Strong allergy to insect bites is a problem that affects so many people. It is much more difficult to fight it, because the body’s high sensitivity to bites usually lasts for a lifetime, and in many cases allergies can increase from one bite to the next.
Often a person has a hereditary predisposition to allergies. The adverse environmental situation, the ever-increasing isolation of a person (especially a child) from nature, as well as some diseases, reinforce this heightened sensitivity to various substances, thereby increasing the likelihood of a pronounced allergic reaction to the bite of almost any insect.
On a note
Poisons, saliva and other insect secretions are considered strong allergens.Sometimes even chitinous hairs in the air, pieces of external integument and insect excrement can cause a dangerous allergic reaction.
However, most cases of the most severe allergies are observed after the bites of hymenoptera. In 7% of cases, these are bees, less frequently - wasps, hornets, bumblebees and tropical ants. Much less often the body reacts heavily to the bites of mosquitoes, midges, fleas, bedbugs and other non-stinging insects.
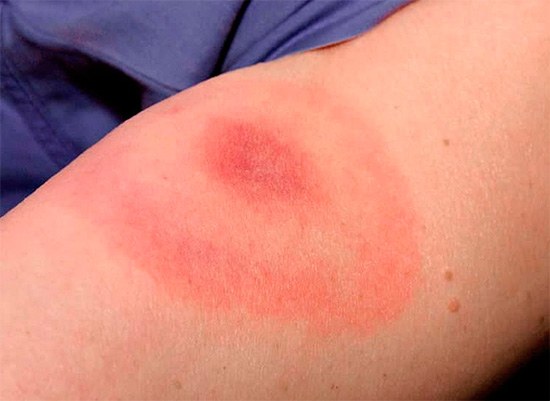
The photo shows an example of a severe allergic reaction to a hornet bite:
The aggressive effect of the venom of hymenoptera insects is due to the peculiarities of its constituent components. For example, bee venom contains the following substances:
- Melitin - this compound actively destroys red blood cells, causes acute inflammation, muscle spasm and impaired tissue metabolism, reduces blood coagulation.
- Apamin - this protein has a significant similarity with the neurotoxins of snake and scorpion poisons, strongly stimulates the structure of the nervous system.
- Hyaluronidase - helps the poison to spread throughout the body.
- Phospholipase A - enhances the inflammatory process and stimulates the hemolysis of red blood cells.
- Histamine - dilates blood vessels, provokes the occurrence of inflammation.
In addition, a special protein that is included in bee venom causes mast cells in the affected tissues to release their own histamine, which is the main activator of allergic processes.
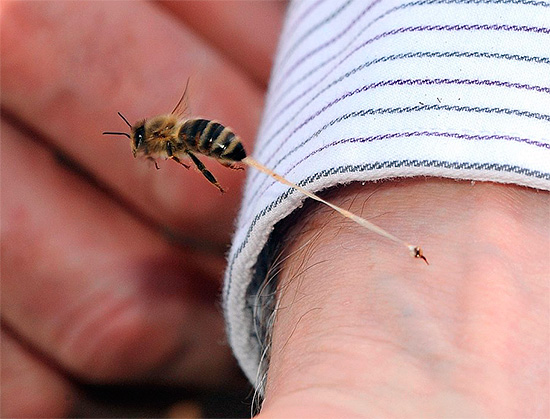


The poison of the wasp is characterized by the presence of the substance kinin, which causes dilation of blood vessels, contraction of smooth muscles and provokes acute inflammation. And the venom of various types of hornets also contains acetylcholine, which slows the heart rate, lowers blood pressure, reduces the muscles of the bronchi and increases the secretion of bronchial glands.
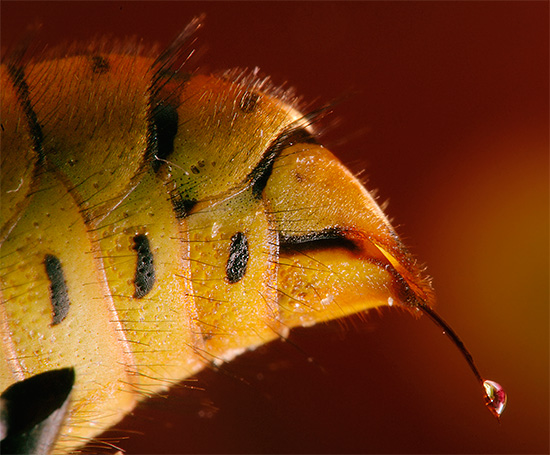

On a note
Around the world, three times more people die from allergic reactions to insect bites than from snake bites, and a person can die from a single bite.
Reaction to bites blood-sucking insects - bedbugs, fleas, mosquitoes, etc. - due to the presence in their saliva of special enzymes that cause allergies (for example, substances that prevent the rapid clotting of blood). In addition, a flea, for example, often literally bites into the skin almost with its head, introducing additional irritating substances into the wound.
The photo below shows a flea at the time of the bite:

In the saliva of adults, bedbugs contain an analgesic, with the result that their bites are practically painless and are usually found only in the morning. Also in the saliva of bloodsucking insects sometimes there are pathogens of very dangerous diseases: malaria, plague, tularemia, hepatitis B, anthrax and others.
Symptoms and forms of an allergic reaction to insect bites
The strength of an organism's allergic reaction depends on the amount and degree of aggressiveness of the allergen injected, as well as on the number of antibodies corresponding to it circulating in human blood. From a bite to a bite by insects of the same type, the antibody titer (i.e., their concentration) can increase. Accordingly, the response force of the organism will increase.

After being bitten by an insect, an allergic reaction sometimes occurs instantly, and sometimes it manifests itself only for several tens of minutes, occasionally - hours. If there is no sensitization to the allergen, then in the area of damage the skin reddens, swells, itching occurs. These symptoms, as a rule, do not last long and disappear without a trace.But in the presence of sensitization, the body reacts much more strongly, and such a reaction is no longer limited to local manifestations.
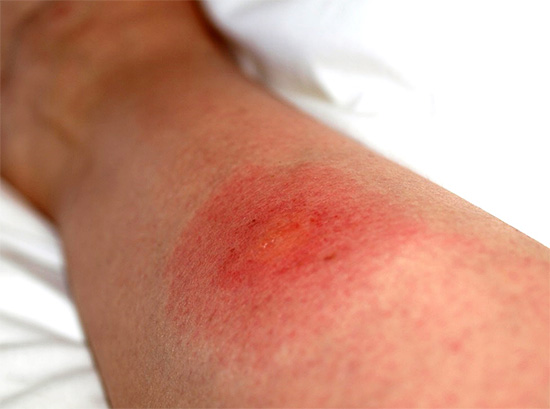
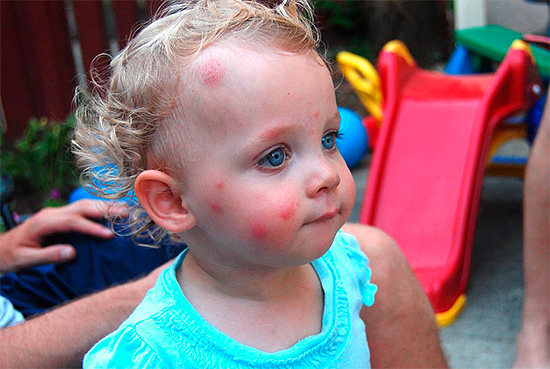
Photograph of an allergic reaction to a bee sting:
Thus, the symptoms of an allergy to insect bites can vary greatly in nature and severity. For example, symptoms may be:
- Local - burning pain, swelling of the skin, swelling or induration, hyperemia, itching, rash;
- Generalized - urticaria, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, weakness, fever with or without chills, dizziness, difficulty breathing, lowering blood pressure, rapid pulse of weak filling, heart pain, fainting.
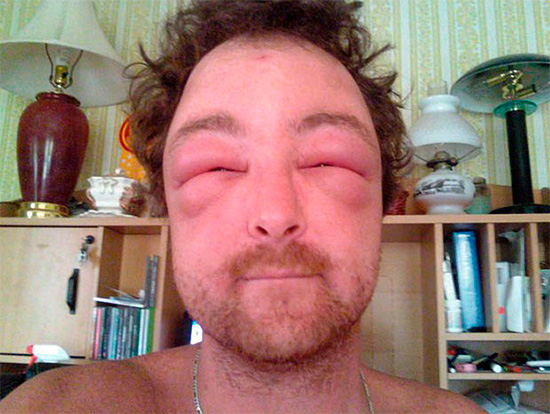
Life threatening conditions such as angioedema and anaphylactic shock can also occur.
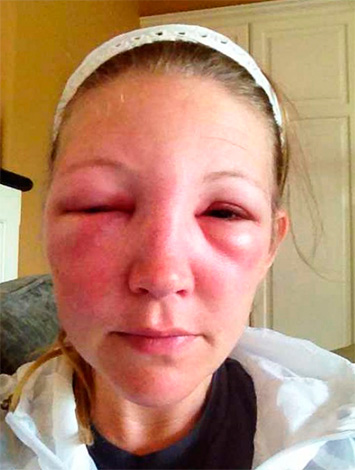
The photo shows an example of angioedema:
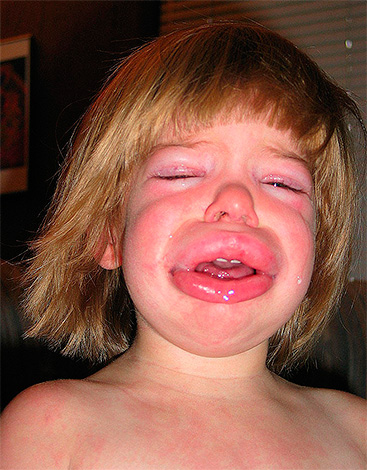
The rash from insect bites can also vary significantly in intensity, appearance and location. It can be blisters, nodules, erythematous spots, erosion, and other variations. In difficult cases, a hemorrhagic, bullous, necrotic rash occurs.
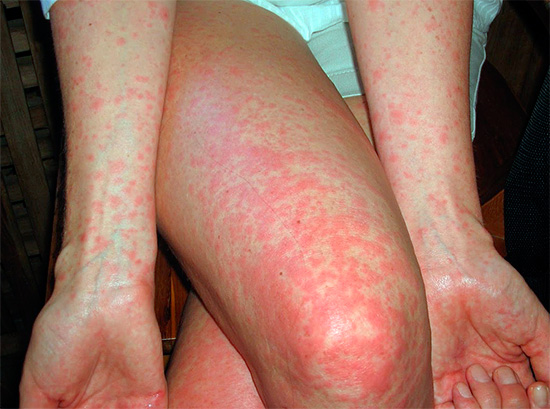
When scratching through the damaged skin can penetrate the infection.At the same time, skin elements are transformed into pustules (pustules), and sometimes into ulcers that do not heal for a long time.
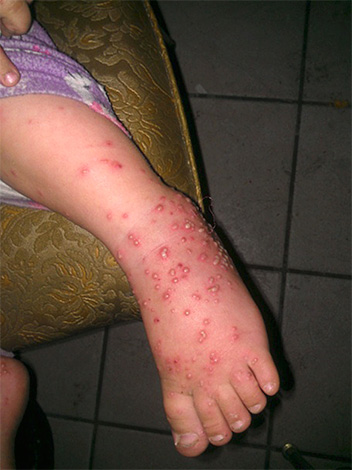
Allergies from insect bites can be masked by other allergic reactions, since skin rashes can be similar. Therefore, in each case, you need to try to find out exactly what caused the rash.
Allergy in a child: how dangerous is it?
Often, children react to the effects of the allergen more strongly and longer than adults (although in some cases the situation is the opposite). Spots from insect bites they may persist for several days.
Often, insect bites itch badly: because of the constant itch, the child sometimes combs the skin to blood with the risk of infection, which can be an additional health hazard.
Feedback
“We had a very bad situation last summer. We went to the Crimea for a week, to Olenevka, and Sasha was bitten by some kind of wasp. He says big and thin. I thought that he was fooling around, because in general he was a calm boy and even if he was hurt, he would not yell. Immediately he turned blue from the cry, we could not hold him, there was the impression that he had some kind of convulsions. Creepy sight. The hand swelled at once, and so that he could not bend it.A rash appeared, and a face spread to the back. And the child is still waving and screaming. Well, the clinic has been opened. We drove him for a while - maybe twenty minutes had passed, his fainting had already begun, the temperature had risen. The doctors injected something, put the drip, said that the child had anaphylactic shock and if we were late, we could have missed it. I later learned what kind of wasps they are. They say that road names are called brown and large, and the bite is the most painful. As a result, we were forced to stay in the Crimea for another week, because only five days later Sasha was released from the medical center. ”
Ilona, Voronezh
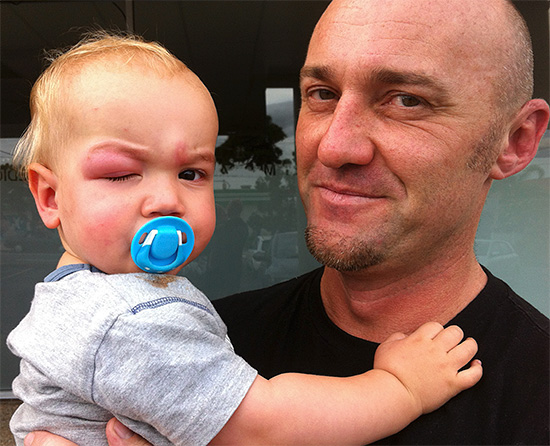
The photo below shows an example of severe irritation from insect bites in a child:
With a high sensitization to the poison of Hymenoptera, after a bite, a child can quickly develop a complicated reaction in the form of angioedema and anaphylactic shock. This moment the parents of the baby should always be aware of: if there is a hives or other pronounced skin manifestations after an insect bite, as well as the appearance of common allergy symptoms, an urgent need to consult a doctor.In this case, it is better not to engage in self-treatment, because many drugs have limitations for use in children.
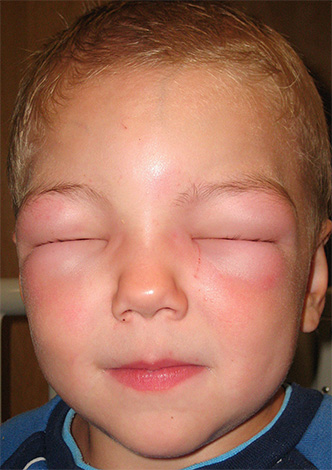
What is the danger of acute allergies?
Urticaria after insect bites is not the hardest manifestation of allergy. The symptoms of general intoxication, a sharp drop in blood pressure, asphyxiation and collapse are much more dangerous - all this can be a threat to a person’s life.
The most dangerous complications of allergy are anaphylactic shock and angioedema.
Quincke edema, or, otherwise, giant urticaria, is a sharply arisen extensive edema of tissues with well-developed subcutaneous fatty tissue. Such edema is caused by a powerful release into the blood of biologically active substances that cause dilation of blood vessels and increase their permeability.
Severe swelling of the larynx and tongue is very dangerous - in this case, there is a high risk of developing asphyxia, and a person may die from suffocation. Also high risk is cerebral edema, as a result of which neurological symptoms can occur: convulsions and paralysis.When these severe reactions to insect bites for the treatment of patient allergies should be urgently hospitalized.
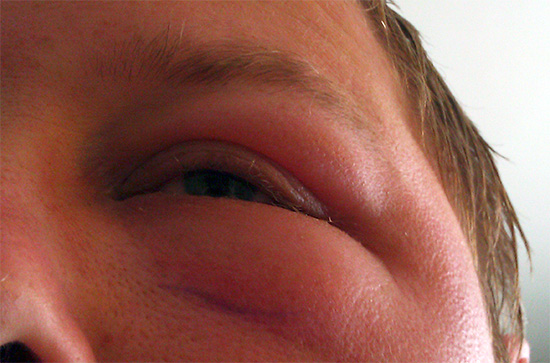
The photo below shows angioedema:
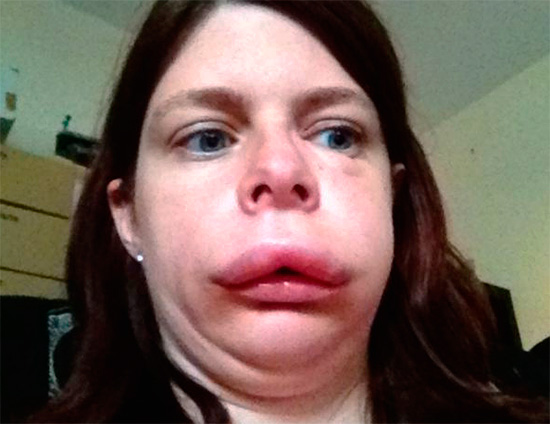
Anaphylactic shock, sometimes also developing after insect bites, occurs due to impaired peripheral and central blood circulation under the influence of biologically active substances that are released into the blood in large quantities (in particular serotonin).
The victim becomes restless. He has shortness of breath, urination is disturbed, confusion occurs. The skin becomes cold, bluish and moist. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea can join.
In the case of a developing anaphylactic shock, skin irritation that has arisen after an insect bite is usually pronounced, accompanied by severe pain and increasing swelling. Local itching quickly spreads over a wide area of the body. Often, laryngeal edema, broncho-and laryngospasm join, blood pressure drops. Without adequate treatment, a person may die within minutes or hours of asphyxiation and an associated vascular collapse.
Antiallergic drugs for insect bites
Antiallergic drugs used after insect bites can be divided into the following groups:
- Antihistamine or, alternatively, H1-receptor blockers: I-th generation - Dimedrol, Diprazin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Diazolin, II-nd generation - Astemizol, Terfenadine, III-th generation - Loratadine (Claritin), Azelastine.
- Mast cell stabilizers: Nedocromil, Ketotifen, Intal.
- Glucocorticoids: Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Betamethasone.
- Symptomatic drugs: adrenaline, salbutamol, fenoterol.
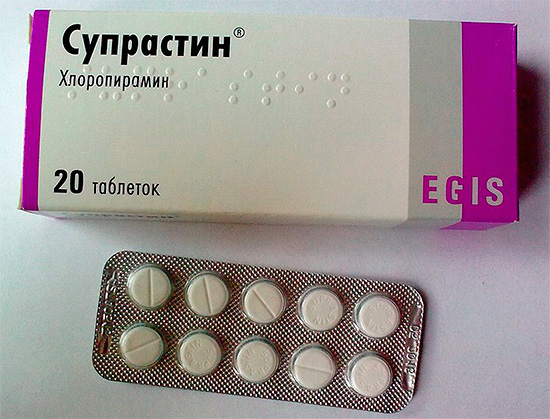

Of the antihistamine drugs for insect bites today are more often prescribed drugs of the new generation (II and III). They do not possess cardiotoxic and hepatotoxic action, do not inhibit the central nervous system, the duration of their action is longer.
Widely used for allergies, including insect bites, received Claritin. However, it is worth noting that in some cases the prescription is also justified by the preparations of the I-th generation, which act not for long, but their action comes faster.
Important:
When taking any medication, including Diazolin, Suprastin,Dimedrol, etc., it is necessary to remember that medicinal substances themselves are capable in rare cases of causing allergic reactions, up to angioedema.
In folk medicine, calendula tincture, onion juice, plantain juice and lemon juice, as well as baking soda solution are used to relieve irritation that occurs after insect bites. From mosquito bites, infusion of laconosa, lice grass is used.
Insect scares the essential oils of clove, anise, eucalyptus and basil.
Hydrocortisone and other glucocorticosteroids used topically, for example, in the form of an ointment, will contribute to the relief of local inflammation in insect bites.
First aid for the development of insect sting allergy
For bites of stinging insects (wasps, hornets, bees), you should immediately give a person first aid without waiting for signs of allergies.
Sometimes it seems to the victim that nothing terrible has happened - you will think, the wasp (or the bee) has bitten. And more often than not, nothing really terrible happens. However, sometimes an allergic reaction develops so rapidly that the score can go on for minutes.

When a bee is bitten, it is necessary to remove the sting with a pair of tweezers as quickly as possible, as the associated bag of poison continues to shrink and inject the poison under the skin.In case of bites of wasps and hornets, the sting should not be sought - these insects in the wound do not leave it and can sting repeatedly.
Not later than 1 minute from the moment of the bite, it can be effective to remove the poison from the wound (this should be done for a short time, also not more than 1 minute, always spitting out).
Then you need to slow down the rate of absorption of poison into the blood, as well as help reduce the local allergic swelling from an insect bite. To do this, you need to put a cold on the bite, for example, an ice pack.
If a person is prone to severe allergy to insect bites, he knows about it, but it so happens that he doesn’t have an autoinjector with adrenaline with him (usually people with allergies always carry it with him), then it will be helpful to take additional measures. When you bite in the leg or in the arm, a tourniquet is applied to the limb - this will allow you to gain time, and the poison will not be able to spread through the body with blood flow. Urgently call an ambulance.
Itch and rash after an insect bite help to reduce special drugs: it can be sprays and ointments containing panthenol, Fenistil gel, hormonal ointments such as Advantan and Hydrocortisone, special balms from insect bites for children from the Gardex and Mosquitall series.

When providing first aid should not:
- Drink alcohol - in order to avoid the expansion of blood vessels and accelerate the absorption of poison in the blood.
- To cool the bite-stricken area with raw earth or clay - this way you can add infection, including infection with life-threatening tetanus.
- Trying to squeeze poison out of the wound — such a massage will only provoke an accelerated spread of poison into neighboring tissues.
- Use Diprazin and other H1-histamine blockers of the first generation in severe allergic reactions. They are ineffective in relation to histamine, but they can drastically reduce blood pressure, which will aggravate the situation even more.
What to do with serious consequences?
Treatment of complicated allergic reactions should be carried out by a doctor.
At the prehospital stage, for the treatment of acute stenosis of the larynx, normalization of arterial pressure, inhalations of glucocorticosteroids are used through a nebulizer (0.25 mg of Budezonide at the compensated stage of stenosis, 0.5 mg for subcompensated, 1 mg for laryngeal stenosis of the III degree). The maximum number of inhalations - 3 with an interval of 20 minutes.
Suprastin with complications after insect bites is used with the ineffectiveness of inhalation therapy.or in the absence of a nebulizer, intramuscularly or orally (with compensated stenosis). Systemic glucocorticoids (prednisolone) are injected intravenously, adrenaline subcutaneously.
To remove the attack of choking, you can use Berodual, Salbutamol - through an inhaler or nebulizer.
It must be remembered that when the first signs of a severe form of allergy after an insect bite appear, the victim must be taken to hospital as soon as possible (you should also consult by phone how to help the person). If there is no experience in providing first aid to others, the victim should be placed on his back, with a roller of clothing under his head, provided with a drink and not given medicines that do not have full confidence. In many cases of acute allergy, it is unprofessional actions of volunteers that contribute to the aggravation of the situation, and therefore the best thing to do is to get a person to a doctor as soon as possible.
Useful video about insect sting allergy: expert comments
How to escape from insect bites in the summer and what to do if they are still bitten




I am terribly afraid of bee stings, fortunately, never once encountered. Yes, and few of them here. Most often disturb mosquitoes and gadflies. I have a strong allergy to the bites of gadflies, I don’t get suffocation attacks, of course, but a swelling appears on the skin and the bite site itches terribly. I try to immediately smear the skin with a lokoid, it quickly relieves itching. And the inflammation passes in two days.
Hello. A month ago, I was bitten by some midge in the garden. A week, probably, or two - the pimple kept from being bitten. Now on this place the swelling is dense, with a diameter of 2.5 cm. When pressed, it is a little painful. Keeps more than a month. Tell me what to do?
I, as an allergic with experience, for myself clearly picked up the drugs with which to escape. And by the way, how to prevent this or that allergy. For example, now I do not eat chicken and fish, it is rather heavy, of course, but I got rid of a number of problems. So if it turns out to exclude an allergen - exclude. With regard to edema and bites, I personally always use loratadine. His Akrikhin produces ours. Saves great. And due to the fact that the manufacturer is ours, these tablets are quite inexpensive.
My friend's child in the bridge of her nose was bitten by midges in the village, and everything passed on to the eye. Now the eye is festering and swollen, it is very far from the hospital and there is no opportunity to go, what is the treatment for it?
Papaverine or No-Shpu with prednisone injections. Suprastin injections.
My child was bitten by a mosquito or midge, I do not know, behind the knee. At first there was a lump, now a pustule has appeared, and so several pieces.What could it be?
I had this in childhood. Combing insect bite under the knee. As a result, it festered, had to go to the hospital, and did the operation.
With the bites of midges, and mosquitoes especially, children need to be led to an allergist. I came with my son late, after three days. And the result is deplorable - she spent a month and a half on purulent surgery. If I turned in time - three days, and home. Diagnosis: Staphylococcus aureus, lymphadenitis.