For those who are accustomed to counting wood insects as insects, it may seem surprising that in reality these creatures are representatives of the order of isopod crayfish, in fact, they are small crustaceans. Their closest biological relatives are large giant isopods of crayfish, as well as a large number of interesting marine crustaceans called sea cockroaches.
But ordinary crayfish familiar to us, although with a stretch, can be attributed to the woodlouse relatives, but rather distant - systematically wood lice and river crayfish have a not very high degree of kinship.

On a note
Thus, to say that the wood louse is an insect is completely wrong, and is a blunder. With insects in wood lice is as much in common as in humans with turtles.And, accordingly, to call wood lice bugs or bugs - also a common mistake of the inhabitants.
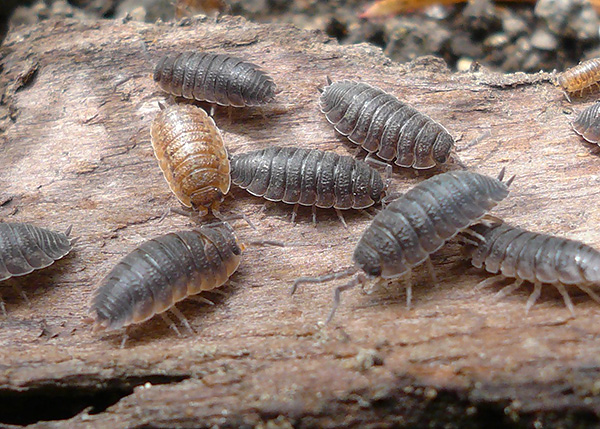
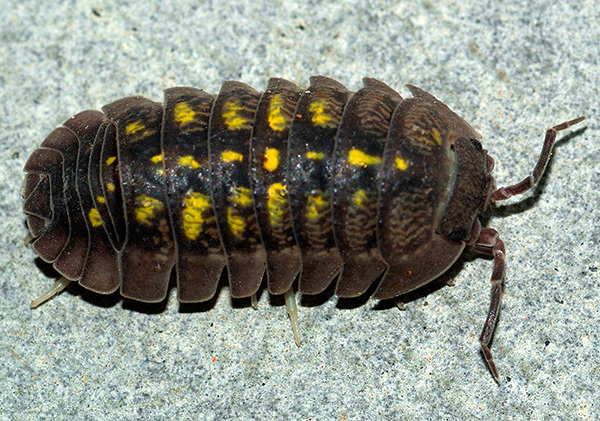
In the photo below - common wood lice (Armadillidium vulgare) at the dacha:

Woodflies are crustaceans, leading a rather secretive way of life and are rarely seen by humans. For this reason, attention is paid to them mainly by biologists, as well as gardeners, with whom these creatures can damage the crop. Nevertheless, there are a lot of interesting things both in biology and in the anatomy of the wood lice - we will go on and talk about these interesting nuances ...
Appearance and photos of woodlice
Almost all types of wood lice have the characteristic appearance of a small “armadillo” with a large number of legs.
Photos of woodlice:
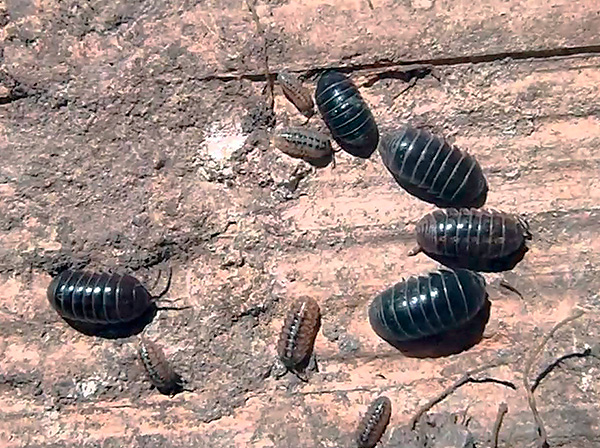
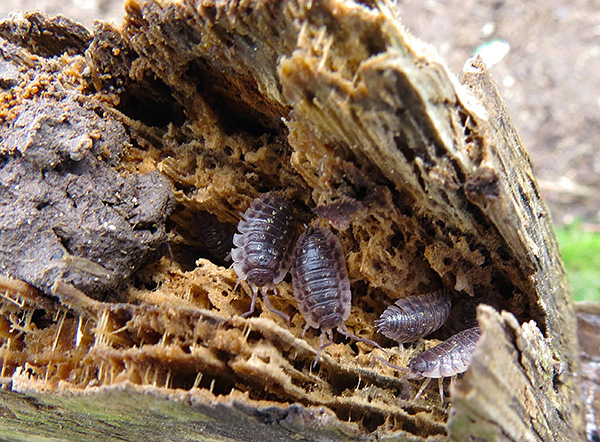



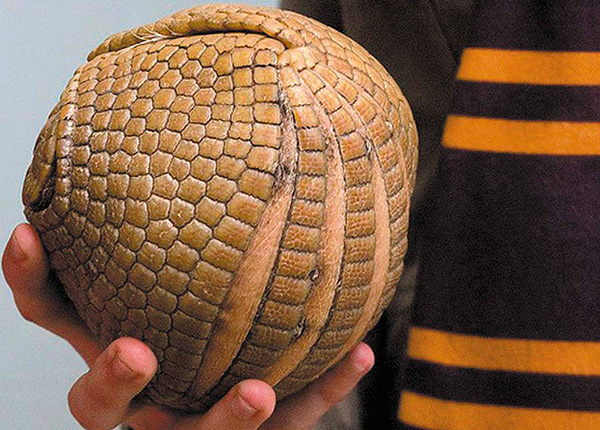
And here is a photo of an armadillo:


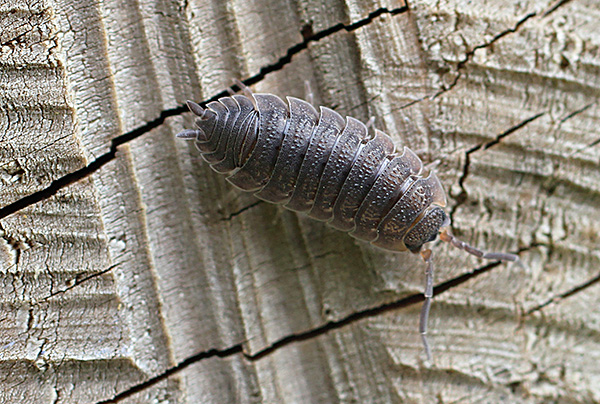
The body of wood lice is covered with rigid and solid chitinous shields protecting it from numerous predators. It is these shields that create the characteristic appearance of wood lice and significantly distinguish it from most insects. For example, beetles or hemiptera insects have two dense wings, but never 9-10 separate segments, like a woodlouse.
Below the photo clearly shows the division of the body of the wood louse into separate segments:

Lackes have 7 pairs of walking legs, which distinguishes them from the same crayfish with five pairs of walking legs and three pairs of legs turned into tools for eating. Insects have only 3 pairs of legs.
The internal structure of wood lice is similar to that of ordinary crayfish. Her respiratory organs resemble the gills, but they operate in the lung mode and are located at the base of five pairs of thoracic legs.
All wood lice have antennae of several segments, along the length and fracture of which sometimes separate species of wood lice differ. In the photo below, these antennae are clearly visible in one of the species:

As a rule, wood lice are painted quite inconspicuously - this allows them to mask themselves on the ground, in the grass and under the stones. The two most common types of wood lice in our country are gray in body color, others may be lighter and with green shades in color. Only in some species on the body there are pictures or stripes.


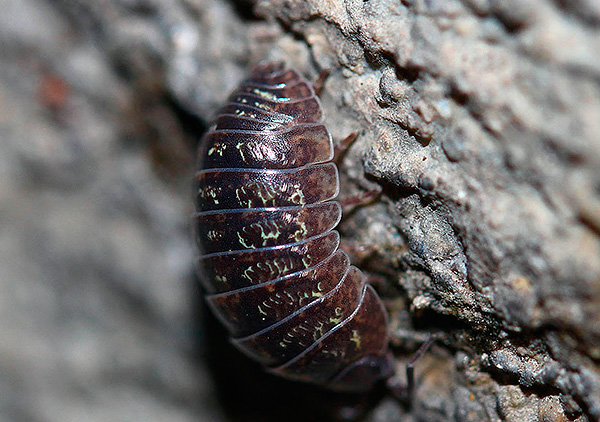
There are no special outgrowths and, especially hair, on the body of wood lice.
Feedback
“For two days, the son told us on the phone how scared he was with his grandmother and how he was afraid to go into the summer shower, because there is a hairy louse sitting on the wall. When they came to pick him up, they went into the shower especially for the sake of interest. There are flycatchers sitting under the ceiling - such brisk centipedes that are eaten by flies.We explained everything in detail to him, but he probably just wanted us to come as soon as possible. ”
Taisiya, Yaroslavl
Here is another photo showing the arctic ironfly, the most common in the European part of Russia:

The usual length of the body of wood lice is 0.5-1.5 cm, and the largest species barely grow up to 3-4 cm in length. Sometimes they are confused with wood lice because of the similar appearance of larger millipedes from the glomeris family:
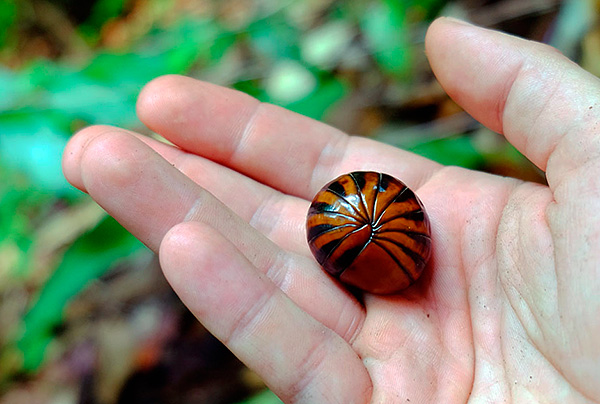

Nevertheless, although the two-pair millipedes are similar in appearance to wood lice, they differ from them in lifestyle and biology.
Types of wood lice: from domestic to oceanic
Today, scientists number more than 5,000 species of woodlice throughout the world, of which only a few dozen species are found in our country. Moreover, wood lice are quite thermophilic creatures, and therefore most of their species inhabit the tropics and subtropical belts.
Despite the similarity of the appearance of different woodlice, even an unprepared person can easily distinguish the most common varieties of them.
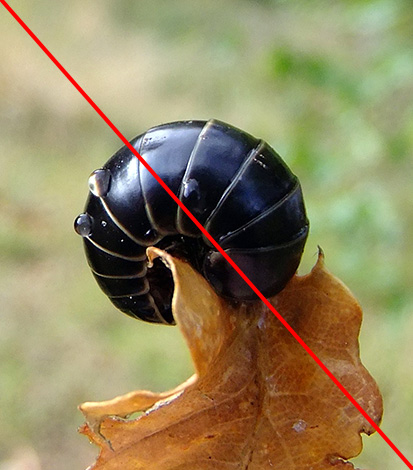
For example, the photo below shows an armadillo common arthritis, rather cumbersome and slow.When in danger, it has the habit of curling up. Some individuals have yellowish spots on the back:
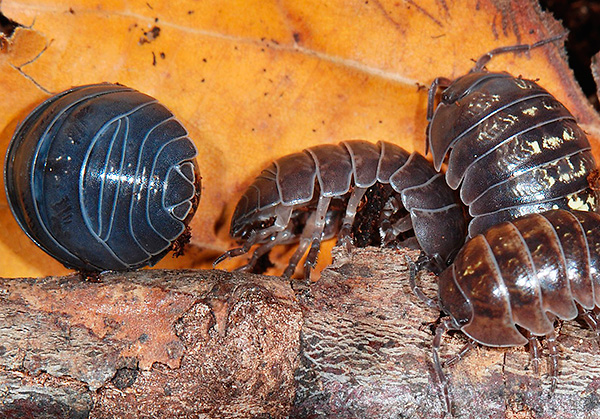

Common woodlice is most often found in gardens, vacant lots and basements.
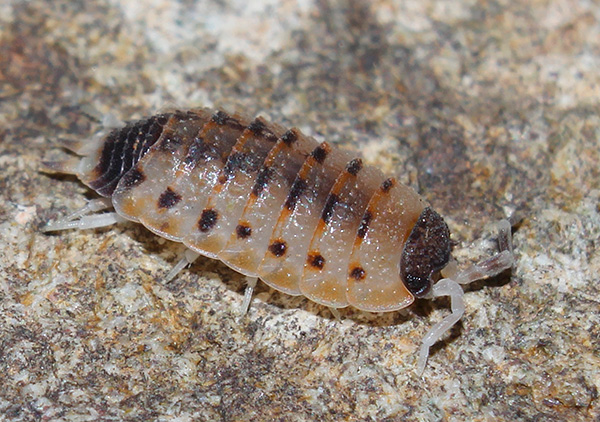
And then in the photo - wood lice rough, more mobile and flat than the previous form. She is known as the house louse, because she often penetrates from the basement into the house:
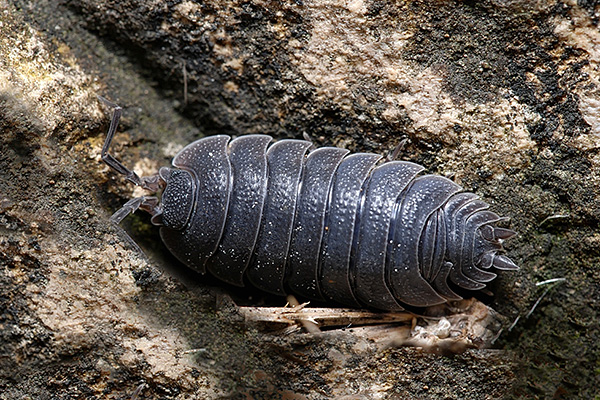

At the same time, like domestic insects, wood lice in the room try to hide in the most secluded places, choosing the most humid corners, and come across the eyes only by chance.
And in the photo below - sea lice, living in the shallow waters of the Mediterranean Sea. This is one of the few species that has returned to its original habitat:
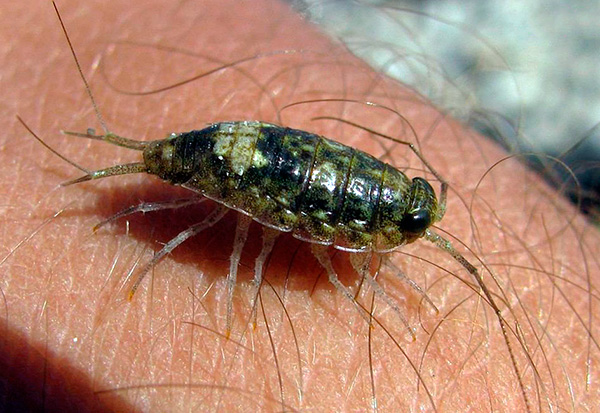

In addition, there are types of woodlice, well adapted to life in a very dry climate. For example, Hemilepistus reaumuri - lives in the deserts of Asia Minor and North Africa, digging for protection from the sun and the heat of a hole with a depth of up to a meter.
In the photo - desert woodlouse goes into the hole:
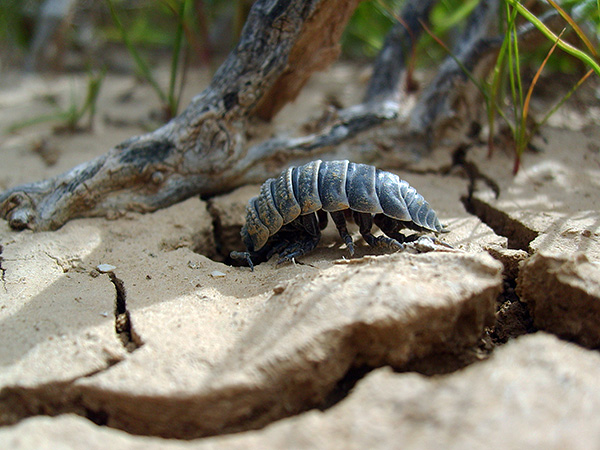

Giant sea isopods, which sometimes grow up to 75 cm in length, are strictly speaking, are not wood bones, and are so called by the people only because of the similarity of their appearance with the appearance of real wood lice.
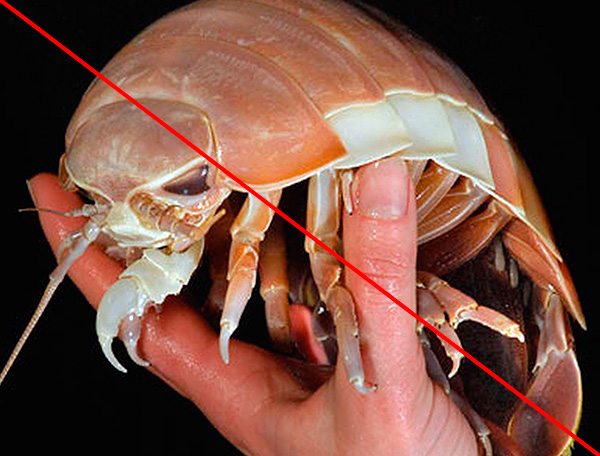
It is interesting
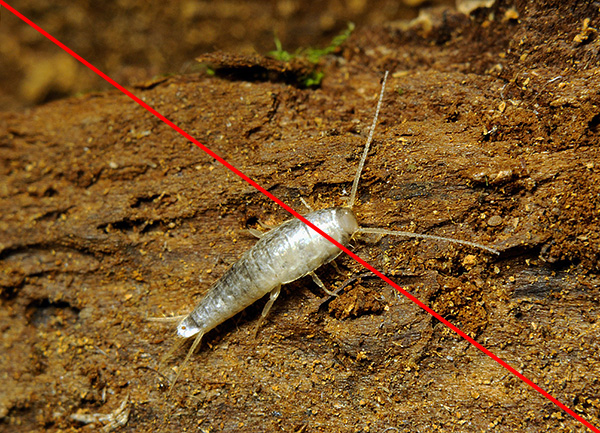
There is a whole set of species of insects and centipedes, which are often called moor-insects, but which do not belong to them, while others are not very similar to them. For example:
- Common silverfish, not at all like woodlice, but which, nevertheless, is so often called;
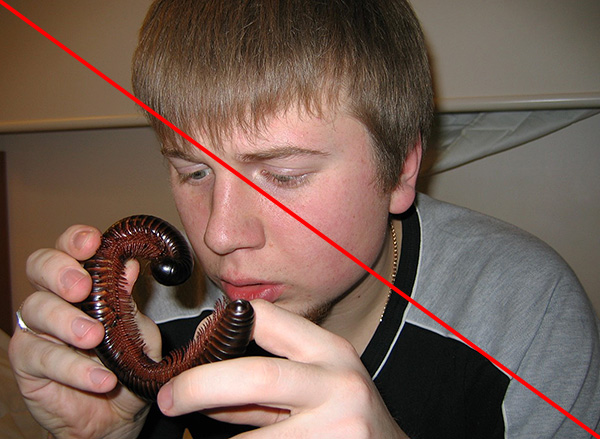
- Kivsyaki - long worm-shaped centipedes, coiled when frightened. They are confused with wood lice due to the fact that they are also found in wet places;
- Glomerises, like two drops of water similar to common woodlice, but they are not.
There are no poisonous species among wood lice, and it is impossible to get poison from wood lice, although this contradicts some medieval treatises. However, the woodlice tastes quite nasty - the brave lovers to feast on crayfish and shrimp claimed that this crustacean gives urea a lot.
It is interesting
At the same time, giant isopods (“giant woodlice”) taste very good, but due to the complexity of their prey, it is extremely difficult to taste such a dish.
Next on the pictures are woodlice, which can be found in almost any garden:
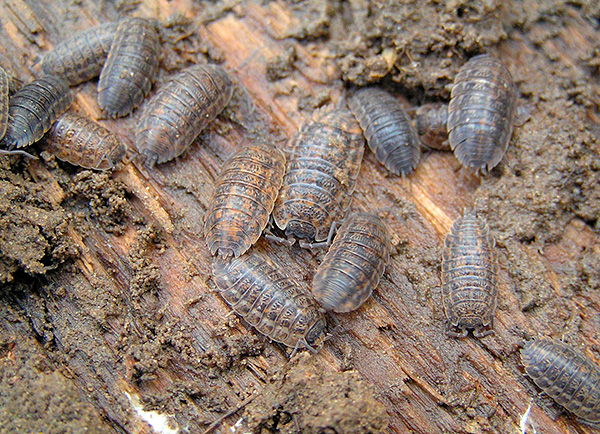


Occasions sometimes look quite original, although the features of anatomy that are characteristic of the whole detachment retain all species.
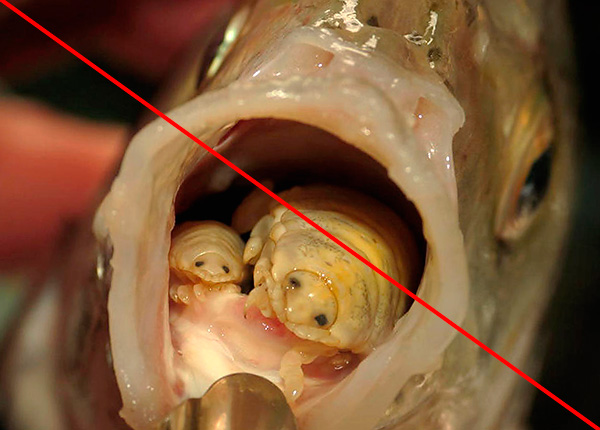
It is interesting
The so-called language wood louse is not a wood lice, a parasitic crustacean attached to the base of the tongue of some species of fish. It feeds on the blood of the host and the mucus secreted by the fish.
Lifestyle and interesting features of the biology of woodlice
Woodflies are the only crustaceans that have completely switched to the land-based lifestyle.
Only a few species returned to the aquatic environment, but at the same time they have kept adaptations to the terrestrial lifestyle. An example of this is the species of woodlice found in the sea (see photo):
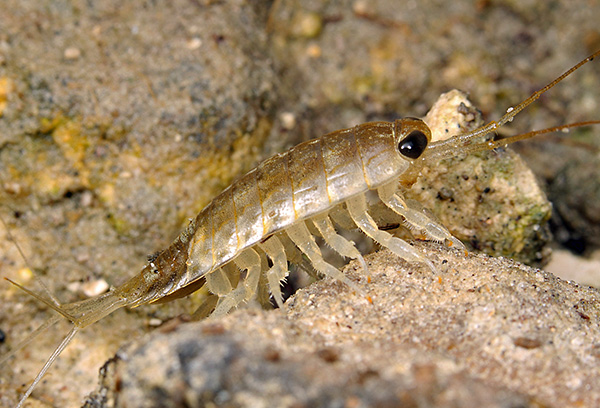

However, woodlice and on land are quite strongly tied to moisture. They prefer to settle in the shade, in moist soil, at the roots of trees, under stones and in cellars and basements - wherever there is moisture and coolness.
The optimal conditions for the existence of most types of woodlice - humidity is about 95% and the temperature is about 25 ° C.
It is interesting
The most heat-resistant woodlice of the genus Hemilepistus, even in the deserts of Central Asia and Africa, dig mink in the sand and live at a depth where the temperature does not rise above 26 ° C and does not fall below 10 ° C and the humidity stays at 95-100%.Of the minks, they are chosen mainly at night and wander through the desert at a comfortable 15-17 ° C.
Domestic wood lice are often the heralds of sewage or water supply problems, or a clear sign that the house has a damp basement or attic with a leaking roof. As a rule, these animals make their way into apartments and houses from basements and damp attics.
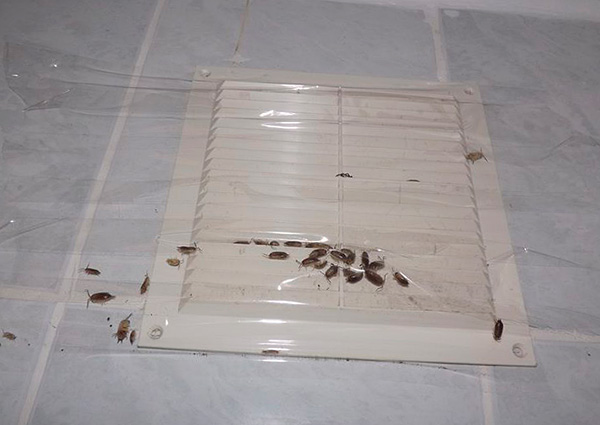

The moornits are night creatures, and in the daytime they can be found active only in the early morning or late in the evening. Mostly during the day, they hide under stones, logs and lingering grass, and at night they leave shelters in search of food.
Feeding on woodlice various plant residues: fruits, roots, rotting leaves, grass, falling flowers. In the apartments and houses they can be quite satisfied with mold fungi, leaves of home plants in flower pots and even just mucus with bacteria and dust in the bathrooms.
It is interesting
Woodflies are extremely dependent on the sources of moisture with which they moisten their gills. With a lack of moisture, the crustacean can die from asphyxiation, since this will disrupt the normal functioning of the respiratory system.
Many woodlice under harsh environmental conditions hibernate. Such, for example, are all woodlice that inhabit the territory of Russia, as well as desert species that are in a state of anabiosis in winter.
How do woodlice reproduce?
The weasels reproduce regardless of the season, but the eggs of the females develop only when the animal is not dormant and well fed. Interestingly, sexual intercourse in woodlice lasts a very long time - the seminal receptacle of the female opens only a few hours after molting, and the male finds it very well in advance and waits in the appropriate posture until the old integuments of his chosen one are thrown off.
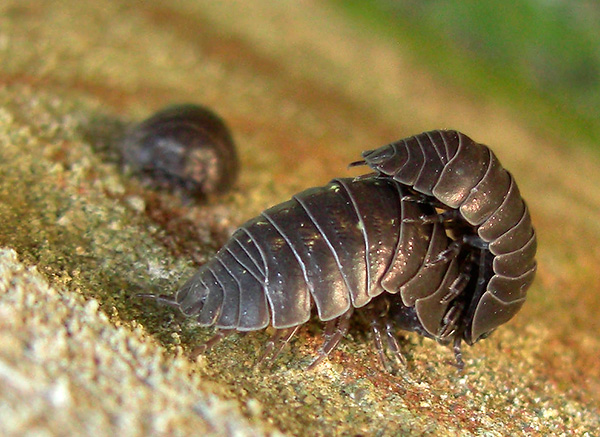

After fertilization, the eggs arrive in a special brood bag, located on the belly of the female in the area of the last pair of legs. Here they are abundantly supplied with water from special glands and are ventilated due to the fact that the front edge of the bag is not closed.
From the eggs come out of the woodlouse larvae, called in the biology "semolina". From the adult individual, the woodlouse larva differs only in size and underdevelopment of the last pair of legs. A few days later, the field of exit from the bag semolina sheds and turns into young woodlice.
The photo below shows the woodlouse larvae just released from the eggs:
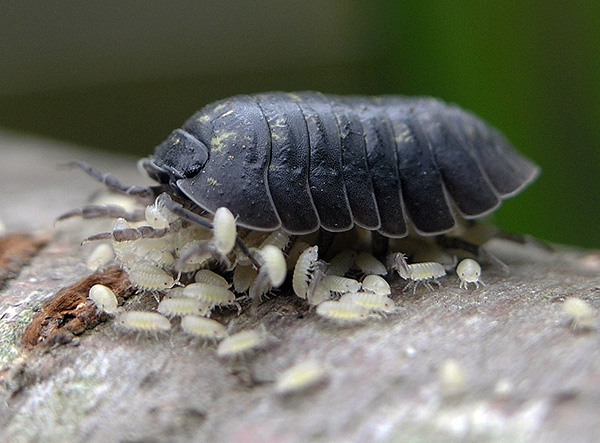

On average (for different species), the development of the egg in the brood bag lasts 30–35 days, and the larvae become mature after about 100 days after hatching.
It is interesting
All wood lice developed care adults for young. For example, the reproduction of desert wood lice occurs in their burrows, and when in danger an adult crustacean crawls to the exit and curls up into a ball, locking the entrance to the hole with its shields. In addition, parents lead their brood to food and water sources up to a certain age.
The total life expectancy of woodlice varies from six months to several years. Species that fall into anabiosis live longer than their tropical counterparts.
Licks in the apartment and in the garden - pests, invaders or occasional guests?
Wood lice are very important participants of soil formation processes in most biocenoses. They recycle hard-to-digest plant residues, and their excrement is valuable fertilizer. In the deserts and steppes, minks of wood lice promote ventilation of the soil and its better moisture.

Woodlice themselves in suitable conditions breed in large quantities and serve as food for many species of insects, birds and reptiles.
Typical pests of woodlice are only in greenhouses and in vegetable gardens, where they can damage the roots of cultivated plants, leaves on bushes and young seedlings. Wood lice in the cellars and basements sometimes feed on potatoes and carrots stored here, but in most cases the losses from them are microscopic, and they cause serious damage only during very large reproduction.
On a note
Woodlice do not infect the garden and are not brought into it - they live here permanently. Only under normal conditions, they are not noticeable here, and with a strong wetting area and interruptions in the digging can multiply in large quantities.
In the main mass of wood lice are those hardly noticeable, but very useful creatures that crawl under the forest or field litter of grass and leaves and are engaged in utilizing the plant components that are not used by other members of the natural community. And if you ever see them, remember that of all the crustaceans, only they had the courage to conquer the terrestrial environment. And this is a great achievement!
Interesting video: arthritis lice (macro)
Interesting biology of woodlice ...






