
Clothes and furniture moths have long been known to spoil clothes, fur and wool products, upholstery and carpets. At the same time, the furniture moth prefers fur, furs and wool, and the clothes moth prefers mostly cotton products. In nature, both species are keratophagic - that is, they feed on animal hair and feathers, and in an apartment they can easily switch from one diet to another.
It is interesting
Among the moles there is a butterfly, the caterpillars of which gnaw holes in the horns of African antelopes and live in them, eating keratin.
In the past, both of these types of room moths were called collectively the clothes moth, and even today this habit has been preserved among the people, although the butterflies themselves are quite easily distinguished from each other. Therefore, later in the text, when describing the general features of biology, both species will be referred to as the dress moth, and if clarification is needed, this will be discussed separately.
First look at the clothes and furniture moths
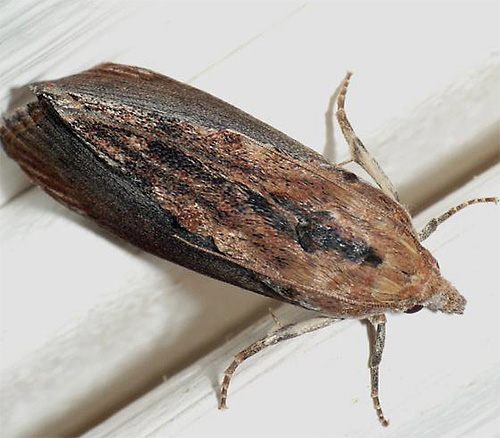
Both types of moth are quite similar to each other. Adult butterflies are small - in length with folded wings, they reach 5-9 mm, and have an inconspicuous straw-yellow color. The furniture mole may be somewhat darker, and it also has slight darkening at the base of the wings.
The clothes moth is almost always light yellow. With the naked eye, the differences between these species are difficult to grasp. For example, in the photo below - clothes moth:

And the following photo - furniture mole:

In the air, a furniture moth looks like a small moth not the most skilled in flight. Fly only in the furniture and in the clothes moth exclusively males. Females have wings, but they do not use them.
It is interesting
The opinion that females of the room moth are wingless is not true. Any indoor mole has winged females and males. The wings of the females are only slightly smaller than the wings of the males, and in principle, the females are able to fly. But they do not use this ability as superfluous - the males themselves find them, fertilize them, and the females lay eggs without long-distance movements.
Inexperienced eyes can hardly find differences between males and females of the clothes moth.From the food moth, for example, a barn moth or a mill, the dressing room is distinguished by the uniform color of the wings. All types of fire spots on the wings have a rather noticeable pattern.

But the most important pest is not at all butterfly moth. The direct destroyer of clothing and furniture upholstery is larvae of clothes moth - inconspicuous small caterpillars, gently and fairly quickly gnawing holes in sweaters, tracks on fur coats and bald patches on carpets.
Larvae and moth eggs: how and where to find them
So, it is the larva of the moth that feeds on our clothes. From wool and cotton, the caterpillar can pull out the minimum of nutrients that are there, and for this it has all the necessary devices:
- sufficiently strong and long mandibles - two large outgrowths that act as scissors for cutting fibers of fabric and wool of fur. Each of them has several teeth that increase the gnawing capabilities of the caterpillar.
- Powerful jaw muscles - almost the entire head - due to which the caterpillar can develop enough pressure for nibbling matter.
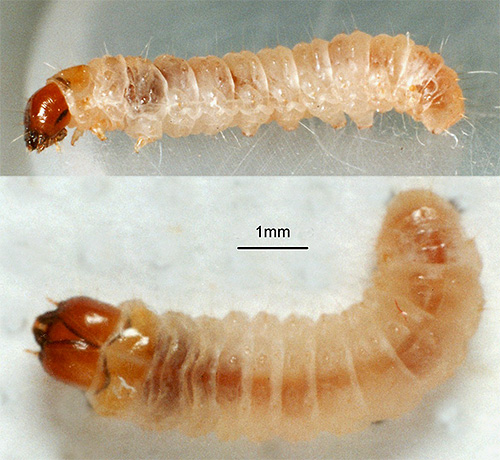

- Huge in comparison with the size of the body, the stomach and intestines,in which a large amount of food is able to accumulate.
At the same time, the larvae of the furniture moth are well distinguished from the larvae of the wardrobe. The larva of a clothes moth can build a simple little cap from its own excretions and food debris, while the furniture moth caterpillar builds a well-marked and durable corridor along the entire route of its movement.

The photo below shows the larva of the clothes moth. It keeps such whitish-yellow coloring throughout all the development:

The caterpillars of the room moth are rather inactive. Only having hatched from eggs, they creep apart for small distances from each other, but after the beginning of a good nutrition they move very little.
It is interesting
Caterpillars of the clothes moth carefully avoid light. If you bring the clothes with them to the light, they try to hide among the folds or in their covers.
If the food is well suited to the larvae of the room moth (it contains little or no synthetics), they grow quickly, and in 18–20 days they manage to molten 12–13 times, after which they pupate. If the caterpillars have to eat low-nutritional food (for example, with a high content of non-digestible synthetic fibers), in most cases the development is delayed to 1-2, and sometimes up to 6 months.
On a note
The development of the larvae of the room moth slows down even in the case of a decrease in air temperature at the place of their presence. The caterpillars themselves become shallow and, when they reach certain temperatures, they hide in cocoons and stop feeding.
Eggs of house moth species are white or whitish-yellow in color, small and do not exceed 0.5 mm in length. The female lays them in small groups of 50-80 pieces directly on clothes or other tissue, which the larvae will later feed on.
An example of laying eggs for a clothes moth is shown in the photo below:
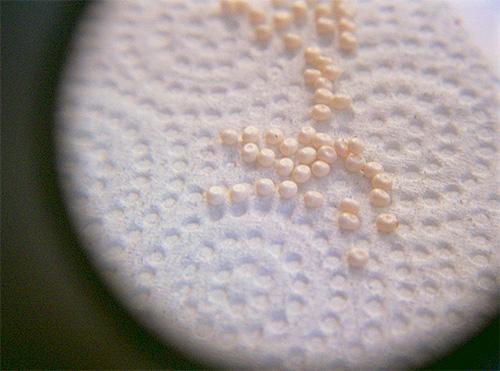

The eggs of clothes and furniture moths develop within 5-6 days, but when the air temperature decreases, this period is delayed, and when it reaches 0 ° C, the eggs generally die.
Food moth and the main harm from it
Adult butterflies clothes moth do not eat at all. The oral apparatus and the digestive tract are underdeveloped, and they do not need feed.
By the way
Butterfly moths live on the strength of a few weeks, more often - 8-10 days. Usually females lay eggs on the third or fourth day after they leave the pupa, after which they rather quickly die.
Moth larvae feed almost at the same place where they hatch from eggs.They eat any natural fabric, fur, wool, they often parasitize on stuffed museum and in warehouses of textile raw materials.

Moth larvae that feed on fur can not move freely in the fur. Therefore, they have on their way to gnaw hairs of fur, which they do not eat, leaving a clipped path and a pile of wool on clothes.
Moth caterpillars cannot eat fully synthetic things. If the fabric is partly synthetic, then it can be eaten by the larva, but on such a diet the caterpillar grows much slower than on natural tissues.
Reproduction and lifestyle of the pest
Coming out of the pupa, the males of the clothes moth begin to search diligently for the female, being guided, first of all, by smell. After mating, after 3-4 hours, the female begins to lay eggs. She lays them in portions, while the furniture mole is much more prolific - one female can lay up to 300 eggs, while in the female of the clothes moth this number barely reaches 60.
The clothes moth does not have seasonality in development and reproduction. Larvae from one clutch can develop at different speeds, and the flight of butterflies from larvae occurs unevenly and separately.In nature, all species of mid-latitude moths have a period of hibernation, usually pupae or caterpillars of recent ages winter.
Fight against moths: are there really reliable means?
Today, there are many ways to get rid of the clothes moth, both traditional and fairly modern. The most effective among them are the following:
- Treatment of clothing insecticidal drugs in aerosol form. Such tools allow you to quickly destroy the larvae and butterflies at any time of the year.

- Freezing contaminated clothes and furniture outdoors at temperatures below minus 5 ° C, or warming them up in the sun on a hot summer day with preliminary thorough shaking out - the larvae do not adhere to the surface of the clothes and easily crumble.
- Washing clothes at the maximum temperatures allowed for it.
- The use of insecticidal fumigators installed in cabinets.

To protect cabinets and wardrobes from moths, they use strongly smelling herbs - tansy, lavender flowers, rosemary, as well as orange peels, tobacco, and special industrially produced sections from moths with various odors.Unfolded in cabinets, they are capable of quite reliably scaring off adult butterflies. It is only important to understand that such odorous agents do not act on the larvae.
But the most reliable way to prevent the reproduction of moths on things is a careful quarantine: checking new purchases, thoroughly washing clothes at high temperatures, avoiding purchases "from the hands" and second-hand. After all, it is always easier to prevent the appearance of a pest in an apartment than to get rid of it later.
Useful video: how to get rid of moths?
Video reviews on effective and proven ways to get rid of moths




Cool article!