
The wasp is far from the only insect capable of very painful bites. Ants, bees, bugs, flies, and even some dragonflies bite no less sensitive, and sometimes much more painful than ordinary wasps.
However, among the bites of all insects, the wasp’s bite is rightly considered one of the most dangerous - in some countries of the world, more people die from os bites than from the attacks of any other wild animals and insects in the region.
It is interesting
The most painful bites among all insects belong to the South American ants, bullets. On a special scale sting force bite of this ant has an index of 4+. In the second place of the pedestal there are bites of road wasps hunting for poisonous spiders - they have an index of 4. And in the third place with an index of 3– there are just paper wasps habitual for all of us.Their painful bites are approximately equal to the bites of the largest predatory bugs.
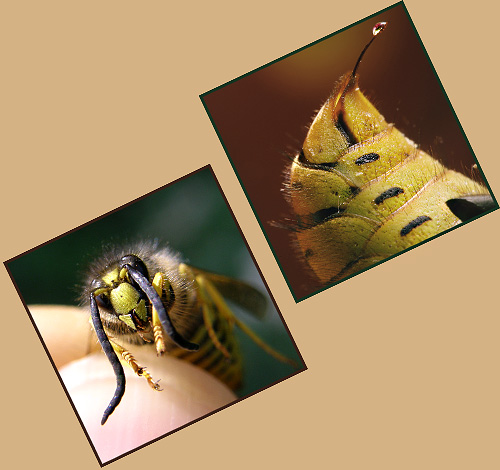
The photo below shows a road wasp whose bites are very, very painful:


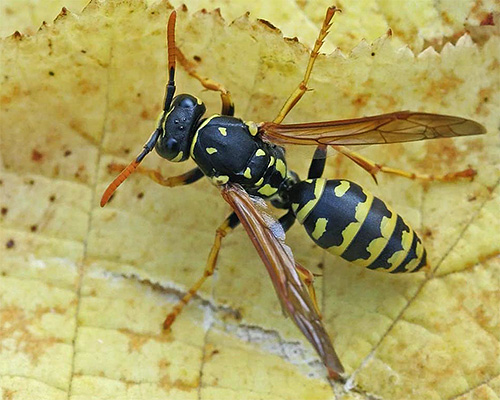
And in this photo you can see the usual paper wasp:

Despite the incredible pain, wasps bites are not at all dangerous for this reason. Although the main purpose of the insect itself in defense is precisely in inflicting pain on a potential enemy to scare him away, the threat to human health is primarily determined by the possibility of an allergic reaction to the toxins in the poison.
Wasp venom is the strongest allergen that causes extensive local edema in most people. However, if a wasp sting happens in a person who is particularly sensitive to toxins of insects, then the probability of developing much more serious allergic reactions will be quite high.
Such an immune response of the body of the victim in some cases can even lead to death; and due to the fact that in some countries there is a large number of wasp attacks, it is precisely such cases that form the sad statistics.
On photo - bite wasps with the body's normal reaction to it:
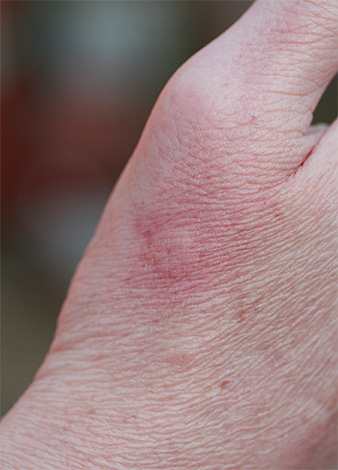
And this photo shows signs of severe allergy with severe edema:
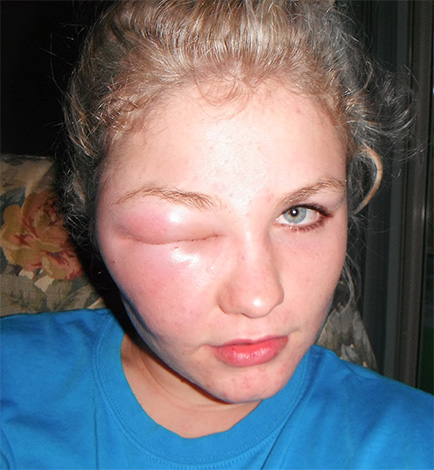
It is interesting
The most dangerous member of the family The real wasps are the giant Asian hornet living in Japan, Vietnam, Thailand, Burma and China. The poison of this insect is very strong and allergenic, the amount of it that enters the victim’s body after the bite is large enough, and the hornet itself often stings several times in one attack. All this leads to the fact that in Japan alone, about 40 people die from the bites of these large wasps each year.
The Japanese huge hornet (endemic subspecies of the Asiatic) is presented in the photo below:

In addition to its toxicity, the bite of a wasp also has a number of interesting features. So, for example, wasps always easily take out their sting from their victim's skin, therefore, it is useless to look for their “weapon” at the site of the bite. This, by the way, distinguishes a wasp sting from a bee sting.
Action of wasp venom
One of the main defining features of wasp venom is the large number of active components in it. Each of them is responsible for one or another reaction in the affected place, but at the same time it complements and in many ways enhances the action of the other.That is why the overall effect of the wasp sting is much stronger than the simple total effect of the different constituents of the venom.
So, when a wasp sting acetylcholine in the composition of its toxin causes severe irritation of nerve endings in tissues damaged by poison. For humans, this means a sharp pain that arises almost immediately, even before the wasp manages to remove its sting.
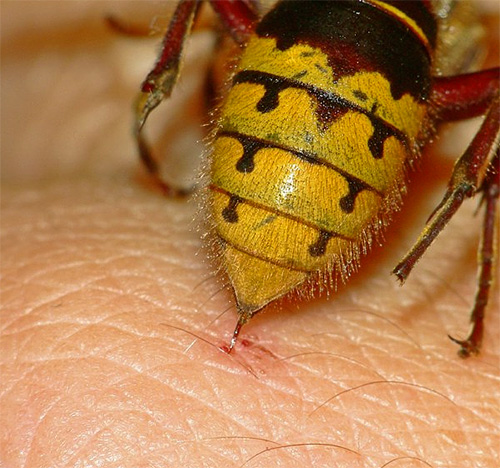

The histamine contained in the poison enhances the action of acetylcholine and stimulates the development of an allergic reaction. That he is one of the perpetrators of the appearance of edema and inflammation at the site of the bite.
The “destroyers” of damaged tissue cells are phospholipases. They start the process of outpouring the contents of cells into the extracellular space and thereby causing inflammation - a protective reaction of the body, aimed at utilizing both the toxins themselves and the contents of cells that are no longer needed.
Phospholipases, on the other hand, destroy mast cells in the affected tissues, which are a kind of reservoirs of their own histamine. As a result, this substance enters the blood in large quantities and is a secondary cause of allergy - moreover, than from the histamine of the wasp venom itself.
Upon contact of the cytotoxins contained in the venom with small blood vessels, their walls are destroyed, and, as a result, hemorrhage occurs. If the wasp stings in the arm or leg, it manifests itself in the form of small subcutaneous hematomas (bruises), but with multiple bites, internal hemorrhages become very life-threatening.
On a note
One of the toxins in the venom of the wasp - mastoparan - is specific to these insects. Its main action is directly in the destruction of mast cells and the release of histamine. However, there is an unusual relationship - in large quantities it prevents the development of inflammation - naturally in such cases. As for the wasp venom, in its composition the mastoparan is in quantities sufficient to trigger an allergic reaction, but too small to prevent the development of inflammation.
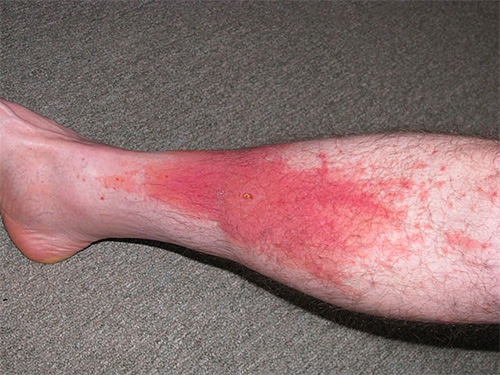
The photo shows a typical inflammation at the site of a wasp sting:
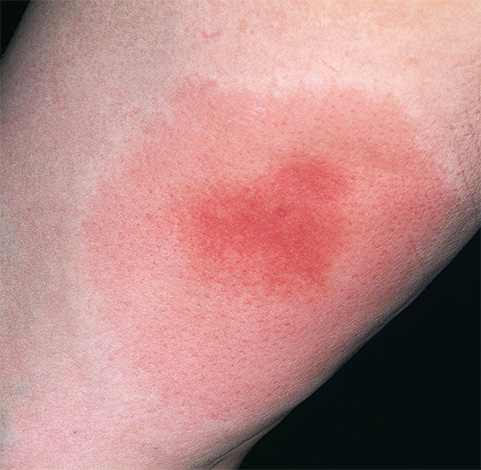
In addition to the above, there are additional consequences of a wasp sting, namely:
- high blood sugar levels, which is very dangerous for people with diabetes;
- increase in cardiac output;
- lowering blood pressure;
- increased breathing.
As a rule, these symptoms are less pronounced in comparison with tissue damage and a local or general allergic reaction, therefore they are often simply not noticed by the injured.
It is interesting
Modern scientists are trying to use the cytotoxins contained in the venom to create a cure for cancer: it has been observed that these substances are able to quickly destroy cancer cells. Today, the scientific task is to force cytotoxins to selectively affect the tumor, but not to touch healthy cells and tissues.
Effects of wasp bites
All the processes described above occur at the micro level, and in most cases the victims are absolutely not worried - they pay attention only to those bite manifestations that are clearly visible with the naked eye.
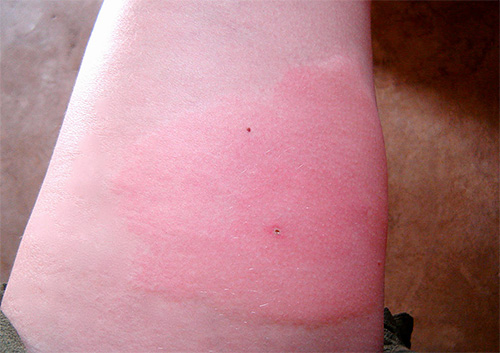
So, the first thing that a person feels (and cannot fail to notice) when a wasp is bitten is severe pain. It occurs at the moment when the sting of the insect is not yet removed from the body of the victim, and goes on increasing, becoming more acute with time.
Further, the bitten person feels more and more new symptoms, such as:
- redness at the site of the bite, which occurs already in the first minutes after the wasp was injected with its poison;
- swelling and edema developing after 1-3 minutes after stinging and gradually increasing in size (it is thanks to them that the bite of a wasp looks like a big red lump);
- itching that always accompanies pain syndrome and is usually present for a little longer than the pain itself (often the wasp sting itches badly).
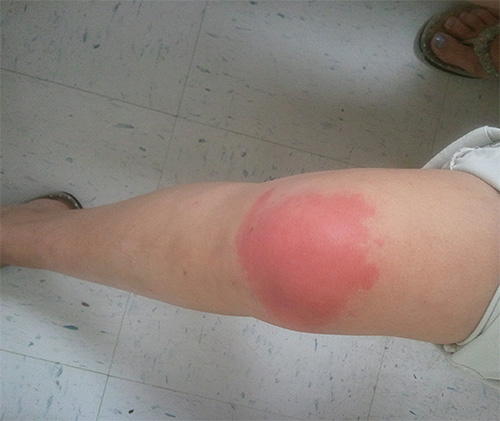
With a normal body reaction to a bite, these effects are usually limited to stinging a wasp. Clearly visible reddening quickly subsides, and edema of the usual flesh color remains at the site of the bite.
In the photo - a wasp sting just a few minutes after stinging:
Feedback
“I don’t understand why these wasps are so afraid. Yes, they bite painfully, but not fatally, in a day this bite passes altogether. I was recently stung by one at work — so what? I washed the water with cold water, put the bottle out of the fridge and by the end of the shift I forgot where I had bitten. So, the bump was small, and that's all. Of course, if you start to extrude something there, smear it, prick it, it will swell up from the drugs themselves. My mother-in-law was like that. She drank three pills, and kept some lotions, and spread the whole thing into half a shelf. And then almost a week passed. ”
Yaroslav, Yaroslavl
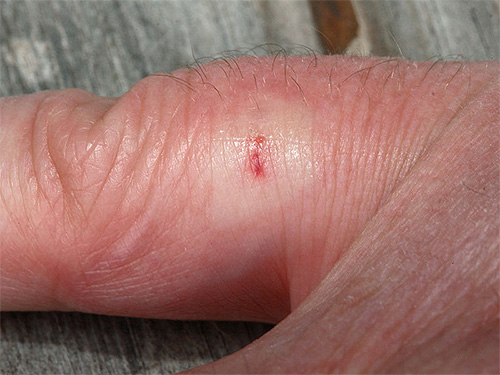
The photo below shows how a wasp bite might look a day after stinging:
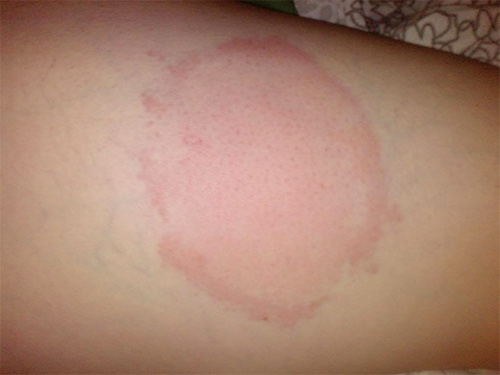
A small amount of lesions on the skin in the area of the bite is also considered a normal reaction, and if the bite falls on the joint area, a slight shiver in it is allowed.
The development of more severe allergy symptoms is much less common. These include:
- far reaching bite edema;
- copious - all over the body - urticaria;
- nausea, fever;
- headaches and abdominal pain, dizziness;
- angioedema;
- anaphylactic shock.
It is very important to understand that different people do not have a single norm on the manifestation of allergy symptoms: some of them develop only a few hours after the bite, while others develop almost instantly, within a few seconds. It is in the latter cases that the bite of the wasp represents the maximum danger, since the victim can simply not have time to provide the necessary assistance.

Wasp bites in parts of the body can be dangerous. For example, a bite in the tongue, throat, neck, or nose can cause the victim to suffocate,stinging in the genitals - to cause the impossibility of committing urination, and the bite in the eye sometimes ends with cataract, glaucoma, atrophy of the iris and other very serious consequences.
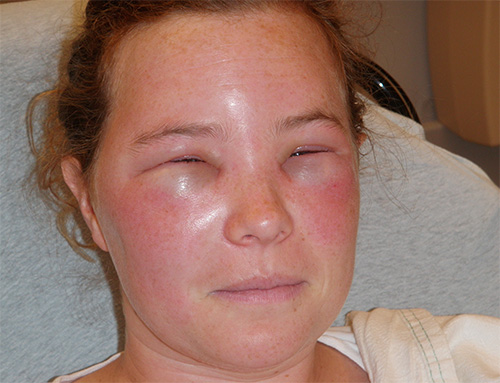
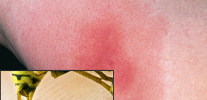
Below in the photo you can see what a wasp sting, complicated by extensive edema, looks like:
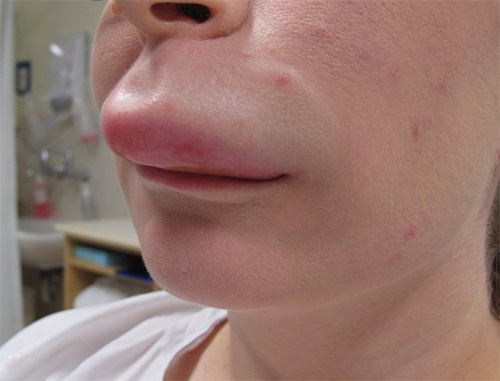
Feedback
“I always treated the wasps with some disdain. Probably because they often bit me as a child, and I just got used to it. Last summer, I only saw a woman on the beach being bitten by a wasp, she lost consciousness in five minutes, probably. At first I wanted to laugh, I thought - it is necessary, to plop out of fear. And then, when I came up, I saw how her face swelled, her neck was full, her eyes were swollen. It is evident that her sensitivity is high. The ambulance arrived, took her away, and I do not know how it all ended. Therefore, if the wasp bites, then it all depends on your body. "
Tatyana, Astrakhan
Multiple bites of wasps and their danger
Separate conversation deserve multiple wasp hops. If a person is simultaneously bitten by several insects, the effect of bites on the body increases in proportion to their number.

For people with a normal reaction to the venom of the wasp, even 5-6 insect bites do not pose a threat to life. The only thing is that they can be accompanied by abundant subcutaneous hemorrhages, if they occur in approximately the same place (there will be a huge bruise).
On a note
A lethal dose of wasp venom for a person who does not have a pronounced sensitivity to the toxin of this insect is 30-40 mg of poison per 1 kg of body weight. With one bite, the wasp injects about 0.4 mg of venom into the wound. That is, for an adult weighing 70 kg, about 700 bites will be fatal. But this is only in the absence of an allergic reaction!
The most dangerous for health, and sometimes for human life are multiple bites of hornets - close relatives of ordinary wasps. Each hornet is able to sting its prey several times in one attack. If insects are gathered by a whole group, then their attack can lead to extensive hemorrhages (including internal ones) and necrotic tissue damage.

In the photo you can see the consequences of the attack of the giant Asian hornet, which has already been mentioned above:
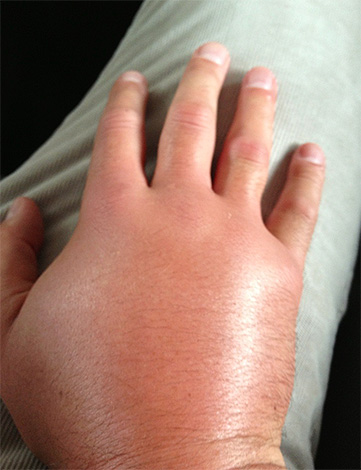
Should I say in this case about allergies,for which even single attacks represent a great danger, and multiple bites of wasps and, moreover, hornets, are generally life threatening. It is logical that in such people an allergic reaction will be much sharper and more serious.
Wasp bite: where and why does it occur most often
Despite all the danger and the seeming aggressiveness of the wasps, their bites are just a way of self-defense and defense invented by nature. Against insects that the wasps use as food for their larvae, poison and sting are rarely used. But the wasp is always ready to meet with a potential enemy.


Most often wasps bite a person in the following situations:
- in nature when it comes too close to the nest;
- on suburban areas, the owners of which may try to purposefully destroy disturbing wasp nests or accidentally touch a wasp sitting on a berry while harvesting;
- in markets where they sell fruit or process fish and meat (wasps here, as a rule, are accidentally caught by the sellers or workers);
- on the balconies, where the wasps sometimes make their nests;
- in case of accidental slamming of an insect, if it got under clothes.
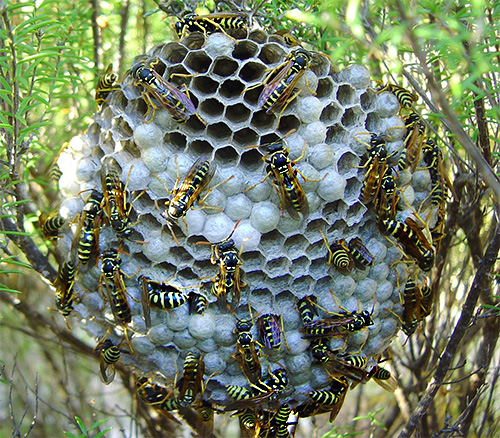
The photo below shows the nest of paper wasps.If such a construction catches the eye, it should be circumvented in order to avoid unpleasant consequences:
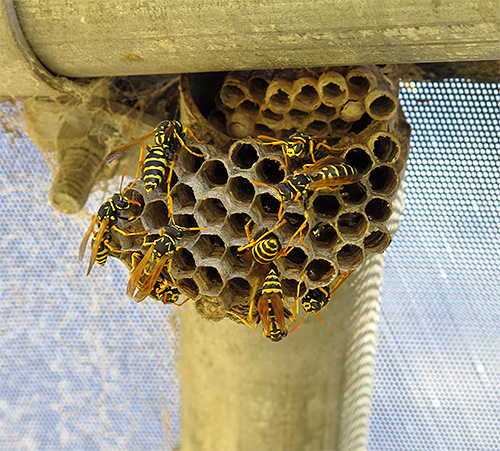

In some cases, the wasps attack, seemingly without any apparent reason, away from the nest. However, a detailed analysis of the situation in most cases shows that the insect was either crushed or scared away from the place of feeding, which is why it took a person to be an offender.
Be that as it may, wasps never attack a person to feed - they have a completely different “nature”. Each bite occurs only within the framework of self-defense, though not always understandable to man..
What to do with a wasp sting?
Finally, let's talk about what to do if a wasp bitten. To minimize the consequences you need to take a few simple steps.
- Try to suck poison from the wound. It is to suck, not squeeze, because when pressed, blood circulation increases at the site of the bite, and the poison spreads even faster under the skin.
- Have time to neutralize at least part of the poison with any available acid - table vinegar, citric acid, a piece of orange or apple. This should be done as quickly as possible, because the wound at the site of the bite of the wasp is very quickly healed.
- Attach to the wound cold compress - ice, meat from the freezer, a bottle of water.
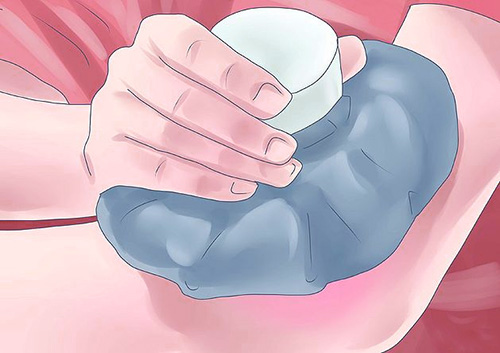
All these manipulations will help reduce the size of the edema and the strength of other symptoms.
If the victim has the first signs of allergy (for example, the general condition worsens, the temperature rises, shortness of breath and chest pain appear), he needs to drink Suprastin or Dimedrol and immediately see a doctor. Every minute lost in this situation can cost lives!
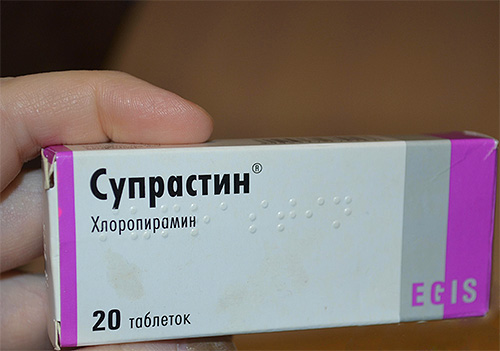
In general, it is much easier to simply prevent the bites of wasps. To do this, it is enough to be as attentive and careful as possible in nature - inspect the place where you plan to sit, carefully pick berries and fruits, and when a cluster of wasps or their nests is detected, slowly and quietly move away.
Do not slam on an insect that just sat on your hand or foot. If the wasp is not going to fly away by itself, it is enough to pick it up with a sheet of paper and let it go - most likely, it will use the opportunity to retire and the incident will be settled.
About the danger of wasp and bee bites (including anaphylactic shock)
An example of how a wasp bite almost proved fatal to humans.
In detail about the allergy to insect bites and the rules of first aid to the victim



Within 10 minutes after the bite of a wasp, my dad died ...
Pity
Pity
Really a pity ...
What for nightmare? Incubator city people ...