
Pubic lice are human parasites, their way of life is very different from other blood-sucking insects. They are also called ploshchitsy, and the complex of symptoms caused by infection with them - pubic lice. Also, the consequences of pubic lice bites and skin irritations from them in medicine are usually called phthyriasis - from the generic Latin name of Phtirusinguinalis plose.
Due to the fact that infection with pubic lice does not appear immediately, and the characteristic symptoms appear only a few weeks after infection, the carrier of ploshchits can infect other people for quite a long time without even knowing it. At the same time, it is not at all necessary that the pubic louse will parasitize only on a person living in unsanitary conditions and not adhering to the basic rules of hygiene. Lice are equally suitable for long time unwashed people, and well-groomed, and they can infect any person.
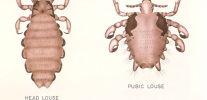
Pubic louse is significantly different from head lice in both appearance and lifestyle. Systematically, these are two different types of insects that cannot interbreed and even usually do not meet with each other if they infect one person. Therefore, approaches to the fight against pubic lice have their own characteristics.

Appearance of pubic lice
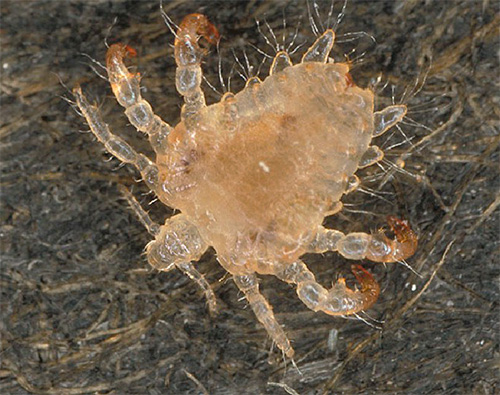
Externally, the pubic louse is a small insect, usually a light brown color. The length of her body is about 2 mm, and in larvae from 0.7 mm. Interestingly, because of their sturdy and massive paws, when placed to the sides, the pubic louse seems to be wider than the length.
The color of the pubic louse is slightly brown. Because of this, it is hardly noticeable on pubic hair, which is further promoted by the overall structure of the hair on this part of the body.
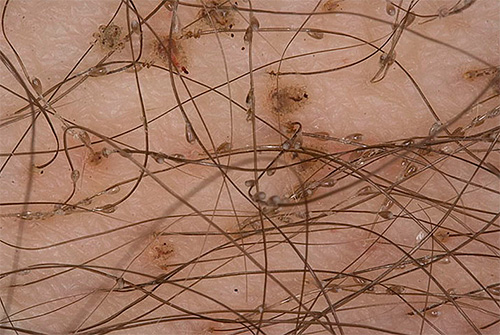
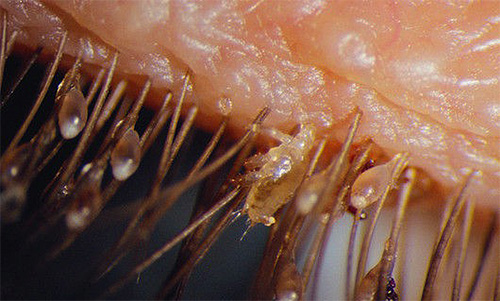
In the photo - pubic lice on the hair:
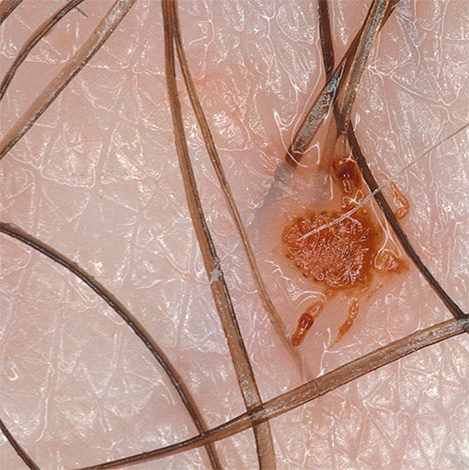
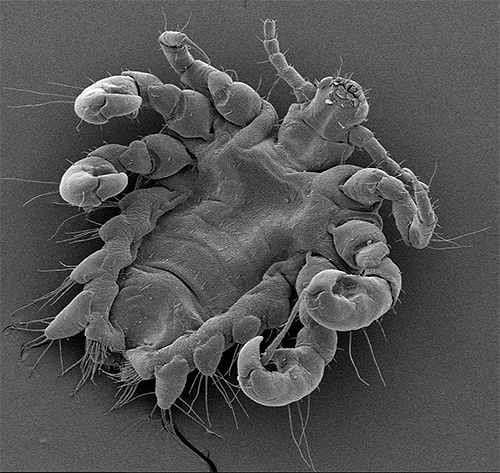
And the next photo - pubic louse under the microscope at high magnification:
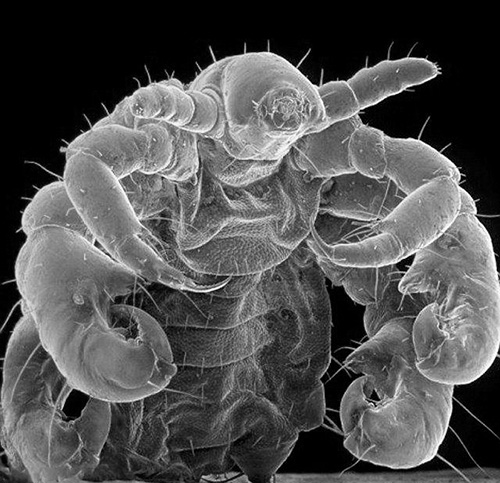

At the same time with the naked eye it is difficult to identify the mopher by its appearance. It looks just like a small seal on the hair.In addition, being usually near the base of the hair, they are less conspicuous.
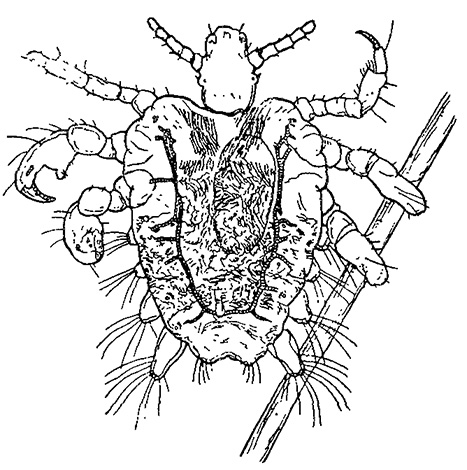
Pubic louses are well adapted to hold onto hair. They have strong paws with the likeness of claws on the ends, and the shape of the body, which contributes to a tight fit to the hair itself.
But with these seemingly relatively massive legs, the louse moves rather quickly across the surface of the skin, looking for a place to bite. In the picture below you can see the details of the body structure of the pubic louse:
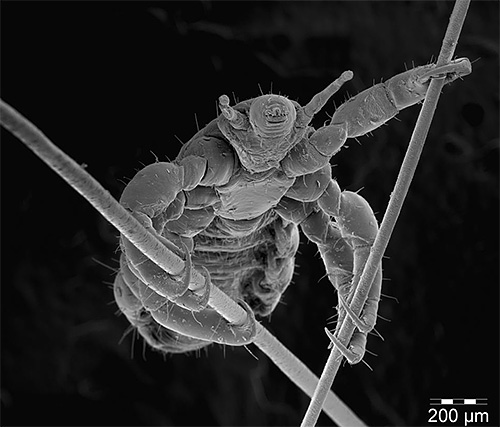
The larvae of the pubic lice are significantly smaller than the adult parasites, and in the early stages of their development have a length of just over half a millimeter. The photo clearly shows how the larva of the pubic louse looks when magnified under a microscope:

Pubic lice are difficult to confuse with other human parasites. In addition to them, only ticks can bite in the pubis area, but at the same time the tick is a parasite rather large. In addition, mites do not know how to move through the hair and have four pairs of legs, while lice have only three:

Bed bugs are much larger than pubic lice, and fleas jump very well. The crawler has neither wings nor powerful jaws, and therefore can only crawl.
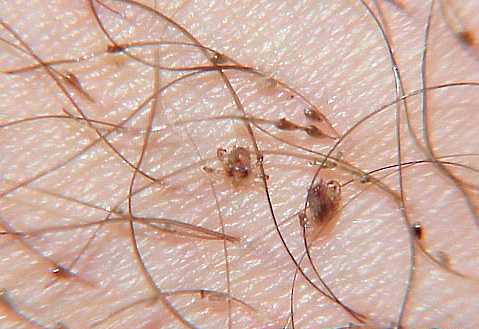
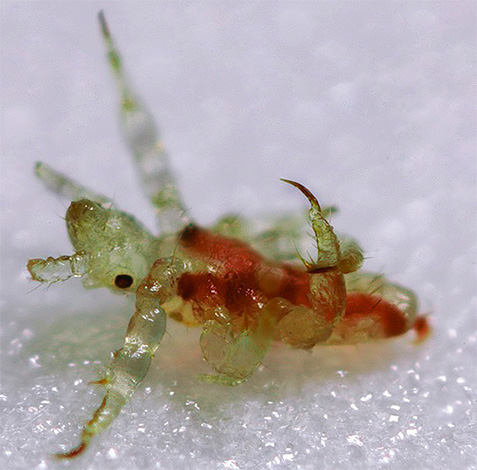
Below are some photos of pubic lice:

It is important that even knowing how pubic lice look like, it is quite difficult to identify them immediately because of the small size. Having seen photos under a microscope, some people think that they will meet on the body the characteristic “crabs” and do not even pay attention to tiny dark spots on the hair. In the photo below you can see how pubic louses look without magnification, in normal conditions:
Lifestyle ploshchits
Pubic lice can only live on the human body. Unlike other parasites living in furniture, garbage or natural environment, and lice do not leave a person for food only for feeding, lice do not leave the hairy parts of the body. And all their evolutionary adaptations are aimed precisely at adapting to the permanent presence on the body of people.
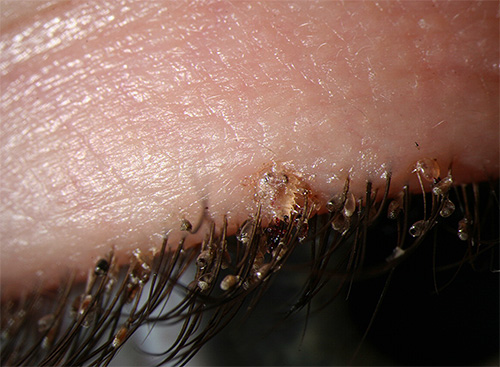
The photo below shows pubic lice:
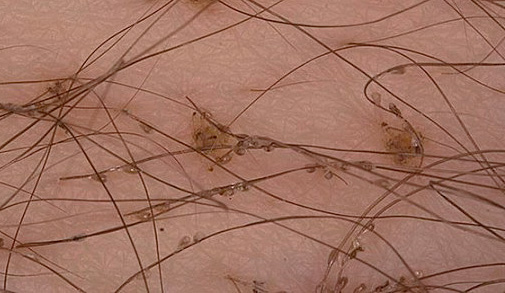
If for some reason the louse is removed from the pubic hair and falls on the bed or in the natural setting, it is likely to die in a few days from starvation. In exceptional cases, if a naked person is in the same place, the parasite can crawl onto it. Usually, the lice are quite inactive and cannot find a new owner through long-distance movements.
On a note
We emphasize once again that pubic lice can parasitize only on a person. No other mammal is suitable for life. Accordingly, it is possible to get pubic lice only from people.
Squabblers can affect hair not only on the pubis. In more rare cases, they colonize the armpits, and can also occur on eyelashes and eyebrows. On the chest, beard and head, pubic lice do not parasitize.
Feedback
“Once I had a terrible headache and I was afraid that it could be lice. I did not know whether pubic lice could live on my head and thought that I had been infected by an ex-girlfriend. Well, the doctor reassured me. It turned out to be a simple allergy to some product (it was after the New Year). And in general, she told me that pubic lice on the head do not occur. Then they are pubic. "
Ivan, Ivanovo
Pubic lice feed only on human blood. To do this, they have small stylet-like outgrowths in the mouth, with which they pierce the skin and reach the blood vessels.
Puncture the vessel wall, the louse begins to expand the esophagus, drawing in blood like a pump. In parallel, through a special channel, it injects an enzyme into the wound that prevents blood from clotting and facilitates its flow into the parasite's stomach.
A person can feel a very light injection from skin piercing, the enzyme itself causes itching like what remains after a mosquito bite, and a slight swelling of tissues in the area of the bite. It is pruritus that is the main worrying symptom of pubic lice.
Then you can look at the photo of pubic lice bites:
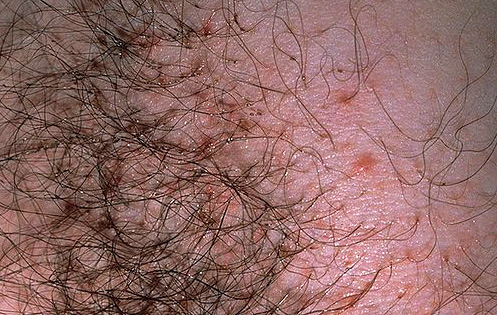
And on the video below, filmed how the pubic louse feeds:
Pubic louse eats several times a day, almost every 4-5 hours. For one feeding, the parasite sucks about 0.5 mg of blood. A louse cannot stay hungry for a long time, and after 1-2 days of hunger strike dies.
The optimal temperature for the development and reproduction of pubic lice is 30-31 ° C. At temperatures below 20 ° C and above 40 ° C lice egg development (nits) is terminated, and adults do not breed. At temperatures of about 1-3 ° C, lice and nits can survive for a week, and at minus 5 ° C and at + 55 ° C they die within half an hour.
Pubic lice have reduced eyes that see almost nothing. Ploschitsy oriented by smell.
On a note
Pubic lice like moist air. In dry air, they lose mobility and are easily showered from hair. This is used in American clinics,treating the pubis of infected people with air from a hair dryer with a temperature of about 50 ° C, and then easily combing the weakened parasites with special combs.
Reproduction pubic lice
Pubic lice breed very quickly. Under suitable conditions, the entire life cycle of the parasite takes approximately 16 days. Of them:
- 5-7 days takes egg development
- about 13-17 days the larva develops, during this time it experiences about three molts at approximately regular intervals
- about noon, an adult female needs to get rid of the larval membrane after molting, drink blood, mate with a male and lay the first egg.
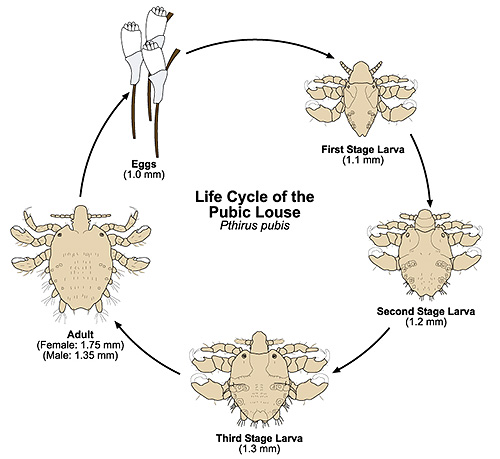
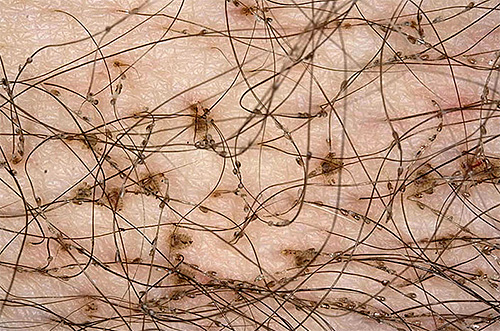
The eggs of pubic lice are called nits. They are a capsule, firmly attached to the hair at a distance of 1-3 cm from the surface of the skin, with a cap and a small leg. With the naked eye, the eggs of the lice look like small bright spots on the hair. The length of the eggs reach 0.5-0.6 mm and have an almost round shape.
Frontal lice larvae are similar in appearance to adult insects and therefore are called nymphs. They also feed on blood and lead the same way of life as mature ploshchitsy. They differ only in small size and lack of external genital organs.
It is interesting
Under a microscope, pubic lice nits are well distinguished from head louse nits.In the latter, the eggs have an elongated, spindle-shaped form. The photographs show the difference between the eggs of pubic lice and nits of head lice:
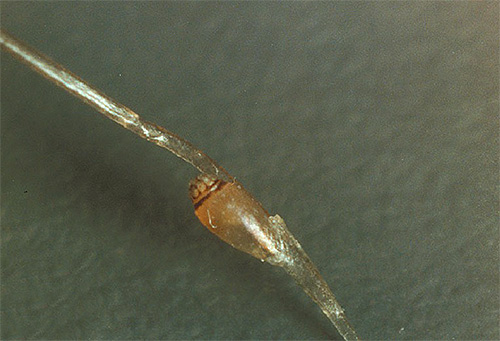

Each female lays 1 to 3 eggs per day. For all her short adult life (the sexually mature insect lives for 20-30 days, in rare cases - up to 40) each female lays from 30 to 50 eggs.
What can be dangerous pubic lice
In contrast to head and body lice, crawfish almost never suffer infectious diseases. However, even their natural activity is enough to cause many unpleasant symptoms and consequences:
- itching and bite marks
- bluish spots on the ground bites, representing the reaction of the skin to the lice-produced enzyme
- papules and pustular inflammations at the site of combed bites, in especially neglected cases, developing into pyoderma.
All of these symptoms in the complex are called phthyriasis.
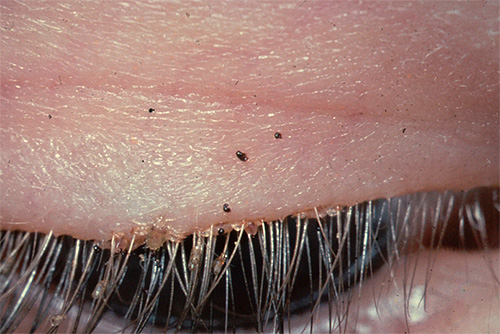
Infection of the eyelids and eyebrows with pubic lice can lead to the development of conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
The photo below shows what the infection of the eyelids with pubic louse looks like:
Methods for transmitting pubic lice and general epidemiological situation
Pubic lice are transmitted almost exclusively during sexual intercourse, crawling from an infected person's hair to healthy hair. Phthyriasis is considered a venereal disease, equally common in both sexes. Male pubic lice are as common as women. They can affect children.
It is interesting
In recent decades, scientists have noted a reduction in the number of cases of infection with pubic lice due to the entry into fashion of shaving pubic hair. More than a century or so ago, the pubis was shaved mostly by workers of the oldest profession, precisely for protection against lice. Today, with the cult of the hairless body, the ploshchitsy literally lose their habitat.
Pubic lice can survive up to two days in the water and therefore, in very rare cases, are transmitted in pools and open water between bathing people.
In general, pubic lice are most common in third world countries, especially in Africa, where sanitation and promiscuous sex reign. It is the frequent change of sexual partners that causes the pubic lice to become infected, and due to the fact that during the month after the infection the person does not feel signs of phthyriasis,he can easily infect other people. For this reason, lice successfully spread even in a society with a high level of sanitation.
Here are some more photos of pubic lice:
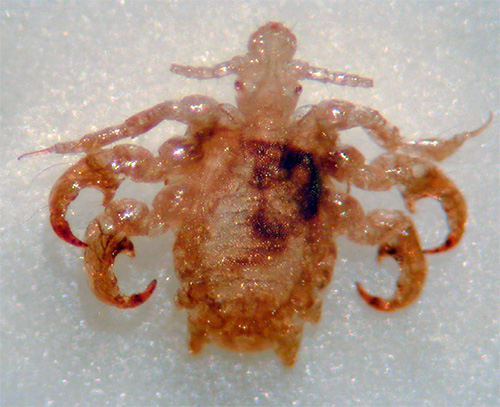


Ways to get rid of pubic lice
The simplest and most effective way to destroy pubic lice is to shave the hair at the place of their dislocation. This procedure takes half an hour and guarantees complete disposal of parasites.
A little harder fight lice using special shampoos and ointments. Such agents should contain powerful insecticides such as Zipermetrin or Deltamethrin, which have a nerve-paralytic effect on parasites, but harmless to humans. During the first treatment of the hair with such a preparation, active adult insects and larvae are destroyed, and during the second treatment - in a week - those larvae that have emerged from the surviving nits.
In order to avoid infection with pubic louse, casual sex should be avoided. For complete reliability, you can regularly shave pubic hair, thereby protecting yourself from the potential transmission of parasites.
Interesting video: infection with pubic lice and how to deal with them
Video capture pubic lice closeup



I have lice there ...