
For a year, dozens of different insect species can sometimes attack a person, and each such bite has its consequences - from practically imperceptible to very pronounced. How the victim reacts to an insect attack depends, firstly, on the type of arthropod, and secondly, on the individual sensitivity of the person.
Insect bites often do not require any special treatment - their effects pass by themselves within a few days. However, this is not always the case, and in certain cases, treatment may still be required.
Here are some examples:
- bites a poisonous or even a stinging insect - the consequences in this case can be very serious, up to severe allergic reactions, anaphylactic shock, internal hemorrhages and death;
- an insect bite is infected — treatment in this case sometimes requires hospitalization,as some blood-sucking parasites are able to tolerate pathogens of deadly human diseases (encephalitis, borreliosis, typhoid, etc.);
- the victim has a high individual sensitivity to insect bites (some people even react to mosquito attacks with severe edema) - in such cases, encounters such as stinging insects can be very dangerous;
- an insect bite does not pass for a long time, and in its place dermatitis additionally develops or wound infection is observed due to constant scratching.
In any case, before treating insect bites, it is highly desirable to identify the “aggressors”: sometimes when attacking poisonous arthropods, the use of special antidotes, which are very species-specific, is required. And in general, drugs used after insect bites have a very limited scope, in which they have the greatest effect.
On a note
Generally speaking, spiders, scolopendras and, for example, mites are not insects (insects have only 3 pairs of legs). However, ordinary people who do not go into entomological subtleties, their attacks are also referred to as insect bites.
In some cases, attacks of arthropods can be difficult to visually distinguish from injuries by stinging plants or, for example, from the manifestation of an allergic reaction. Unfortunately, there is no universal rule for clearly distinguishing bites from other skin ailments.
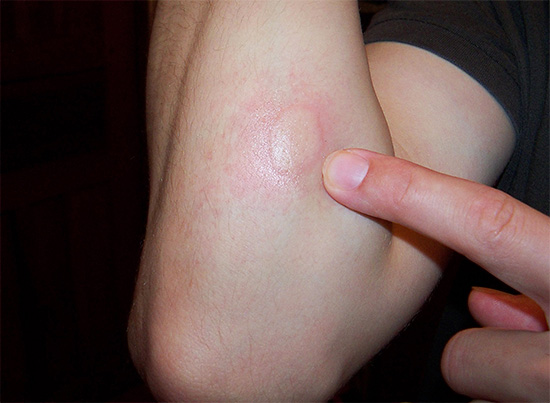
As a rule, the bite is identified by a small point through which an insect sting or proboscis was introduced into the skin. In the future, it is around this place that characteristic inflammation and swelling of tissues occurs.
The photo shows what a wasp bite looks like after 2 minutes from the moment of the insect attack:
On a note
In order to take into account the incidence and the causes of public appeals to medical institutions in the Russian Federation, a regulatory document of the 10th revision with the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) was adopted. According to ICD 10, the insect bite has the code W57 (means "Bite or sting by non-poisonous insects and other non-poisonous arthropods"). This code is universal for hospitals around the world, and it is indicated in the extracts and references. The code of the insect bite according to ICD 10 does not depend on the type of insect and the severity of the consequences.
In medical practice there is no separate specialization of the doctor who treats insect bites. It all depends on the effects of the bite.Allergologists, toxicologists, infectious disease specialists, and in especially severe cases surgeons and resuscitators can take part in the treatment. If the bite symptoms do not threaten the life and health of the victim, treatment is usually performed by a therapist.
Different insects, different bites
Different types of insects can bite a person for different purposes - for the purpose of self-defense, or within the framework of their parasitic lifestyle. Depending on this, it is conditionally possible to distinguish two corresponding groups of bites:
- Bites of stinging and poisonous insects (as well as some other arthropods). These include bites (stings) of defending wasps, bees, hornets, ants, street bugs, spiders, scolopendras. The encounter with these creatures sometimes ends up with serious consequences for a person - for example, severe pain, inflammations and swelling, which even by themselves can be life-threatening, not to mention possible complications.
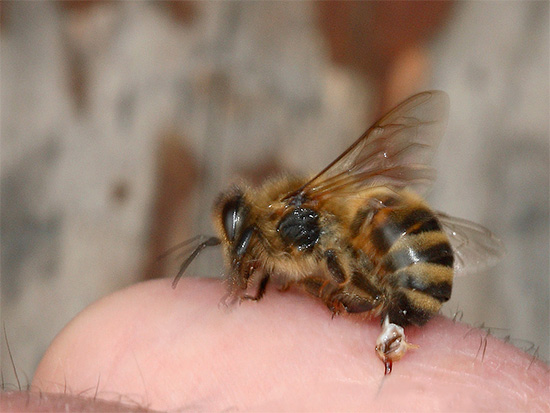

- Bites of parasitic arthropods - mosquitoes, bed bugs, fleas, lice, ticks, gadflies, bloodsucker (example - elk flea) and others. Their attacks are usually not very painful, causing itching and slight swelling of damaged tissues.The greatest danger of such bites lies in the fact that biting, these arthropods often transmit to humans the causative agents of serious diseases.
Feedback
“We only sighed with relief that the mosquito season was over, and here in mid-October we were again showing marks of bites. Both my husband and my husband have all feet fleas fleece, in some places above the knee, and the child even found red dots on the body. These fleas climb from the basement to all the lower apartments. They called the SES, now we are sitting, waiting for the fights. ”
Svetlana K., Tver
Even in related insect species, bite symptoms can vary greatly. For example, bedbug bite it looks like a red and slightly itchy swelling, while the sting of a water bug is very painful, is similar in symptoms to the sting of a wasp and usually causes severe swelling. And the difference is that the bed bug bites to quietly drink blood at night, and the smooth bites a person only in self-defense.
The bites of the most frequently attacking insects are useful, as they say, to know "by sight". Let's characterize and remember their main distinguishing features.
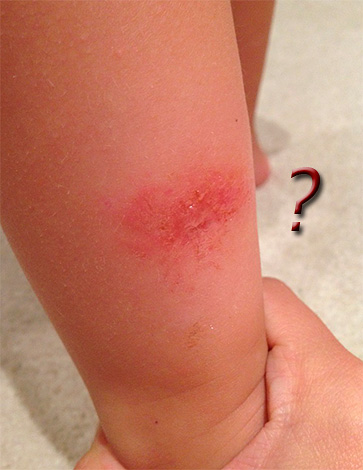
So, the bites of bed bugs, which have already been mentioned above, are usually located in well visible chains, due to which they are easily recognized:
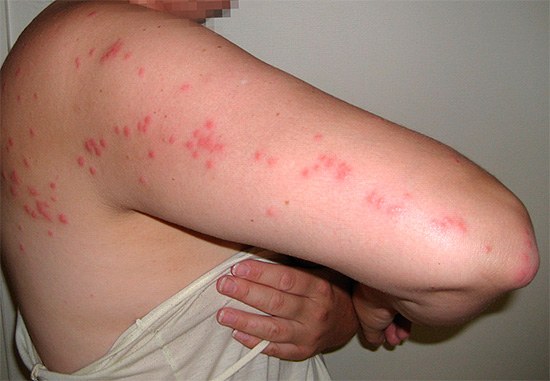
The attacks of these insects are relatively safe: there are no known reliable cases of transmission of any infections by them. However, occasionally the symptom of the bites of these insects, especially in children, may be a brightly pronounced allergic reaction with severe edema and fever.
The photo below shows the bedbug bites on the baby's foot:
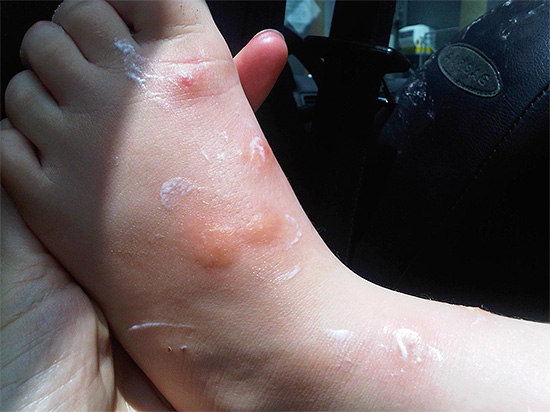
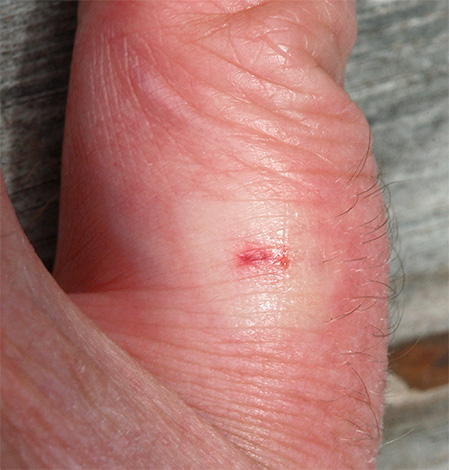
Flea bites are quite painful, and differ from the attacks of bedbugs by a clearly visible red dot in the center (during a bite, the insect literally bites into the skin of the head - see the example in the photo below):

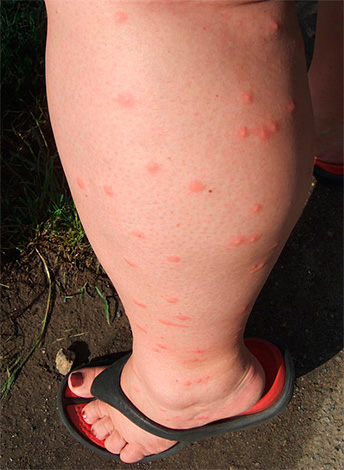
In rare cases, these insects can cause infections with highly dangerous infections - plague, encephalitis, anthrax, brucellosis, and some others.
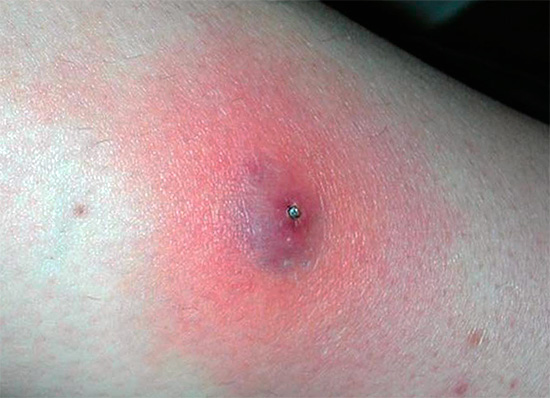
Tick bites cause compaction of soft tissues and the formation of noticeable bumps. Often, in the place of penetration of the tick under the skin, there are lesions characterized by a characteristic “ring” arrangement: the brightly colored center is surrounded by a pale ring, and then again by the red area:
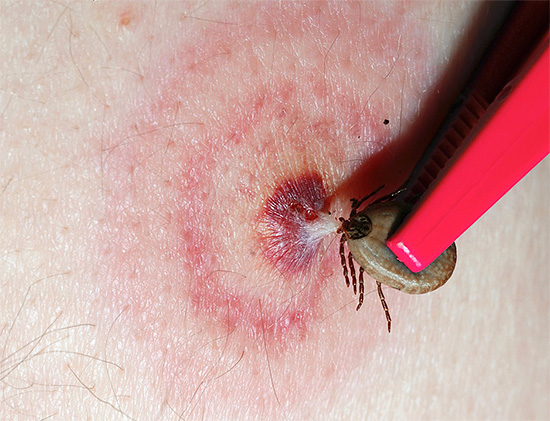
Ticks are the cause of infection with encephalitis and no less dangerous Lyme borreliosis.
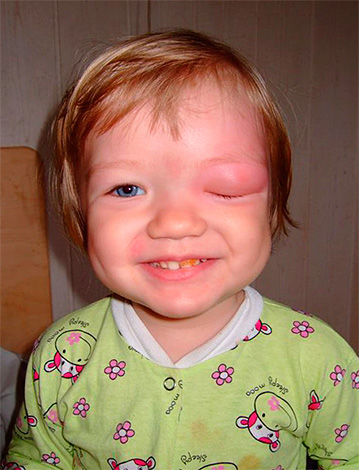
The bites of bees, bumblebees, wasps, hornets, scolopendras, tarantulas, scorpions and some spiders are very painful and lead to the development of severe tumors and edema in victims, and can also cause serious intoxication and allergies.
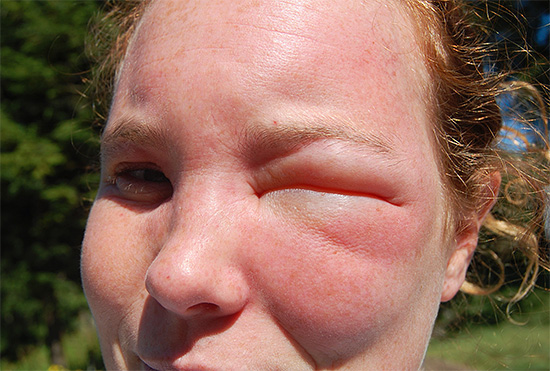
The photo shows the effects of a wasp sting in the face:
The bite of a karakurt spider, which prefers sandy habitats in the southern regions of Russia, is not very painful compared to other arthropods, but, however, leads to incredibly heavy, affecting virtually the entire body of the affected person. In the case of a female attack during the mating season, a bite can lead to death.
Lice bites usually cause severe itching and slight redness. As a rule, these parasites attack in large quantities, because of which they are able to seriously deprive a person of calm. In addition, lice can infect their victim with typhus.

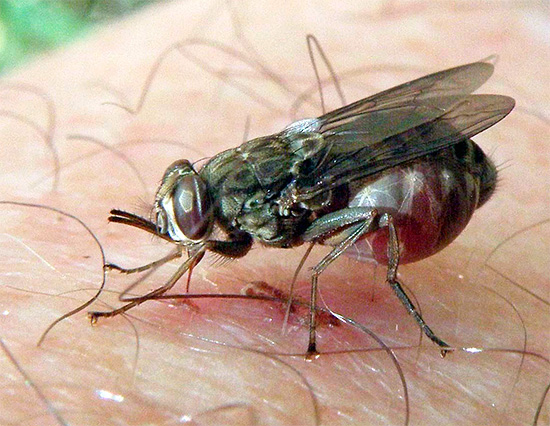
The bites of leeches and gadflies are "famous" for profuse bleeding and small local edema.
The bites of the so-called sandy fleas are large painful bumps - this is the swollen body of an insect that has penetrated the skin.In our country, fortunately, it will not be possible to meet with sandy fleas, however, for example, on the beaches of Thailand and India, these parasites can be hooked up.
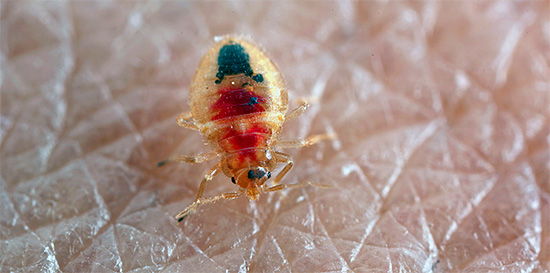
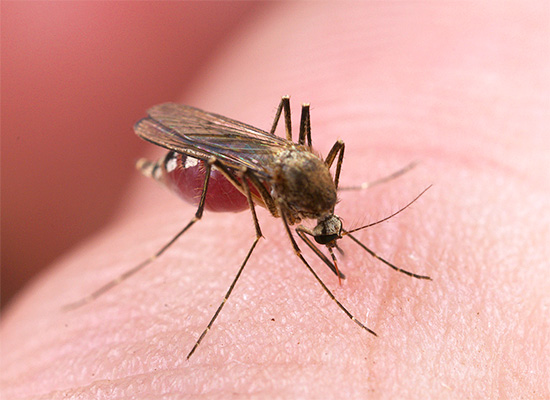
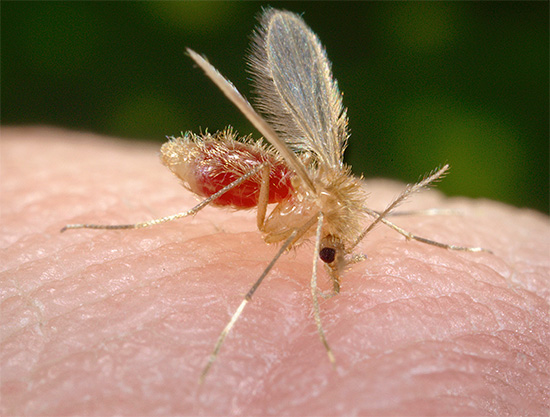
And finally, mosquito bites are well known to all of us. As a rule, the result of the attack of these insects is a relatively mild (and in some people - almost imperceptible) itching. However, when a person is massed, a person’s condition can deteriorate dramatically, including fever, nausea and vomiting.
In the photo - a mosquito at the time of the bite:

Despite the fact that the bites of many insects have certain distinctive features, it is nevertheless always useful to accurately determine which insect has bitten. This is especially true for pregnant women and young children, when the treatment must take into account all the pros and cons, making a decision about taking this or that drug.
Counseling for parents (by doctors) about insect bites is greatly complicated, if it is not clear who, in fact, bit the child. The treatment of the bite of an “unknown” insect may not be optimal, and it does not always guarantee a reliable result: imagine that a poisonous spider bit the child, but the parents vaguely assume that it was, for example, a wasp sting ...
Feedback
“If you talk on sensations, it is very painful. Pain - the first thing that comes to mind. At first I thought that they had stumbled upon a wasp nest, but the wasps did not bite so painfully. Yes, and I never observed a special reaction - it was swollen and swollen, but here it is in the heat, then it throws into the cold, some bluish leg, it shakes all over. The neighbors then enlightened that they were accustomed to the hornets, and I was lucky that I got off with two bites. But this is really horror! I’m afraid to think it would be if they bit the baby. ”
Elena, Ryazan
Some symptoms and complications of insect bites
As mentioned above, insect bites can be different: it depends on the sensitivity of the victim, and on the species of the arthropod. So, for example, the result of an attack of a stinging insect is mainly determined by the reaction of the human body to the injected poison, and the view of the insect here goes to the background.
In general, the following are the most common symptoms typical of insect bites:
- local redness of the skin, characteristic of the bites of almost all insects;
- itching or pain, the degree of manifestation of which depends on the individual sensitivity of the person and the composition of the enzymes injected under the skin;
- small or extensive, and sometimes extending to the whole body swelling;
- dermatitis that occurs in response to mass bites;
- high temperature, characteristic for the most part of victims of stinging insects and spiders (however, the temperature can rise with multiple bites of bed bugs and even mosquitoes);
- general intoxication of the body, accompanied by headaches, nausea, chills, swollen lymph nodes.
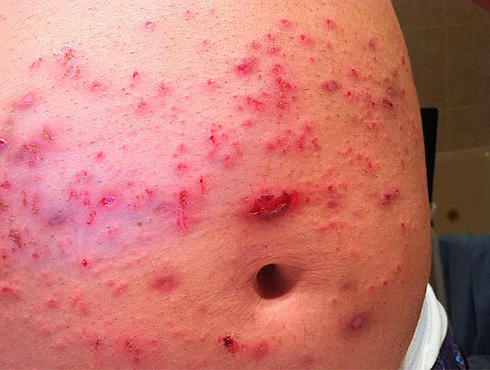
In some cases, in response to the bites of poisonous spiders, tropical ants, or hornets, extensive subcutaneous hemorrhages, angioedema, and anaphylactic shock may develop. Another serious and rather dangerous symptom can be ulcers, appearing, for example, at the site of non-healing tropical flea bites (sand) fleas (more precisely, they are not even completely bites, but the consequences of implanting a flea under the skin).
In the photo - parasitic insect bites (laundry lice), whose treatment did not start in time, as a result of which pustular inflammations developed in the affected areas:
As a rule, small swelling and itchy bites do not require special treatment: within a few days they will pass by themselves.First of all, those bites that are accompanied by severe edema, inflammation, allergic reactions and poisoning require treatment.
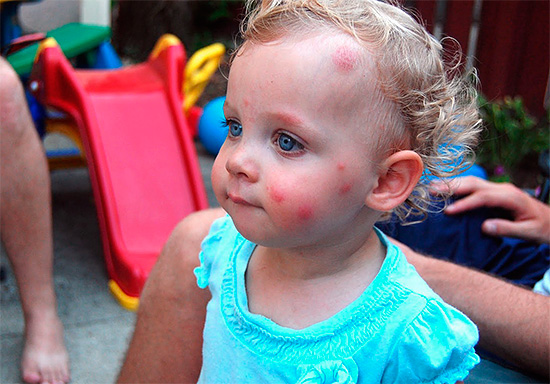
Insect bites in children
In general, when insect bites in children develop the same consequences as in adults, however, in children, individual symptoms sometimes are strongly pronounced, and sometimes even take a dangerous form. Extensive rashes appear most often in children, the temperature rises, for example, in the case of an attack of hymenoptera (bees, wasps, bumblebees, hornets).
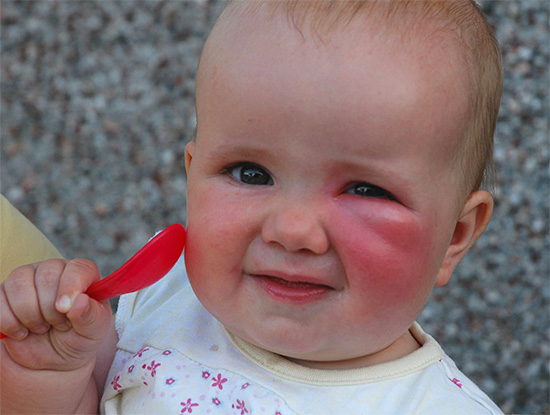
At the same time, children are not characterized by hypersensitivity and, as a result, they have less Quincke edema or anaphylactic shock, compared with adults.
As practice shows, one of the problems with insect bites in children is their nervous excitement in response to pain and itching, as well as the constant scratching of the affected skin, which can cause infection in the wound. The task of the parents in this case is, if possible, to treat the bite site with suitable means for children to relieve the itch, to antiseptic the wound, and also to distract the child from his misfortune - for example, with an exciting game.
Treatment of mosquito bites, fleas, bedbugs and other small bloodsuckers
Usually, the main task in the treatment of bites of small blood-sucking insect-parasites is to relieve itching and reduce swelling of the affected skin. More often, this problem has to be solved in children, especially the smallest, who sometimes react very sharply even to seemingly harmless mosquito bites.
The first thing to do is to smear such a bite with a suitable ointment or cream. Hydrocortisone ointment, Menovazin, Fenistil-Gel, Moskitol or Off for the treatment of insect bites in children are well suited for this. It is important only before applying to study the instructions to the tool and assess the possibility of its use in this particular situation - taking into account the age of the child, his health, etc. (It is recommended to consult a doctor).
In those situations when the child is strong, before the blood, combed the bites, it makes sense to grease them with Rescue or Levomekol balsam. This will protect the wounds from infection. With severe itching and swelling, it is useful to put cold in place of the bite and distract the child with the game.
On a note
Homeopathy with insect bites is useless.Such means except soothing the bitten thought that he was treated. Homeopathic ointments have no therapeutic effect.
In some cases, after the bites, even small parasitic insects of the victim must be taken to the hospital - in particular, when the following alarming symptoms appear:
- Fever;
- Chills;
- Headaches;
- Vomiting;
- Swollen lymph nodes.
Diseases that can carry parasitic insects, many. These are life-threatening typhus, malaria, plague, brucellosis and many others. Therefore, at the first symptoms of the victim described above, you must immediately show the doctor.

On a note
The vast majority of people with malaria worldwide are children under the age of 5 years. Therefore, their condition after mass mosquito bites should be monitored especially carefully.
What to do if bitten by a bee, wasp or hornet
The first thing to do if you are stung by an insect is to check if there is a sting in the wound (although it is left only by the bees that have a jagged one, unlike wasps and hornets).
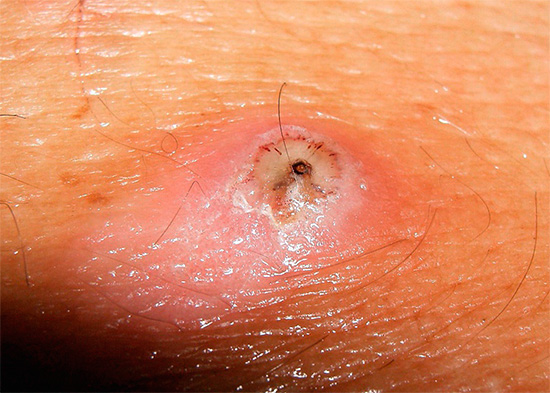
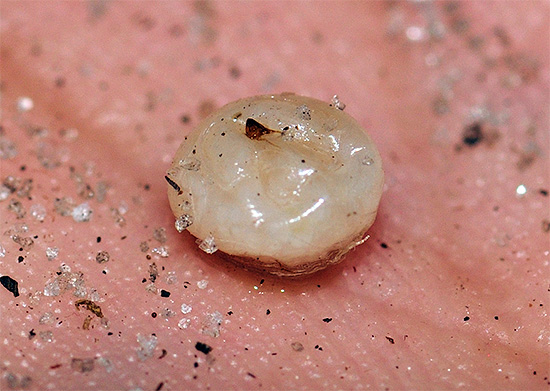
If a bee stings, you need to carefully remove the sting from the skin (for example, tweezers) as soon as possible.Keep in mind that if you try to grab the sting with your fingers, you will squeeze a vial of poison that is above the severed sting (see the example in the photo below), and an additional part of the poison will flow under the skin, increasing the pain.
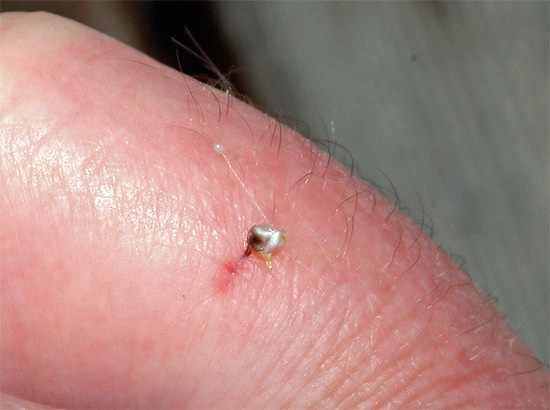
Then from the fresh wound you need to try to suck the poison. At the same time it is impossible to squeeze it with your fingers - it only increases the blood circulation and leads to the rapid growth of edema. Two or three attachments to the mouth of the mouth will be enough, it is not worth spending on sucking the poison for more than 1 minute.
On a note
It is useful immediately after the suction of part of the poison to lubricate the wound with any antiseptic - for example, hydrogen peroxide.
Then a cold compress is applied to the site of the bite: cold will constrict blood vessels and reduce the rate of absorption of poison into the blood (for allergy sufferers this is especially important, since it minimizes the dangerous effects of the poison on the body as a whole, while the toxins continue to decompose continuously in the skin without getting in large quantities into the blood).
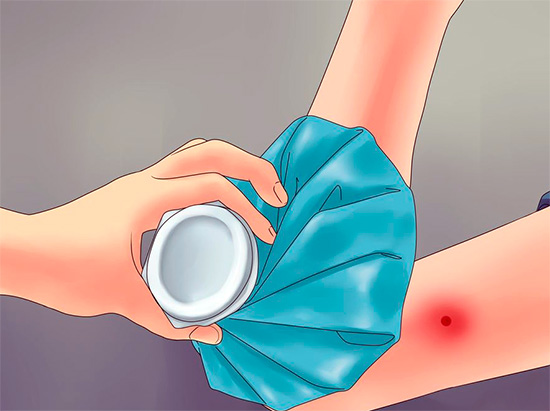
The person who was bitten by a stinging insect should be carefully monitored. When the alarming symptoms of a dangerous allergy (dyspnea, headache, pain in the heart, etc.) appear, you must immediately call Ambulance and get the appropriate advice.Most likely, recommendations on taking antihistamines (Suprastin, Dimedrol) will be given at a minimum, while a doctor is expected to arrive.
Important!
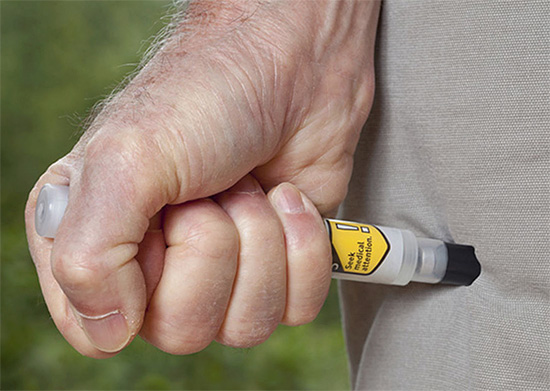
If the victim has previously experienced severe reactions to insect bites, he should always carry with him a special autoinjector with adrenaline (epipen), or a set of syringes and injectables, which the doctor prescribed for him. Such means should be applied immediately after the bite, without waiting for the manifestation of an allergy: in some cases, an allergy develops so rapidly that literally two minutes is enough for a person to lose consciousness.

Tick bite treatment
The first thing to do if the tick has already sucked is to carefully remove it from the wound.
It is dangerous to try to unscrew the tick from the wound. At first glance it may seem that he so deeply immerses his head in the skin that it is impossible to simply pull it out, but it will only work out to unscrew it. This is a mistake: when unscrewing a very high risk that the head of the tick will come off and remain in the wound.
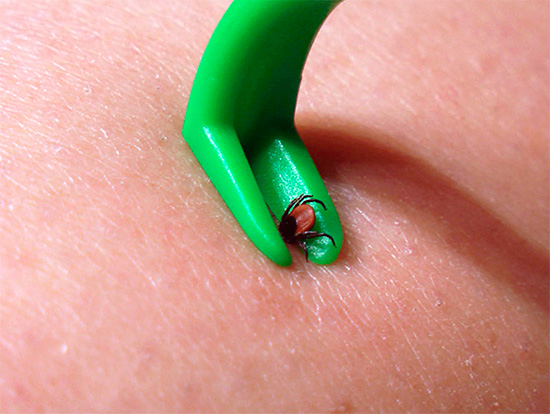
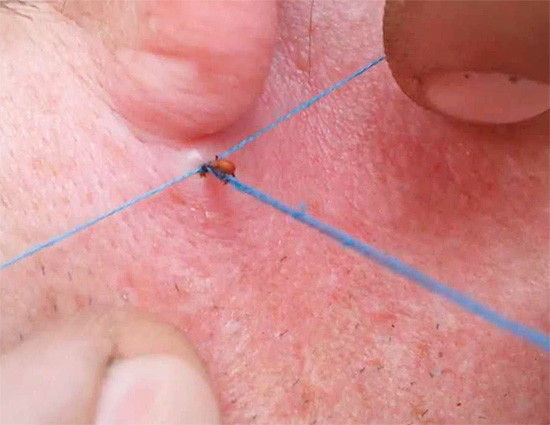
After extracting the tick, a small bump usually remains at the site of the bite. This is not scary - it is enough to smear the wound with iodine or hydrogen peroxide for disinfection. The same is done if the head of the parasite still remains in the wound.
After a tick bite, you should consult a doctor in the following cases:
- If the tick is bitten in the area with a high risk of infection with encephalitis. For Russia, it is the Urals and Siberia up to the Far East, for Kazakhstan - the mountainous areas in the east of the country, in Ukraine there are no such areas. Usually, people know that they are in an encephalitic area, and they take steps to prevent tick bites in advance.
- If there are clearly delineated red circles and spots at the site of the tick bite (this is a sign of Lyme borreliosis, which can only be treated in hospital).
- If a few days after the tick bite, symptoms of encephalitis began to show up - a headache, nervous disorders.
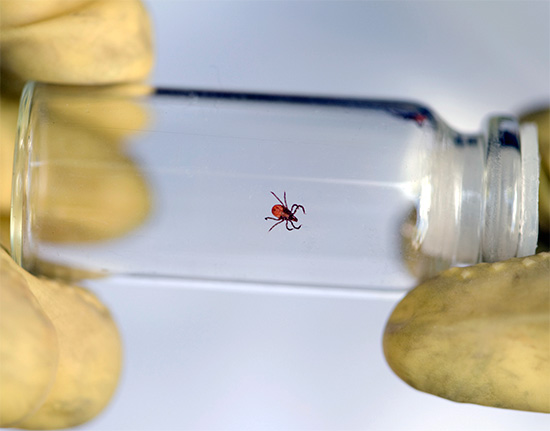
Mite taken from the wound, you must put in a glass vial and pass it for analysis.

No antibiotics for tick bites cannot be used alone! All funds are assigned only after diagnosis and only in the hospital.
If the patient is diagnosed with Lyme disease, he is prescribed a course of antibiotics.
If the victim is bitten in the encephalitis zone, he is injected with a special serum with anti-encephalitic antibodies. It is expensive, and not every hospital has such facilities.However, no home treatment in this case will help.
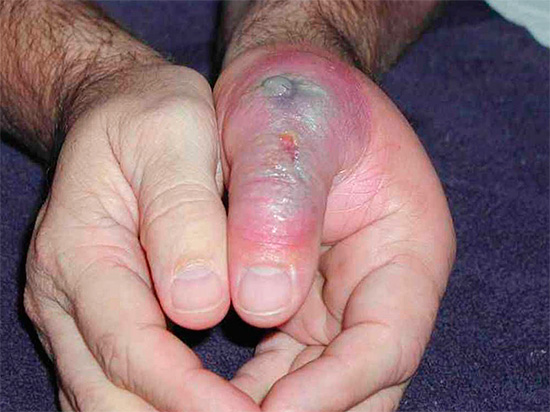
First aid for poisonous spider bites
The treatment of poisonous spider bites is somewhat similar to that of wasp and hornet bites, but due to the increased danger of poison to human life, it is even more radical.

The first thing recommended to do:
- Suck poison from the wound. Some naturalists even recommend making a cut with a blade or knife on the wound and squeeze out blood, but in the absence of experience and a clean knife at hand such actions can be dangerous, therefore it is better not to carry them out;
- Gently cauterize the wound until the protruding blood is black;
- Get to the nearest hospital as quickly as possible.
No antihistamines and pills for bites of karakurt and scorpions will not help. The only effective agents in this situation are special sera with corresponding antibodies. During the delivery of the victim to the hospital, he can be treated symptomatically: to bring down the temperature, if it is too high, to give painkillers.
But in the ideal case, insect bites should not be treated, but warned. To do this, when going on nature should:
- Wear clothes with low-key colors and one that covers the maximum of the body surface;
- In places with a lot of ticks, wear long-sleeved shirts, fill them with pants, and fill with socks. It is also advisable to wear a windbreaker with inlays on wrists and ankles;
- Do not drink from opaque vessels - if a wasp climbs into the bottle, and then enters the esophagus and bites from the inside, the situation can be very difficult;
- Use in nature a minimum of sweet;
- When a stinging insect, spider, wasp nest is found, slowly walk away;
- Do not check the hollow and burrow;
- Regularly examine each other for the presence of mites on the body. Particular attention should be paid to the scalp, ears, armpits, groin;
- Use repellents for those areas of the body that are not covered by clothing;
- Use mosquito nets and mosquito nets.
Remember: from insect bites all over the world in general and in our country in particular, more people are constantly dying than from the attacks of large mammals. And in most cases, such deaths occur because of inattention, neglect of the elementary rules of safe behavior in nature and the certainty that "perhaps it will carry it over." Therefore, be careful and careful, take care of yourself!
Useful video: what is important to know about insect bites, methods of treatment and emergency care
Folk remedies used to prevent insects from biting



