The human louse is a parasite, the characteristics of its biology and parasitic lifestyle are no more than any other insect harmful to humans. On closer examination, lice turn out to be very original bloodsuckers, in many respects more than other “competitors” adapted to life on the human body.
In more detail about these interesting features of human lice and the specifics of dealing with them, we'll continue and talk.
It is interesting
Evolutionary lice can be considered a kind of transitional stage in parasitism between typical “blood hunters” such as bed bugs and fleas, whose whole life goes away from people, but which attack it only for food, and internal parasites - such as a scabby tick, which all life spends under the skin of man. The human louse has already become completely dependent on the human body, but has not yet had time to penetrate its veils.This determines both the specifics of lice problems and the relative ease of dealing with them.
How dangerous are human lice?
The main dangers from the presence of human lice on the body lie in the reaction of the organism itself to the bites of parasites and in the lice carrying of pathogens of some dangerous diseases.
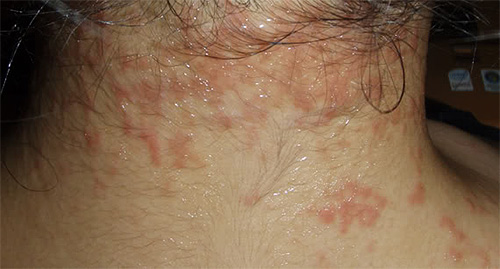
Usually, lice in humans cause a complex response of the body, called pediculosis in medicine. Such reactions are expressed in the appearance of:
- severe itching at the bite site
- rashes on the body, and not only in those places where the bites were localized, but also on the surrounding skin areas
- the appearance of cyanotic spots due to the redistribution of pigments
- sometimes a generalized allergic reaction with fever, headaches and nausea.
When running, pediculosis can cause the development of ulcers, boils and the appearance of deep scars on the skin.
In addition, linen lice in humans are carriers of microorganisms from the rickettsia class, some species of which are the causative agents of typhus and relapsing fever. At one time, it was these deadly diseases spread by lice that mowed down soldiers in the Russian army,and today, their epidemics continue to flare up in some countries in Africa and South America.
On a note
Head and pubic lice very rarely tolerate typhoid. However, due to the potential danger, they are actively fought in children's groups and health care facilities.
But how to distinguish between different types of human lice - a separate big question ...
Types of lice in humans
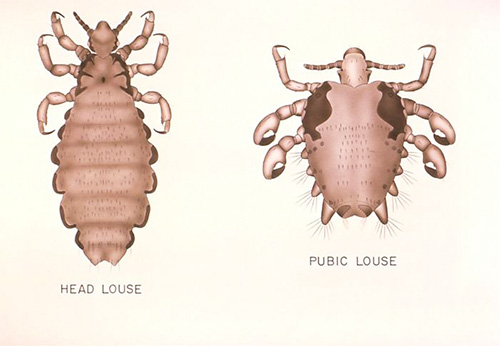
Generally speaking, a person has only two types of lice - the so-called pubic and human. At the same time, the human for all the time of the neighborhood with the person managed to divide into two forms - the head and the dress.
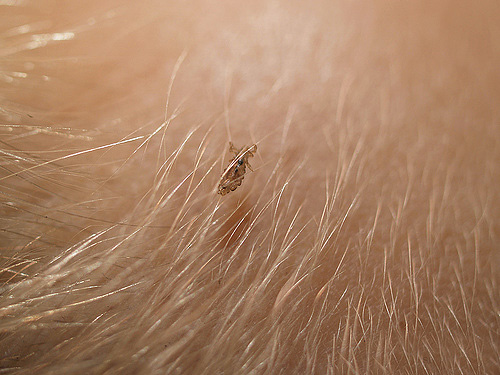
In the photo below - head louse on severely infected head:

And then - photos of pubic lice:

Below that is a photograph of clothes (underwear) louses on clothes:


It is interesting
Lice - parasites, very strongly tied to one owner. Human lice can not live on other animals, and therefore, lice can only be infected from people. And vice versa, lice eaters in animals never parasitize on humans.
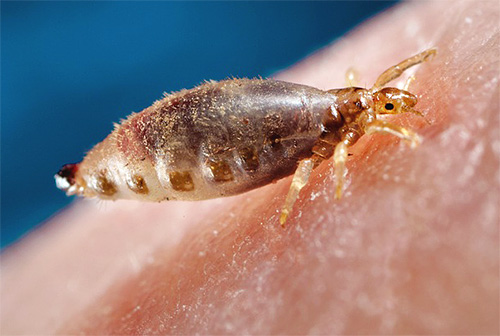
The pubic louse is known to be found mainly in pubic hair, occasionally in the armpits.The man’s pubic louses look quite specific - they have a very short body and long powerful legs. Here is another photo of pubic lice:
Pubic lice size - up to 2 mm.
Human lice have a slightly longer body than pubic lice. Head lice slightly darker, wardrobe - almost completely white. At saturation, the abdomen of the lice darkens due to the blood in the stomach, and each insect becomes a bit like a flea or a bed bug eating larvae (see photo):
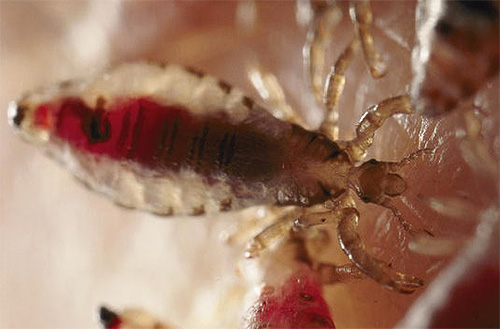

In length, human lice reach 3-4 mm, but due to the fact that they live among the hair or folds of clothing, they rarely catch the eye. The photo below shows an adult insect:

Regardless of the type and form of lice feed only on blood. They can not penetrate the skin of a person and can not live long outside the body. Pubic and head lice most of the time spent on the hair, and the wardrobe - mostly on clothes that people almost never takes off.
What do human lice look like?
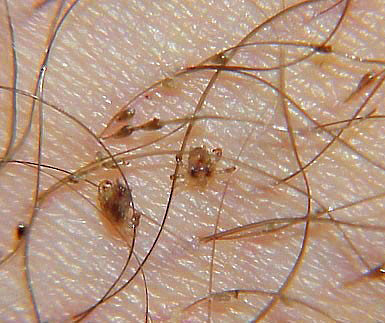
The human louse is a very small insect. The photo below shows the lice and their eggs (nits):


The maximum length of an adult louse is about 4 mm. Lice look like a man like small wingless bugs. In this case, the head and body lice have a body of light white color with translucent covers, and the pubic louse is brown.
Lice are barely noticeable in human hair: they are mostly found at the base of the hair and on the scalp. Nits are more noticeable here - they look like very small white dots, located at different distances from the base of the hair. Nits are lice eggssecurely attached to the hairs by the female.
The photo below shows the abundance of nits on an infected head:

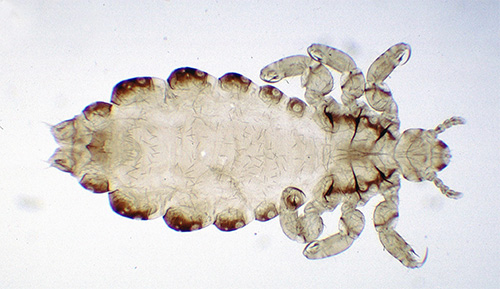
And on the following photo you can see how a person’s lice look like during feeding:
On a note
The human louse is particularly remarkable for the way each foot looks. When examined under a microscope, it is clear that the last segment of her paw is a hook, which is well adapted to clinging to hair. By the mere structure of the paws, it is easy to distinguish lice and lashes from other parasites, but you cannot do without powerful optics.
Lice differ quite well from the most common human parasites:
- Bed bugs have larger sizes and brown body color. Their larvae can resemble lice, but they move much more quickly and do not occur on those parts of the body where lice in humans usually parasitize.
- Lice and fleas in humans are usually not found on the same areas of skin - fleas prefer to bite on the legs, sometimes on the sides of the body. For the hairy parts of the body, fleas hardly bite.
- Ticks bite a person mainly on the legs and are distinguished from lice by a dark body color, 8 paws (there are 6 of them in lice) and very long blood sucking.
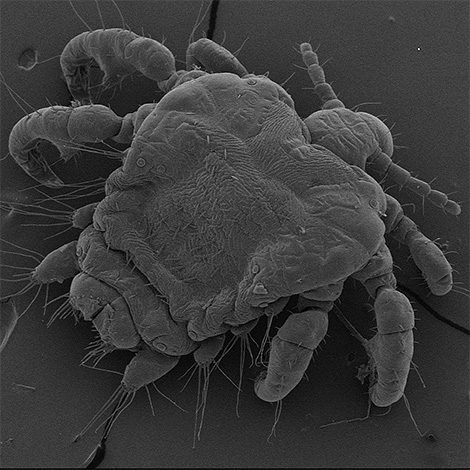
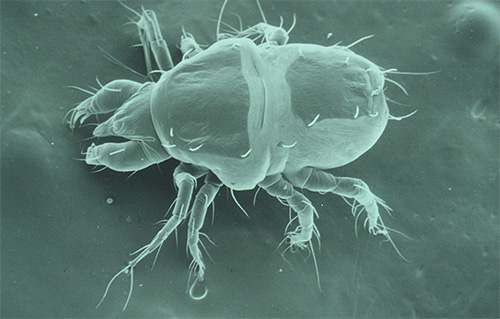
- Itch mites are significantly smaller than lice and live exclusively under the skin. It causes itching, but bites characteristic of lice do not appear from its activity.
Photo bed bug:

Flea photo:

Photo tick:

And this is how itch mite:
From the other blood-sucking parasites of human lice can be distinguished by the appearance of the bites themselves. In bedbugs and fleas, bites are often located on the same line - the insect bites several times, moving a few centimeters from the previous place of sucking blood. Lice do not. And ixodic mites leave behind a fairly large hard knob - lice bites significantly smaller in size.
Below are some more photos of human lice, allowing you to learn more about the appearance of these parasites:
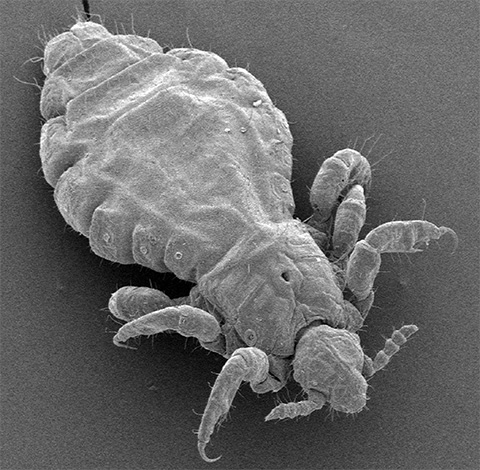


Feedback
“When the child began to scratch his head in September, I thought that the bugs were biting him again, six months ago it was like that, they only bit behind my back and sides. Again they hounded the apartment with Karbofos, they did everything well, but the scabies did not go away. Started to look closely and found nits. I didn’t believe at first, I thought the lice had long since disappeared, I decided to see what a human louse looks like, and for sure - Andryusha had exactly such things on her head. I had to buy shampoo, put bags on my head and slack off. Most likely, in the summer camp he picked them up. ”
Maria, Vologda
Reproduction of lice, their nits and larvae
All life and reproduction of lice take place on the body of a person (or on his clothes - in the case of body lice). In this case, there is no difference, there are head lice in an adult or a child - the peculiarities of their biology do not change.
An adult human louse lives up to 40 days and females lay eggs literally from the first day of their adult life. The egg, which is also a nits, is fastened with a special sticky mucus to the hair, and after 5-6 days the larva, which resembles a copy of an adult louse in miniature, is taken out of the nits.
Up to 20-25 days, the lice larva feeds, sheds several times and turns into an adult insect.
In the photo below you can see what the larva of a human louse looks like:

In body lice, eggs are laid in the folds of clothes. The development of larvae also occurs there.
Lice larvae feed on blood, like adult insects.
It is interesting
At temperatures below 22 ° C and above 40 ° C, human lice do not reproduce - the larvae do not hatch from their eggs.
The larvae of all types of human lice under a microscope seem transparent and look as if they were deprived of wings.
In pubic and head lice, the adult individuals darken a little, while in the ward they remain as light as the nymphs.
How are human lice spread and transmitted?
Lice are usually transmitted through close contact with an infected person. Children who are easily in contact with each other and are not subject to special restrictions in games and fights are especially susceptible to lice infestation.
Also, head lice can be transmitted through combs, elastics and hairpins. Body lice can crawl from one thing to another when clothes are stored together.
Pubic lice are transmitted almost exclusively with sexual intercourse. Only sometimes they can infect a person by falling on the bedding and moving to the one who lies on the bed next.Such cases occur, for example, in cheap hotels.
On a note
Extremely rare, but there are reported cases of lice transport in swimming pools and public bathing areas. Lice are resistant to oxygen deficiency and in water can survive for 2 days.
Now, knowing what the lice look like, it will be easy for you to determine whether you or your children have been infected and take appropriate measures in time. It is also useful to remember about simple preventive measures that will limit your acquaintance with human lice only theoretical information.
About human lice and diseases that they are able to endure
Useful video about lice and how to deal with them




Super article
Not that word
Girls, there is nothing better than a comb of nit fries and their means of pediculosis. That just did not try, everything is useless. Products Nit Free helped the first time. So don't waste your money, buy what really helps.
In the barbershop, they found lice in me and disgraced me with other clients, it was unpleasant. Do they have the right to behave like this? And they have the right to refuse to do a haircut, if a person has pediculosis? Tell me.
Not
Are human lice jumping over?
Yes, of course, lice tend to jump ((
NOT! Human lice do not jump. Fleas jump on dogs and cats, and human lice can only crawl!
Yes
I'm terrified of it, I have no words
I never had lice, I saw them and started to vomit!
How to deal with these creatures?
I bought a spray at the pharmacy!
Oh my God. I have not been able to get rid of lice for almost 2 months now. Someone tell me how to overcome them? Nothing helps me.
Ksenia, in the pharmacy there is a wonderful spray (made in France), I do not remember the name. Spray on the roots, hair, wait 10 minutes, rinse with shampoo. Important! To process all used things, something in a package for 3 days, something to iron, and something to be rubbed at 60 degrees.
Lice and nits spray is Nuda! It helped the first time)
And this nuda dear?
687 rubles
First she found a big black louse for one daughter. I thought it was a flea - there are no nits, and the head is clean. Then I found the same in my second daughter. I do not understand what it is, there is no nits, the hair is blond, and the bugs are black ... And, it seems, it doesn’t look like louse.
Maybe not lice, but to prevent protection does not hurt!
If there are too many nits, then trim.
No, you can not cut it!
The article is amazing! Very accessible, interesting and as relevant. My daughter is 9 years old, I have never come across this before, I heard that someone has such garbage, but that this happened to us ... I noticed that Sasha was scratching for the second day, in the morning she began to braid her and saw an insect! It's just awful what. Well, now I read it, I bought different things, I smeared my hair, and they have long hair. We will wait for the result ... ((
And we brought out hellebore solution. It is worth a penny, but the result is obvious))
Tell me, please, my classmate has lice and she can’t get rid of them. Already the whole class picked up, including me. I hate and won't go to school until she takes them out.