What if a baby was bitten by a wasp? First of all, do not panic along with the baby (as young mothers sometimes do) and remain calm. Overwhelmingly, the biggest annoyances from wasp sting the child will be quite pronounced swelling and severe pain.
However, these symptoms are sometimes enough for a whole day on vacation or in the country to be spoiled both in a child and in adults. In addition, the Internet, to which young parents will first of all turn, is simply replete with various “terrifying” “life” stories, which will not add peace of mind either. Of course, the described severe consequences of wasp bites sometimes happen, but it happens so rarely that it makes no sense to accept them as a mandatory outcome.
Adults know that if a wasp has bitten a child, severe pain will certainly appear, but in about a day it will almost completely disappear.

Next, we will look at what parents need to do in the first place, so that the consequences of a baby wasp sting in a baby go away as quickly and painlessly as possible. We also note what to do in those rare critical situations when the child’s life may directly depend on the correct actions of the parents.
But first things first…
On a note
The wasps are different. Ordinary paper, most common, sting, quite painful, but not in any comparison with long, very slim, brown or black road wasps - they are considered to be the owners of one of the most painful bites in the insect world in general. After the attack of these wasps, even in an adult there can be a painful shock, and there’s nothing to say about the child. However, fortunately, road wasps are much more rare than paper wasps, and bite only in exceptional cases.


In fairness it should be noted that part of the "horror" on the subject of bites wasps still has a real basis. However, in the overwhelming majority of cases, all this does not happen to children: various complicated allergies, systemic reactions of the body and intoxication are more characteristic of adults.
The reason for this is rooted in immunology: sensitivity to allergens that make up wasp venom increases with each new bite. In this regard, the child's body is a “blank sheet of paper”, which simply has not yet had time to accumulate the necessary “experience” for the development of a violent allergic reaction.
As a rule, hypersensitivity to any substance appears in an organism that has already encountered this allergen repeatedly. Simply put, for each subsequent sting, some people (and their minority) react more and more sharply.
The average adult healthy person does not have such a response, as his body is able to produce protective antibodies and quickly neutralize the poison that has entered the blood, and the baby’s immune system is simply not familiar with it.
Thus, if a child was bitten by a wasp, the consequences of this would in most cases be entirely due to poison toxins, and not the development of an allergic reaction. Pain and inflammation, of course, will be - but without allergy symptoms (for example, urticaria and fever).
Only occasionally, in exceptional cases, a child may begin a systemic reaction to the wasp sting. This is a topic for a separate discussion (we will consider it a little lower), because such situations are already much more dangerous and require the use of potent drugs, and sometimes even hospitalization.
First actions after the bite
So, if a child was already stung by a wasp, first of all you need to try to remove or neutralize at least part of the poison that fell under the skin.
For this you need:
- suck poison from the wound - if you start to do it immediately after the bite, you can significantly reduce the degree of edema;
- Attach a swab dipped in table vinegar or lemon juice to the bite site (alternatively, a piece of apple or onion) - the wasp poison has an alkaline environment, therefore it is partially neutralized with acid;
- after 2-3 minutes, apply a cold compress to the bite site.
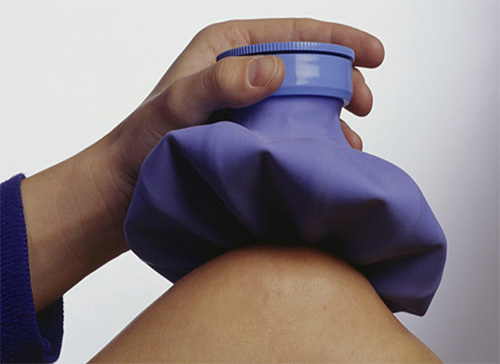
It is important to understand that completely avoid the appearance of pain and swelling will not work, because you still have to deal with a very strong poison. Therefore, after the wasp has bitten a child, all actions should be aimed at reducing the amount of poison in the tissues - firstly, and, secondly, so that the unpleasant painful sensations pass as soon as possible.
In addition to first aid measures, you also need to know what you shouldn’t do with a wasp sting:
- there is no point in wasting time looking for the sting in the wound: the sting of wasps, unlike bees, never leaves the body of the victim after the bite;

- you can’t panic and fuss: this will make the child even more worried, it’s better to just take pity on the baby and try to explain to him that everything will pass soon;
- It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out the poison: it will not back out, but it will be necessary to spread faster in the tissues due to increased blood flow during pressure;
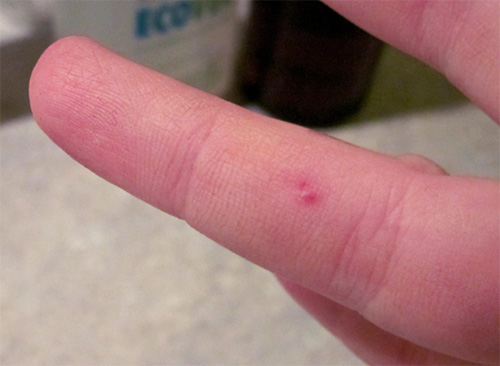
- in the absence of obvious symptoms, it is impossible to smear the bite site with any allergy remedies from your first aid kit: a child’s side effects from “adult” ointments may be even worse than the effects of the bite itself.
It is worth noting that most often the wasp bites the child by the finger or hand, and this, fortunately, is the “easiest” option. Worse, when an insect is attacked, for example, the face or, especially, the baby's neck or throat.
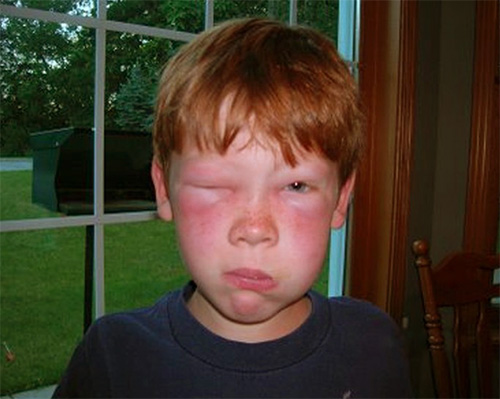
In any case - no matter what part of the body the wasp bit on your child - you should know which methods will help reduce pain, swelling and subsequent itching.
Methods for eliminating pain, itching and swelling
To combat the characteristic effects of wasp stings, there are many good and proven remedies.All of them can be divided into three main groups:
- Special (and necessarily appropriate to the age of the child) drugs after insect bites. As an example, children's balms Gardex Family and Gardex Baby, spray balm Mosquitall, balms Insectline and Picnic Family. For the most part, these remedies only reduce itching. Pain can be treated with drugs like Fenistil, Soventol and Menovazin, but their use in a child is possible only in strict agreement with the doctor.

- Soap solution and ammonia (standard "Zelenka" and iodine can be used only in the last place).

- Folk remedies: chopped parsley root, dandelion juice or garlic.

It is important to understand that swelling from a wasp sting will be observed in a child in any case: even when the drugs are dull or relieve pain. The fact is that the edema is due to the destruction of the cells of the tissues affected by the poison, so until the body cleans up everything, the place where the wasp bitten will be inflamed.
The bites of wasps in the face, throat or ear area are very dangerous: the poison here can cause edema threatening with breathing difficulties.

Even if a wasp has bitten a child by the ear in the area of the lobe, adults need to carefully monitor the condition of the baby, and if he has any doubts, take him to the doctor.In the case when a wasp bite fell on the mucous membranes of the eye, you can not hesitate - you must immediately go to the hospital or call the ambulance.

Finally, if a wasp bite occurred in the throat area of a child, the developing edema is more likely to cause serious breathing problems. It is this cause that accounts for a significant percentage of deaths as a result of insect bites, so the condition of the child requires special observation and, in the case of deterioration, speed of reaction.
Feedback
“We had this last summer. I do not even know what to advise you. Lesha was then three years old, his wasp bit in the neck, but only in the back. He did not immediately show us, but he endured for a long time. He is a Spartan. They themselves noticed that his neck had disappeared somewhere. But besides a strong edema, there was nothing, breathing normally, eating. After a couple of days everything went away, we didn’t even smear anything. ”
Kira, stanitsa Severskaya
Wasps bites in infants
Of course, any parent is very worried about his child, especially if the baby is only a few months old. Nevertheless, babies do not have any particular specifics of wasp bites.
The main problem that the parent of the bitten baby waspus must face is the strong anxiety of the child.If the baby was bitten by a wasp, an adult should take the measures described above to neutralize at least part of the poison, reduce swelling and severe pain.

More experienced parents advise at this time to distract the child with something, for example, to bathe him in cool water, in which he will cease to focus on the pain of a bite. However, special products are also available for infants - for example, Gardex Baby, designed for children from one year old, but in the absence of an allergic reaction, which can be used for babies from 6 months old, or Savior cream, approved for children of any age.

In addition to these drugs, folk remedies such as garlic, soda and parsley root can be successfully used in a young child.
It should be noted that in infants the pain of a bite of a wasp usually passes faster than in older children, but the “bump” itself, if it appears, then persists for a longer period.
Feedback
“Our one-year-old child was bitten by a wasp. Well, the cry was, an hour, probably could not calm him down. And then immediately let go. Moreover, the wasp bit him on the ear, we were afraid that it was as if it didn’t spread to the face, but there wasn’t even a lump there.So, only the ear stuck out. He could not sleep on this side, woke up. Smeared him with the Rescuer, the grandmother rubbed sour cream. I don’t remember exactly how much this swelling was holding, but the bite had stopped hurting the very next day. ”
Elena, Krasnoyarsk
First aid kit to the country: what you need to have with you to always help the child
When planning a trip with nature for a baby or just outside the city, it is necessary to prepare a first-aid kit in advance, which should include a small set of tools to help the child in time for bites of wasps or any other insects.


You can roughly focus on the following drugs:
- The rescuer is a universal means of first aid (including for wasps bites);
- gel fenistil;
- delicate baby spray or balm type Gardex;
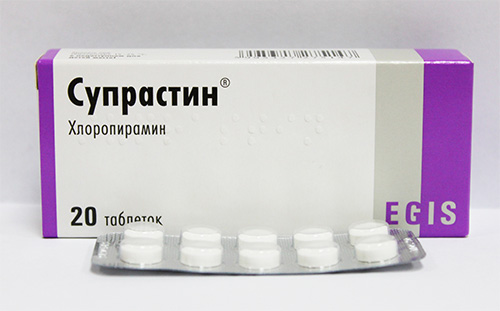
- Suprastin - for every "fire" case (along with the drug you should definitely take instructions to be able to correctly calculate the dose for the child).
After your baby was bitten by a wasp, and you gave him first aid, the child should be watched anyway - despite the fact that the danger seemed to be over.
If a wasp’s bite fell on an eye or mouth,if the child has started to increase body temperature, a rash appeared at the bite site or in other parts of the body, there was a headache or nausea, the baby should immediately be taken to the hospital.
Before this, it is advisable to call an ambulance and, having described the situation, ask for advice. Perhaps, on the way to the hospital - on the recommendation of the doctor - the child will need to be given Suprastin to drink, but self-treatment in this case is unacceptable.
Be attentive on vacation, take care of yourself and your child, and if trouble still occurs, behave correctly and maintain composure.
Useful video about the effects of wasp bites: practical advice
What if you were bitten by a wasp ...