
The potato moth has always been a natural neighbor of the famous Colorado potato beetle. It was in South and Central America that it harmed tobacco and potatoes from the time of ancient Indian civilizations, and only at the beginning of the last century began to spread throughout the world.
At first, the countries of Southern Europe submitted to it, then the south of Russia and Africa, and today it is the potato moth that is considered the main pest in New Zealand and Australia. It can be considered a real cosmopolitan, who has already managed to spread across all continents of the planet.
Such an increase in the range may seem especially surprising, given that the potato moth is a very thermophilic insect. It is believed that its populations can multiply steadily only in places where the average annual temperature does not fall below 10 ° C. In such areas, this butterfly can be a real scourge of farmers.
Appearance and characteristic differences of the form
Potato moth looks rather unsightly. The general background of its wings is dirty gray with numerous black spots, which form two distinct dark stripes when the wings are folded. The photo below shows a potato mole with folded and spread wings:

The potato moth butterfly has characteristic long antennae and a reduced oral apparatus. She cannot eat, and does not live long - usually several days, very rarely - several weeks.
The length of the butterfly with folded wings is 6-7 mm, and the patronizing coloring allows it to remain invisible even when looking straight from a short distance.
The larvae of the potato moth are small — about 13 mm have a caterpillar of the last age. Such a larva weaves a little case, in which it pupates and turns into an adult butterfly. The pupa is about 10–12 mm long.

The caterpillars are white-green or white-pink with a pale stripe along the entire back.
Eggs of potato moth is difficult to notice, even at close range. Having a length of about half a millimeter, they are placed by the female on the underside of the leaves in small groups and develop very quickly.


Immediately after laying such eggs are pure white, and later darken a little.
Food, reproduction and pest lifestyle
Under optimal conditions, the entire life cycle of a potato moth, from an egg to the laying of new eggs by an adult, lasts only a short time — about 33-35 days. In winter, this period extends to several months.
In the conditions of middle latitudes, butterflies do not spread far to the North, because they do not know how to winter, and at temperatures below minus 4 ° C they die. As a rule, their distribution is limited by a line, beyond which in winter the soil freezes below this temperature. With a slight frostbite of potato tubers, the caterpillars in them can remain alive. It is believed that they often move from harvested fields to storage facilities, they multiply there in winter, and in spring with seed potatoes they are again buried in the ground.
Sometimes butterflies and pupae can winter under a layer of leaves in open ground.
Caterpillars of potato moth feed on various plants of the family of the nightshade. It can be potatoes, and tomatoes, and nightshade, and eggplants, and pepper, and even belladonna, and numerous wild solanaceae.

In this case, the larvae gnaw the leaf blades, and also gnaw the legs of the leaves themselves and feed on the tubers.It is because of this universality that the potato moth has the ability to spread very widely and quickly.

Butterflies of potato moths are active at night and have a huge number of enemies. They are fed by all and sundry - other insects, bats, and birds. At the same time, the life span of an adult butterfly is on the strength of several weeks, during which it manages to mate and lay eggs. For one summer season in the south of Ukraine the mole manages to give 3-4 generations.
Potato moth equally well propagated in closed warehouses, on agricultural land and in the wild. However, it is in the first two places that its reproduction is practically not controlled at all by natural enemies, and the butterfly can reproduce at a super fast pace. And already its tracks will cause major harm.
Danger and harm of potato moth
The main danger of the potato moth is as follows:
- weakening of the bushes of agricultural plants due to the destruction and mining of leaves
- damage to potato tubers and reduced crop quality
- reduction in the quality and volume of potato seed
- weakening and death of young bushes of tomatoes and peppers.
A potato tuber, struck by 9-10 caterpillars at the same time, will look like a sponge, in which the larvae almost completely eat away the core.
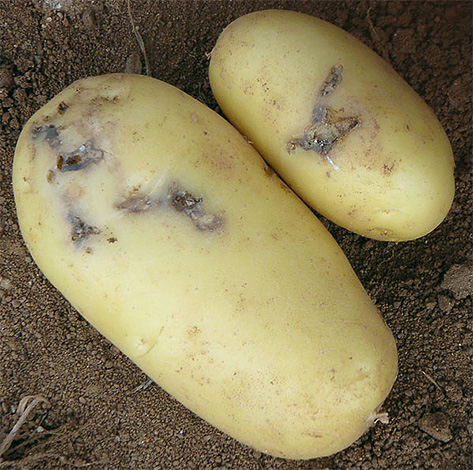


In the presence of a large number of insects and favorable breeding conditions for them, the mole multiplies faster than the fodder culture develops. At the beginning of spring, a small number of larvae diligently destroy young and tender seedlings, later they harm adult plants, and the maximum number of caterpillars appears when the tubers and fruits develop on the bushes.
In places with strong infection with potato moths, up to 80% of the crop is not suitable for export due to the loss of the ability to be stored and processed.
Fighting potato moths: measures and means
One hundred percent methods of dealing with potato moths are not developed today. The fight against it should be comprehensive and consist of both liquidation and preventive measures.
The following means are used to destroy the butterflies and caterpillars themselves:
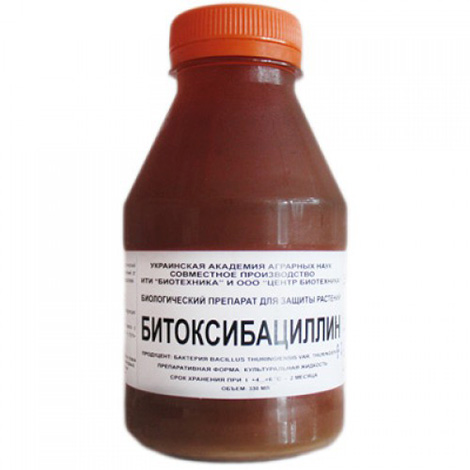
- Preparations based on bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis - Bitoxibacillin, Dendrobatsillin, Entobakterin, Lepidotsid.They process bushes at any stage of development before the appearance of ovaries, and such measures ensure the death of a part of the larvae, a decrease in fecundity of females and a delay in the development of the moth at each stage;
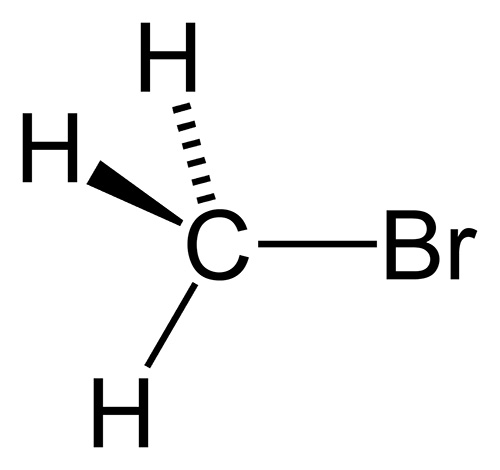
- Methyl bromide is a gas that allows you to fight potato moths after harvesting potatoes (using fumigation with methyl bromide, stored tubers are processed);
- Special traps for butterflies and larvae.
Measures to combat potato moths also include a competent crop rotation, hilling potato and tomato bushes, and laying only healthy tubers at the maximum depth for the variety.
A good preventive way to get rid of the potato moth is to grow only early varieties of potatoes, which the pest is almost not afraid.
The tubers themselves before sowing must carefully check and sift those with signs of damage. This will help if you do not completely get rid of the potato moth, then at least significantly reduce the scale of damage to the site by it. It is even better to warm the tubers for several hours at 40 ° C - this does not reduce their germination, but will kill a significant part of the moth larvae.
It is also very important to control the growth of weeds on the borders of the cultivated area.

All wild solanaceous around the site are natural pest reservoirs, from which the mole easily moves to garden crops.
On a note
Many farmers in South Africa attract a special species of wasps, which are parasites of potato moth larvae, to their farms. In the northern hemisphere, these wasps do not live.
Today, many countries observe quarantine measures against potato moths. For example, the import of potato tubers by private individuals is prohibited in Ukraine, and potatoes imported into Australia are subject to heating and insecticide treatment. But even despite such measures, the potato moth successfully continues to conquer the world.
Useful video: about the danger of the invasion of potato moths
Rosselkhoznadzor about potato moth and quarantine measures



