
Lackes in general are an integral and rather important part of many natural communities. With the advent of human settlements and cities, they were quite successfully able to integrate into the urban landscape and found here quite comfortable conditions for their life. Especially since wood lice feed on a very varied food and can feel provided with food almost everywhere.
Food addictions have played an important role in the rapid adaptation of wood lice to human settlements: it can be said that these creatures can always and everywhere find something edible for themselves. Suitable food for them is available on agricultural land, and in parks and squares of cities, and directly near town houses, in basements, in attics, or even in our bathrooms and toilets.
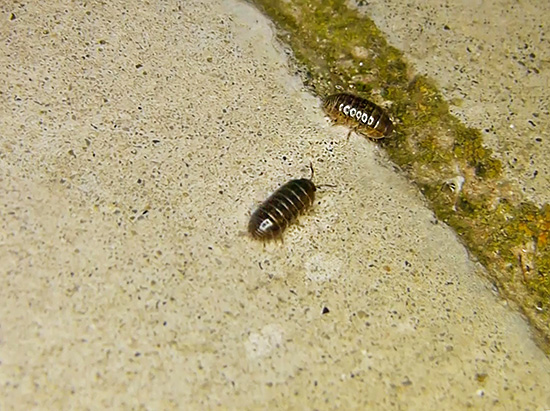

Not surprisingly, wood lice can be found almost everywhere. But at the same time, they are not particularly visible - their nocturnal lifestyle, stealthiness and love of dampness affect. Sometimes even where the wood lice are many, one may not be aware of their existence for a long time.
The owners of the same garages or cellars, as a rule, find “strange insects” by chance, surprised to find whole clusters of them under different objects standing on the floor or the ground. Woodlice here eat, breed, and lead their active, albeit unobtrusive lives.
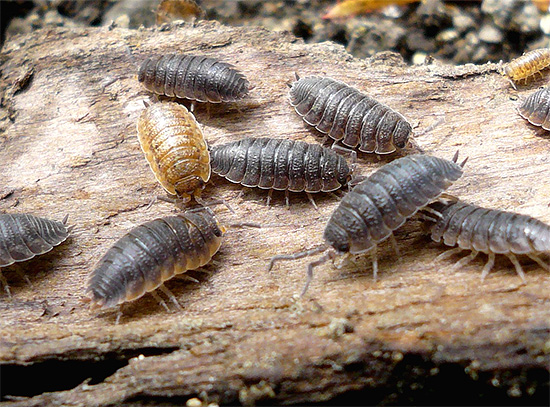

On a note
They are insects - they belong to the class of crustaceans.
Diet of wood lice: simplicity and minimum calories
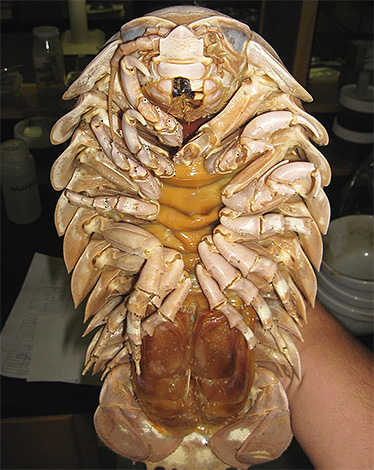
Overwhelmingly, wood lice feed on plant food. However, it is worth mentioning also large deep-sea decapods: they, strictly speaking, do not even belong to wood lice, but they are very similar to them and are often referred to as giant wood lice. These creatures also eat mostly algae, benthos, remnants of various dead animals, but they can also eat live sea cucumbers, sea anemones, as well as other marine creatures with a soft body, unable to move.
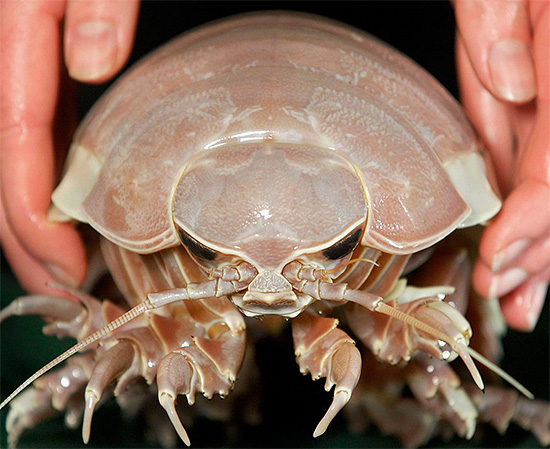
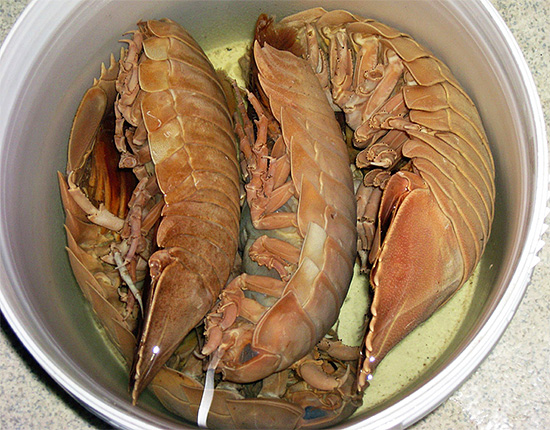


Most of the woodlice are typical processors of dying off and rotting plants. In the forests, in the fields, in plantings and even deserts, they feed on parts of withering plants, their roots, rotting fruits, seeds, and falling leaves. Considering the fact that there is a lot of such organic matter in nature, the wood lice usually have no problems with finding food.
Most often wood lice find food under stones, under old snags or under fallen leaves. Here, away from sunlight, plant materials are readily available and easier to rot, and the crustaceans themselves are safe and less accessible to predators.
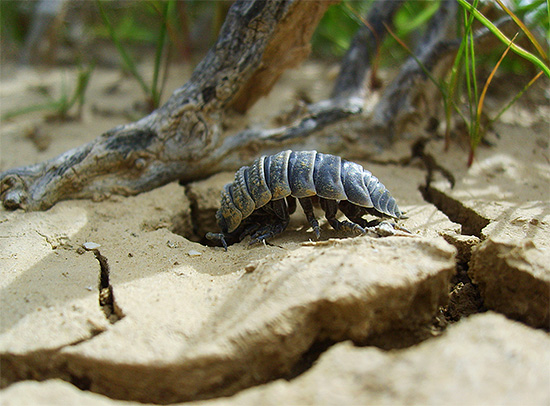

On a note
In the digestive tract of wood lice bacteria live capable of digesting cellulose fibers. They are not as versatile as symbiotic bacteria in termites, but still ensure the normal uptake of fairly coarse plant parts.
Generally speaking, according to the type of their food, wood lice are true minimalists. Their food is quite low-calorie and contains very little fat.
As a rule, wood lice feed practically without harm to living plants and are usually satisfied with the fact that it falls down and begins to rot (however, there are exceptions when these picky creatures still damage living parts of garden plants, causing them harm).
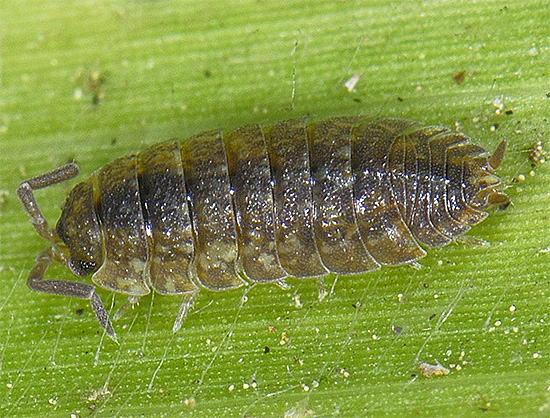

Due to this way of eating, woodlice turns out to be very useful for biocenoses by organisms that process and utilize large amounts of rotting plant debris.
And how abroad?
Interestingly, wood lice, inhabiting the tropical regions of the globe, in their food preferences are no different from domestic "watermelon". They also crawl under the forest floor, old stumps and stones, and at night they crawl on the wet ground, looking for fallen fruits and seeds.

In the tropics, thanks to the greater biodiversity, woodlice has a much wider food base: here decaying organic matter is found in abundance, and requires more “scavengers”. Accordingly, wood lice in tropical forests are more numerous, are represented by a large number of species, and are generally larger in size. Although, more than 5-6 centimeters, they still do not grow.

There are several types of wood lice, returning to the original element of the crustaceans - in fresh and salty water bodies. Keeping close to the coast, these species eat rotting remnants of plant and animal origin.
Enemies of wood lice: for whom “Arbuzi” is a delicacy
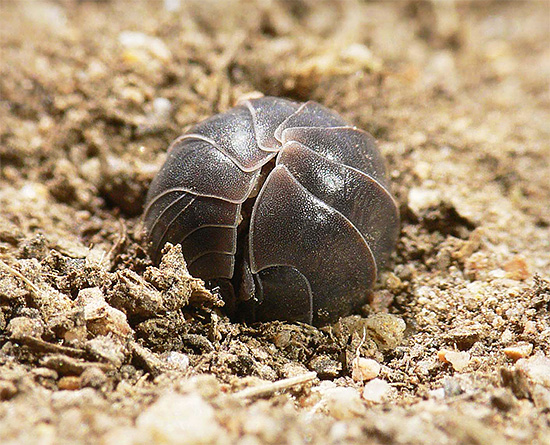
But lice themselves are good food for a large number of animals. Even in spite of the fact that their body, it would seem, is reliably protected by hard chitinous shell, and at danger they can curl up into a ball, protecting a softer belly, they are happy to be caught and eaten by the following living organisms:
- Large insects - predatory beetles, flies, wasps.
- Spiders - there is even a species of spider Dysdera crocata, which specializes in feeding on woodlice. It has elongated chelicera, and is able to bite even coagulated "watermelon" between the shields of the shell.
- Amphibians and reptiles. Perhaps only tritons and salamanders do not particularly often feed on land crustaceans. Frogs, toads, lizards and small snakes are happy to eat wood lice, especially young and soft ones, and for some species these creatures are even the basis of the diet.
- Birds - especially small owls, feeding just when wood lice actively crawling on the soil surface.
- Mammals - shrews, hedgehogs, rats.

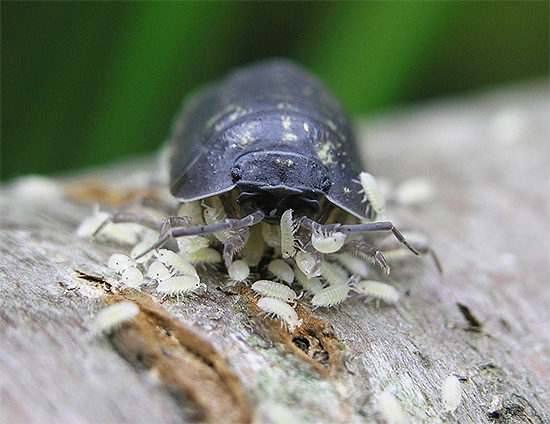
Many terrariumists (amateurs and professionals who have lizards, snakes, and spiders at home) keep wood lice in special cages, breeding them as a source of food for their pets.Compared with crickets, cockroaches and mealworms, crustaceans with shell, of course, are less attractive food, but as an additional variety of ration, it is quite suitable.
There are even methods of breeding woodlice with their natural enemies in one terrarium. These crustaceans are very convenient in content, because they do not impose special requirements to the microclimate, and feed on any food waste of plant origin.

What eat woodlice in houses and apartments
It should be understood that in the dwelling of a person and near him wood lice do not change their “food addictions”. Here they also find decaying plant debris, sometimes even those that the owners of the dwelling do not even suspect.
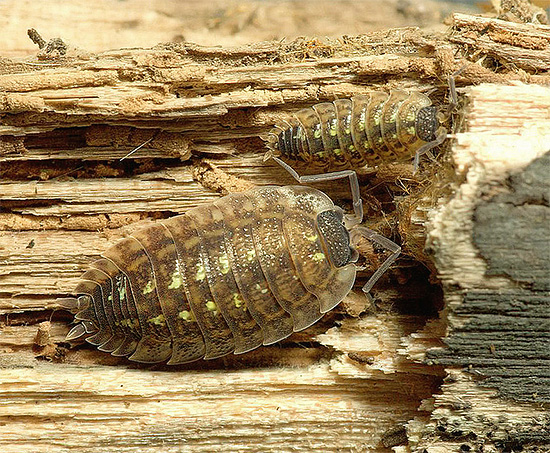

There are no problems with food for wood lice settling in basements with leaking pipes. Here the seeds flying through the cracks are constantly germinating, mold and lichens are growing. And although it is not very plentiful and nutritious food, but it is quite enough for woodlice. Moreover, sometimes it allows them to multiply in huge quantities, after which they begin to occupy the lower apartments.
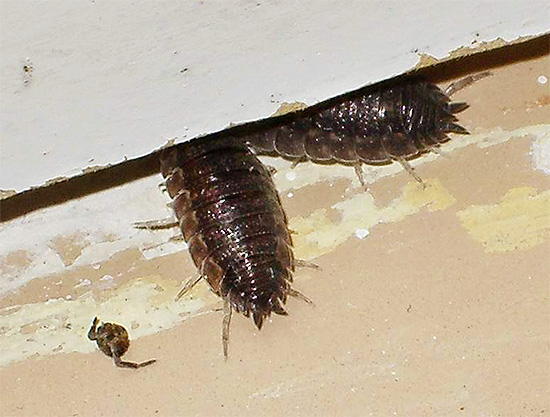

On a note
There are cases when residents of lower apartments due to the constant penetration of woodlice from the basement had to wage a long struggle with these arthropods - no less tense than, for example, with cockroaches.
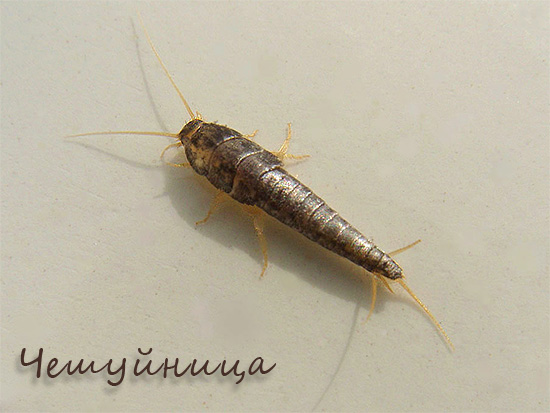
Do not confuse woodlice with scales. The latter, on the contrary, love dryness, and feed on sugar and grocery residues in the dust. Proper identification of arthropods in the apartment will help make the fight with them more effective.

Woodlice live luxuriously in rural cellars: here they are constantly fed on with dried potatoes, onion and carrots. Sometimes they are content with the same food on the balconies of apartments.
Wood lice can live well in toilets and bathrooms only if there is always a high level of humidity in these rooms (poor ventilation, leaking pipes, corners of the mold). Therefore, remember: if the house has woodlice, the sanitary situation in it requires urgent intervention.
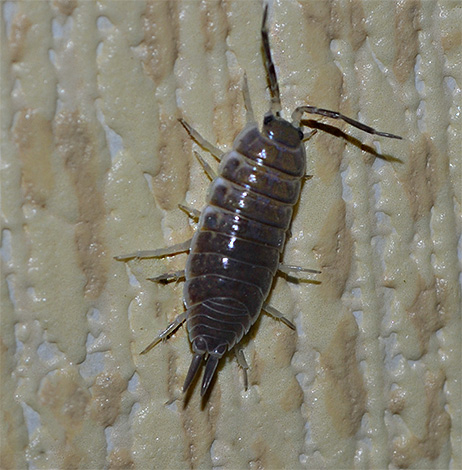

It also happens that woodlice multiply en masse in the attics of houses with a leaking roof, and then through the cracks and ventilation ducts penetrate toilets, bathrooms, and the kitchen.Even if your apartment is relatively dry, but the attic is already overpopulated with crustaceans, then in this case wait for the “guests”.
Useful video on how to deal with woodlice in the apartment: a few effective recipes
An example of how tenants suffer from the invasion of wood lice
And here is what a giant woodlouse looks like (video)




Great article, very touching warm "watermelon". I agree with the author and consider woodlice very charming.