection, the frequency of severe forms of encephalitis was significantly reduced, yielding to lighter ones.
Anti-encephalitic antibodies are obtained from the blood of vaccinated donors. When a donor is vaccinated, the immune system creates an “illusion” of infection (through the use of an inactivated CE virus), which causes the body to produce immunoglobulins in large quantities. Just at this time they can be borrowed from the blood plasma.
The drug is purified in several stages so that only a fraction of the desired proteins remains in it.Due to the fact that people are involved in the production as donors, anti-encephalitic immunoglobulin (or gamma globulin is an older name) is a rather expensive drug.
Human immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis is used for prophylaxis in the form of a single injection, which should be carried out as soon as possible after the established fact of a tick bite. The dose is calculated according to the weight of the patient.
On a note
Immunoglobulin injections are also used in the treatment of already developed tick-borne encephalitis, but usually in the form of a course and in completely different dosages, which increase depending on the severity of the patient's condition.
It is important to bear in mind that antiencephalitis immunoglobulin is a strictly specific drug that is effective only against tick-borne encephalitis virus. For example, for the prevention of borreliosis, it will be completely useless (this disease is caused by bacteria, not viruses, and it is treated with antibiotics.) In addition, the immunoglobulin is used only for humans. For example, dogs and cats are generally less susceptible to viral encephalitis, so for them an emergency "antidote" for this infection is not provided.
On a note
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis and emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis is not the same thing. When setting up a vaccination, the patient's body is provoked to develop its own antibodies against the virus, whereas in case of emergency immunoprophylaxis, the human-ready antibodies, obtained from the blood of vaccinated donors, are introduced to the person. And if the vaccination is done long before the bite, then emergency prevention is carried out immediately after the tick attack.
How to find out if emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis is necessary when a tick bites
Annually due to bites ixodic ticks in Russia alone, about half a million people go to hospitals. At the same time, only about two thousand of them become ill. That is, the chance of becoming a victim of infection is relatively small - but this does not mean that precautionary measures can be ignored.
It is important to note that immediately after a bite, it is impossible to learn about the fact of infection. Despite the fact that there are tests, they can determine the development of the infection no earlier than two weeks after the tick has bitten a person. The only relatively quick way to find out if prophylaxis is needed is to check the tick in the laboratory for an infection (many people hope to recognize an infected tick by external signs - in this regard, seealso a separate article How to distinguish an encephalitis tick from a normal non-infectious parasite).
For verification, it is better to keep the parasite alive, because it is more difficult to detect the presence of viruses in a dead tick or its fragment - the probability of an error increases. Thus, immediately after removing the tick, you need to place it in a jar with a tight-fitting lid and go to the nearest laboratory, which performs the appropriate tests.
The result of the analysis of the parasite will show whether an emergency prophylactic injection of immunoglobulin is needed. The study is not free, and sometimes the result has to wait up to two or three days, and the delay affects the effectiveness of immunoglobulin in the event of infection. Therefore, people often prefer to immediately give an injection, especially if the tick bite occurred in an epidemiologically dangerous region for tick-borne encephalitis.
It should also be borne in mind that lifelong immunity after tick-borne encephalitis is not formed. Therefore, even if a person has once suffered from this disease, after a few years there is a chance to get sick again in case of infection.
On a note
Tick-borne encephalitis can not be infected if the tick just crawled through the body, but did not have time to bite. In this case, you should carefully remove the parasite from the body and destroy it (it is only important not to crush it with your bare hands). Donating a tick for analysis in such a situation is not necessary.
Emergency prophylaxis of TBE must be carried out by people who have been bitten in an epidemiologically dangerous area, without having taken a tick for analysis and have not vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis.
Conversely, if you are bitten in a region that is not dangerous for tick-borne encephalitis, or if you have a vaccine, there is no need for the introduction of immunoglobulin.
Manufacturers and preparations of tick-borne immunoglobulin
Present on the market for immunoglobulin tick-borne encephalitis - domestic production. In Europe, its manufacture was abandoned for two main reasons. First, the entire population in European-endemic areas of Europe is being vaccinated, and there is simply no need for an anti-tick immunoglobulin. Secondly, since this drug is protein in nature, it can cause allergic reactions, and sometimes quite severe ones.The use of such funds is associated with a certain risk, not always justified.
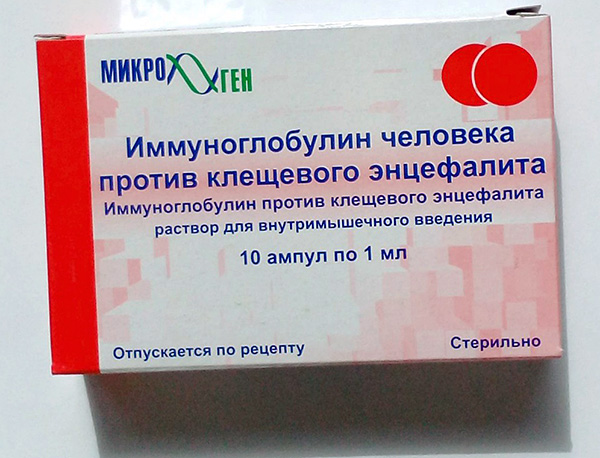
In the Russian market at the moment, only immunoglobulin produced by NPO Microgen can be found on sale. It is sold exclusively by prescription, in packs of 10 ampoules, 1 ml each. The price of a full pack of 10 ml in Moscow is approximately 7,000 rubles. The titer is indicated on the drug box, that is, the protein concentration in a unit volume of the solution is expressed.
On a note
Among the components of the drug is only two: the human immunoglobulin itself, obtained from the blood plasma of donors, as well as the stabilizer - glycine. The manufacturer guarantees that all donors have been tested for antibodies to HIV and hepatitis C and B. The preparation does not contain preservatives and antibiotics.

Doses and order of use of immunoglobulin
For emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis, the dose of globulin is determined at the rate of 1 ml per 10 kg of body weight. Thus, an adult person weighing 70 kg needs to inject 7 ml (that is, 7 ampoules) of immunoglobulin once.
Injection is always made only intramuscularly, it is prohibited to inject a vein in accordance with the instructions for use.After removing the ampoules from the refrigerating chamber, they are warmed to room temperature before the injection.
On a note
In the case when an already developed tick-borne encephalitis is treated with an immunoglobulin, the dosage is calculated according to the same principle, but the injections are given several days in a row with a certain periodicity - this depends on the severity of the disease in each case.
Store the drug can only be in the refrigerator, and transport at a temperature of 2 to 8 degrees Celsius. A suitable solution of immunoglobulin is transparent - it can be colorless or slightly yellowish. The presence of sediment is acceptable, but it must quickly dissipate when the ampoule is shaken. If large stable flakes are visible in the solution, such a preparation is unsuitable for use - most likely, its storage conditions were violated.
In Moscow and regions endemic for CE, it is possible to inject immunoglobulin free of charge for children under the age of 18 years (in some cases up to 14 years). When it is established that a tick attacks, adults can also receive this service at a state hospital free of charge upon presentation of an OMS policy.However, there may be such a situation that there simply will not be a drug at a state clinic, and you will have to contact paid medical organizations where the cost of the injection is quite high - for example, with a body weight of 50 kg, the cost of one drug (without the cost of work) can be as 3500 rub.

It is important to know
The more time passes from the moment of tick bite, the less effective emergency prevention will be. After four days, it is practically useless to place the immunoglobulin.
What side effects may occur after injection
The manifestation of any side effects of immunoglobulin against EC on the body are extremely rare. Sometimes swelling and pain in the injection site are possible for the first couple of days. This is the most common complaint of those who underwent the procedure. To avoid such reactions, the entire dose is divided into several injections, which are carried out in different parts of the body.
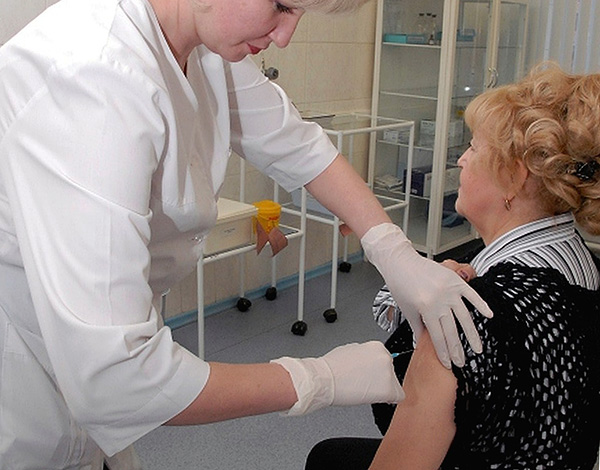
Usually, injections are made in the area of the gluteus muscles, the forearm, and the external muscles of the thigh - these are the most convenient areas for injection. After the injection, an increase in body temperature up to 37-38 degrees can also be observed (usually decreases to the norm during the day). If the temperature lasts longer than 24 hours, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
There is currently no official information about drug overdose: since the procedure is performed strictly in a hospital setting, and the dose is clearly calculated, there were no cases of overdosing. The number of times in a life that is acceptable to repeat injections of an immunoglobulin is not limited. However, emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis can be carried out no more than once a month (only in the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis, injections are often made).
On a note
It is extremely rare in highly sensitive people that immunoglobulin can cause a serious allergic reaction - anaphylactic shock. This condition occurs very quickly after the injection, and in the absence of timely antihistamine therapy can lead to the death of the patient. This should be taken as seriously as possible, especially if the person knows about his predisposition to allergies. After the injection, you should not immediately leave the medical institution - you are supposed to sit here for at least 30 minutes.
You can not take ampoules with immunoglobulin with you on trips and, moreover, do an injection outside a medical facility.Firstly, if the storage regime is violated, the drug will quickly deteriorate, and secondly, the consequences of such initiative can be unpredictable.

In interaction with other drugs in human immunoglobulin against CE, there are no particular limitations. The only thing worth refraining from for three months after the injection is immunization with serum of live viral vaccines. This is due to excessive loading of the immune system, which must be given a "rest" after an anti-encephalitic injection. If you prick the drug with viral particles immediately, the body may react inadequately.
A few words about contraindications for emergency injection
There are no bans that strictly exclude the use of immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis. Even somatic diseases in the acute phase (ARVI) are not a contraindication - the injection will still be put against the background of the main treatment. But they observe the reaction of such patients especially carefully.
Official data on studies on the use of immunoglobulin during pregnancy and during lactation does not exist, so it is prescribed with caution, weighing the possible risks and benefits for the health of the mother and child.
Alternative methods of preventing tick-borne encephalitis by tick bite
There are several drugs that today with varying success are used as analogues or aids to the injection of gamma globulin. Like an emergency injection, they cannot provide absolute protection, but, as some experts believe, they help prevent the disease.
Most popular analogues:
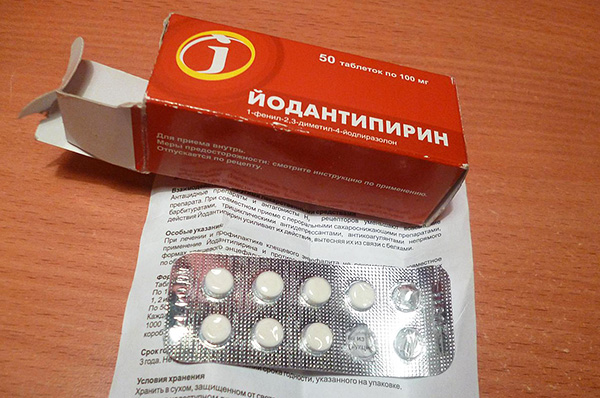
- Yodantipirin - pills used specifically against tick-borne encephalitis virus and hemorrhagic fever, transmitted by the same ixodic ticks. Named drug according to the active substance. The manufacturer claims that jodantipirin has an immunostimulating effect, and also stabilizes the cell membranes of the body, delaying the penetration of viruses into them. For prophylaxis after a bite, it is recommended to take a 9-day course of taking the drug, gradually reducing the dose from nine tablets per day to three. Yodantipirin is prohibited for use in disorders of the thyroid gland, as well as the liver. Its indisputable convenience lies in the fact that the reception can be carried out in the field, and medical supervision is not necessary.Some studies even claim that jodantipirin acts more efficiently than an immunoglobulin injection, but these experiments were carried out on the order of the manufacturer, and so far no independent expert evaluations have been carried out. Nevertheless, jodantipirin is used today sometimes both for prevention and for the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis;
- Remantadin is a broad-spectrum antiviral agent. It is used less frequently than the previous preparation, but it has proven activity against arboviruses, to which the tick-borne encephalitis pathogen belongs. The active ingredient blocks the reproduction of viral particles, disrupting the processes of their assembly in the cells of the human body. Previously, rimantadine was actively used against influenza, but then all strains of the influenza virus developed resistance to it, and today the drug is practically ineffective against this infection. The specific regimen for the prevention of encephalitis in the instructions to the drug is not indicated at all, therefore, they follow the standard regimen. Remantadin should be used with caution in the pathologies of the kidneys and liver, and it is also forbidden to combine with alcohol.The opinions of specialists regarding its effectiveness against tick-borne encephalitis are contradictory, and the medical community still does not have a definite opinion on this subject;
- We should also mention Anaferon, on which many people pin their hopes on tick bites. It is a homeopathic drug whose manufacturers claim that it helps stimulate the body’s own immune response against infection and the production of endogenous human interferon that protects cells from viruses. In fact, the manufacturer himself does not conceal that the drug does not contain any specialized active ingredients, and is only a placebo remedy. For this reason, it is definitely considered by professionals to be useless with respect to any viruses in principle, and because of this, also harmful, because when it is used, people lose time on ineffective measures. But this drug still continues to actively move through advertising.
Thus, there is no reliable alternative with a proven clinical effect in emergency prevention with immunoglobulin.
Is it possible to replace vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis with immunoglobulin
The main advantage of an immunoglobulin injection before vaccination is that it can be pricked upon the fact of a bite, and if the tick of a person has not bitten, then it is not necessary to enter anything. But to carry on yourself all the "charms" of vaccination (sometimes you have to endure its side effects) and you have to pay money for it, regardless of whether the tick bites a person in the future or not.
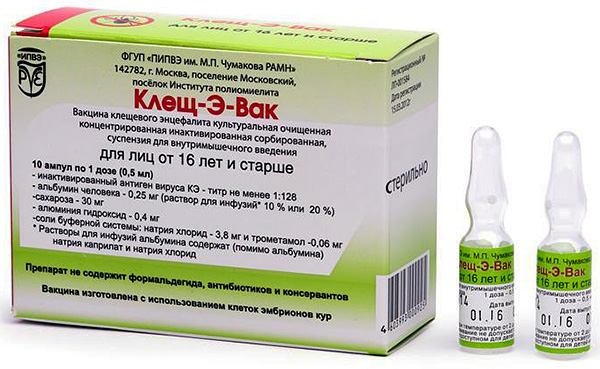
The photo below shows an example of tick-borne encephalitis vaccine Tick-E-Vac:
In addition, immunoglobulin injection is a fast-acting agent, unlike vaccination.
On the other hand, the effectiveness of such an injection is much less than that of vaccination, carried out according to all the rules. And if you do an injection a few days after the attack of the parasite, then its effectiveness becomes negligible.
A vaccinated person may not be afraid of tick-borne encephalitis - if there is a vaccine, then the level of protection is approaching 95%. Even in rare cases of encephalitis in vaccinated people, the disease proceeded easily and without consequences.
However, the obvious disadvantage of vaccination is the duration of the course. Reliable immunity is formed only a month after the second vaccination, which can be done no earlier than two weeks after the first.
On a note
If a person has been properly vaccinated, then even in the case of a bite from an infected tick, immunoglobulin is not delivered. There is no need for this, since such a patient has enough of his own antibodies in the blood. Moreover, emergency prophylaxis to a vaccinated person can even be harmful - a surplus of immunoglobulins, and of different origin, can cause unwanted reactions from the immune system.
However, if the vaccination course was not fully completed, then an immunoglobulin injection with a tick bite can be given. It is also possible to use it if the vaccinated person is still sick, although such cases are extremely rare.
Be that as it may, according to the main parameter - effectiveness - today there is no prevention method that has shown itself to be better than vaccination. If there is enough time, then it is necessary to give preference to her.
If you have personal experience of using immunoglobulin after a tick bite - be sure to share the information, leaving your feedback at the bottom of this page.
Useful video: first aid for tick bites
What is important to know about the prevention of tick-borne encephalitis (including emergency)